By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 1 Earth Movements students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 1 Earth Movements
→ Hills, mountains, plateaus, valleys etc., are the landforms formed due to internal and external processes.
→ The earth’s surfaces changes slowly and continuously due to forces like tension and compression.
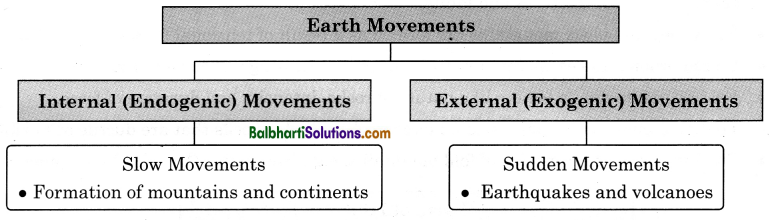
→ Earth Movements:
1. Internal (Endogenic) Movements:
Slow Movements: Formation of mountains and continents
2. External (Exogenic) Movements:
Sudden Movements : Earthquakes and volcanoes
Slow Movements :
- The earth’s movements which are the result of internal forces are known as tectonic movements.
- Based on the direction of slow movements they are classified as vertical and horizontal movements.
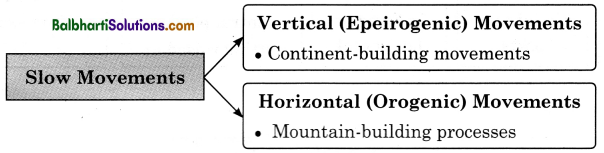
Slow Movements :
- Vertical (Epeirogenic) Movements :
Continent-building movements - Horizontal (Orogenic) Movements
Mountain-building processes
Vertical (Epeirogenic) Movements :
- These movements occur due to the forces in the interior of the earth and the travel of energy.
- Slow movements take place either towards the centre of the earth or away from it towards the
crust. - Due to these movements, an extensive portion of the crust is either raised up or it subsides.
This portion of the crust, raised above sea-level leads to formation of continents. - Slow movements also cause formation of extensive plateaus.
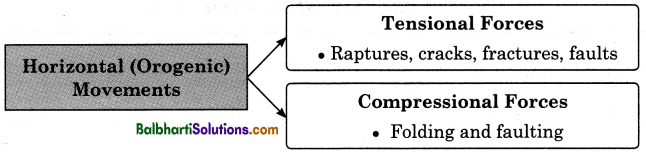
Horizontal (Orogenic) Movements:
- Horizontal movements work in horizontal direction, creating compression or tension in the rock
strata. - These movements lead to folds or cracks in the surface of the earth and gives rise to mountains.
These movements are slow movements causing folds or faults, after which, fold mountains or
block mountains are formed. - Horizontal movements are further divided into tensional forces and compressional forces.
![]()
Horizontal (Orogenic Movements):
- Tensional Forces: Raptures, cracks, fractures, faults
- Compressional Forces: Folding and faulting
→ Tensional forces move away from each other causing stress in the rock strata thus, creating raptures, cracks, fractures and faults.
→ Rift valley and block mountains are formed as a result of tensional forces.
→ Compressional forces operate towards each other; causing various folding.
→ Folding occurs due to factors like nature of rocks, intensity and duration of force.
→ Folding occurs when compressional forces are applied to rocks that are ductile or flexible.
→ Folding results in formation of fold mountains, e.g., Himalayas, Alps, Rockies, Andes, etc.
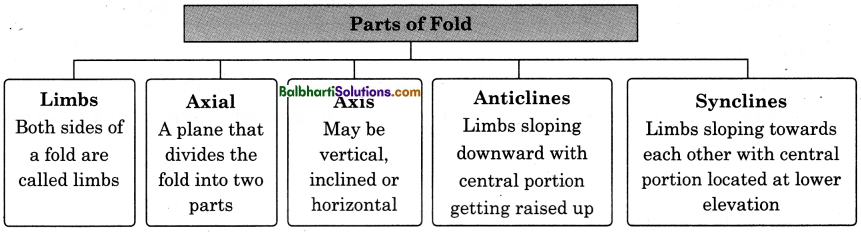
→ Parts of Fold:
- Limbs
Both sides of a fold are called limbs - Axial
A plane that divides the fold into two parts - Axis
May be vertical, inclined or horizontal - Anticlines
Limbs sloping downward with central portion getting raised up - Synclines
Limbs sloping towards each other with central portion located at lower elevation
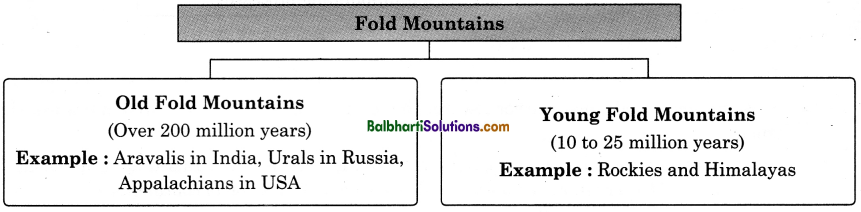
→ Fold mountains are classified depending on their age.
→ Fold Mountains:
1. Old Fold Mountains (Over 200 million years)
Example : Aravalis in India, Urals in Russia,
Appalachians in USA
2. Young Fold Mountains (10 to 25 million years)
Example : Rockies and Himalayas
![]()
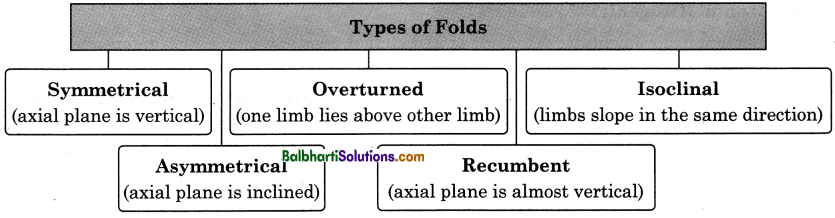
→ Types of Folds
- Symmetrical (axial plane is vertical)
- Asymmetrical (axial plane is inclined)
- Overturned (one limb lies above other limb)
- Recumbent (axial plane is almost vertical)
- Isoclinal (limbs slope in the same direction)
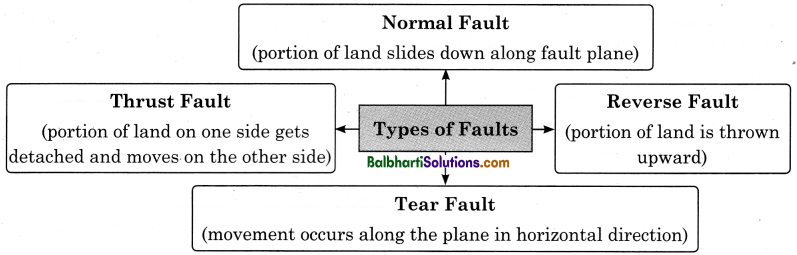
→ Faulting :
- Faulting can be classified according to displacement in rocks. The plane of fracture is called fault.
- Faulting results in the formation of block mountains and rift valleys.
→ Types of Faults:
- Normal Fault (portion of land slides down along fault plane)
- Thrust Fault Reverse Fault (portion of land on one side gets detached and moves on the other side)
- Reverse Fault: (portion of land is thrown upward)
- Tear Fault (movement occurs along the plane in horizontal direction)
→ Tensional forces tend to pull the crust apart and faults are developed.
→ The tension may cause subsidence in the central portion of the crust between two adjacent faults, forming graben or rift valleys, which have steep walls. For e.g., African Rift Valley, Narmada and Tapi Rift Valleys in India.
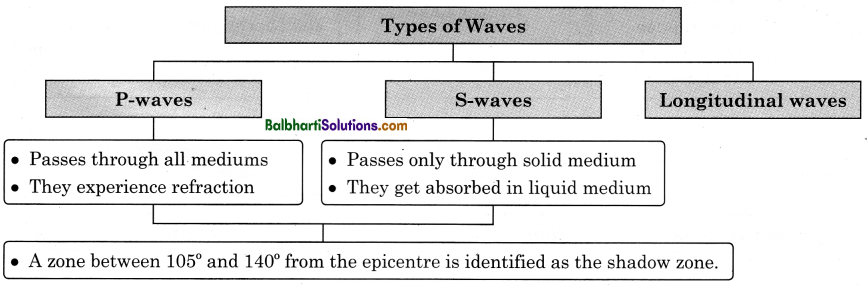
→ Sudden movements refer to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Earthquake refers to shaking of the ground due to release of stress and energy.
→ The point where the accumulated stress gets released within the earth’s crust is called seismic focus.
→ A point directly above it, on the surface of the earth is the epicentre.
→ The earthquake waves are recorded by an instrument called seismograph.
![]()
→ Causes Of Earthquakes
- Volcanicity
- Tectonic movement
- Anthropogenic causes

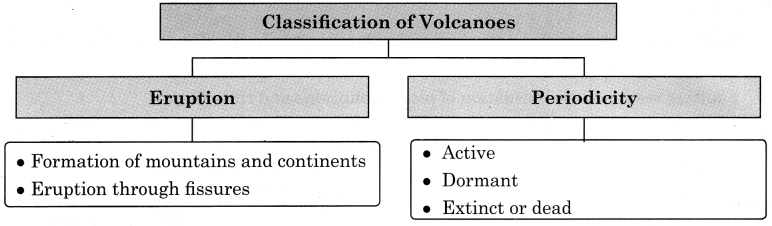
→ Classification of Volcanoes:
Eruption:
- Formation of mountains and continents
- Eruption through fissures
Periodicity:
- Active
- Dormant
- Extinct or dead
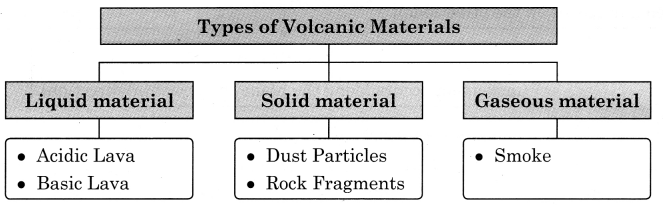
→ Types of Volcanic Materials:
- Liquid material
- Solid materials
- Gaseous materials
Liquid material:
- Acidic Lava
- Basic Lava
Solid materials:
- Dust Particles
- Rock Fragments
Gaseous materials:
Smoke
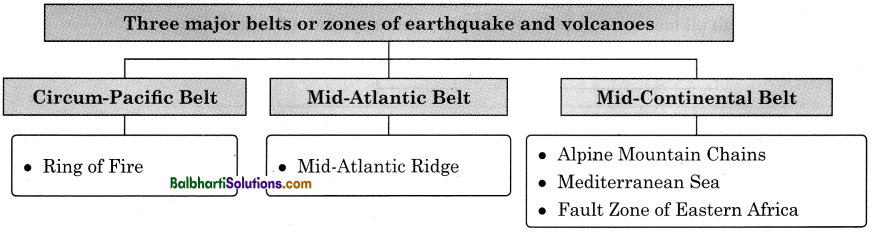
→ Three major belts or zones of earthquake and volcanoes:
- Circum-Pacific Belt
- Mid – Atlantic Belt
- Mid-Continental Belt
Circum-Pacific Belt: Ring of Fire
Mid – Atlantic Belt: Mid – Atlantic Ridge
Mid-Continental Belt:
- Alpine Mountain Chains
- Mediterranean Sea
- Fault Zone of Eastern Africa