By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 12th Notes Chapter 5 Emerging Modes of Business students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 12th Notes Chapter 5 Emerging Modes of Business
→ Policy: Definite course of action followed by a business firm, government, etc. to achieve its objectives.
→ Negotiate: To deal or bargain with others as in working out the terms of a contract.
→ Registration: A process of entering the name and other relevant details like e-mail id, card details, etc. with the internet.
![]()
→ Repository: A container or place where things are deposited or stored.
→ Infrastructure: The basic facilities like roads, electricity, water, etc., that are required for the smooth running of a business, factory, etc., in particular and economy in general.
→ Marketing: The activities of a business enterprise that are connected with acquiring, maintaining and expanding markets for its products and for ensuring that its product reaches the consumers in time.
→ Recruitment: The process of searching the prospective and capable employees and encouraging them to apply for jobs in the organisation. It aims at attracting potential employees to the organisation to create a large pool for better selection.
→ Hacker: A person who is excellent at computer programming and uses computer systems illegally for private gain.
→ Off shore: Company makes contract with the foreign company in respect of outsourcing services.
→ Onshore: Company makes contract with another company of home country in respect of outsourcing services.
→ Near shore: Company makes contract with a company of neighbouring country in respect of outsourcing services.
E-Business-
Introduction: E-business is an abbreviation of electronic business. In 1997, the term e-business was first used by International Business Machines (IBM). Before that the term e-commerce was in use. E-business implies use of internet to connect people and process. International trade for goods and services started growing rapidly due to use of internet. In brief, e-business, means the use of Web, internet, intranet, extranets or some combination thereof to conduct business. E-business helps to open new door to the customers, brings closer and builds responsive relationship with partners, employees, suppliers, etc., makes new inventions and innovative ways to . add value to existing products, e-business with the help of internet and web support provide opportunities in different areas such as selling, customer relationship, product/service design, geographic expansion, etc. e-business is nothing but business on internet.
![]()
Meaning:
The electronic business i.e. e-business is originated from the two terms e-mail and e-commerce. Thus electronic business commonly referred to as ‘e-business’ or ‘an internet business’ may be defined as the application or utilisation of information and communication technologies (ICT) in support of all business activities, e-business involves purchasing and selling on internet processing orders electronically, making online payments via credit cards or debit cards, direct fund transfer handling customer services and co-operating with business partners using with technical or customer support. The term e-commerce and e-business are different. In fact, e-business includes e-commerce.
Scope of e-business:
The scope of e-business is extended to online shopping, online stock, online transactions, e-commerce and use of software. Most of the business are now aware of the advantages of e-business and are now started incorporating e-business in their policies and strategies. It facilitates direct and better communication between the consumers and business houses and makes purchasing easier for large organisations.
The scope of e-business becoming vast because almost all kinds of business functions such as production, finance, marketing, personnel administration, management functions like planning, organising, co-ordinating, controlling etc. are now carried out via computer networks. The different business and payment apps such as Phone Pay. Google Pay, Swiggy, Ola, etc. are used in e-business transactions. The various types of e-business transactions are:
Types of E-business transaction-
- Business to Business (B2B)
- Business to Consumer (B2C)
- Consumer to Business (C2B)
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
- Business to Administration (B2A)
- Consumer to Administration (C2A)
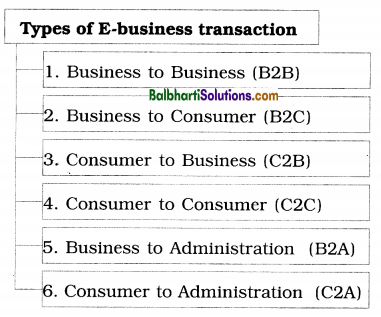
1) Business to Business (B2B): Under B2B, one business firm communicates and interacts with other business firms for different varieties and ranges of services. Example is value added services like catering and also providing manpower. It does not involve individuals.
2) Business to Consumer (B2C): Under B2C, business firms sell goods and services to the consumers. Firms use their website for various marketing activities like promotion, information, review, etc. Examples are www.flipkart.com, www.yebhi.com, etc.
3) Consumer to Business (C2B): Under C2B, the consumer posts his request with a set budget online, quote price for specific service or goods to the business. The companies review the
customers’ requirement and finalise the order. For instance, pest control service, door step food delivery, taxi services, etc.
4) Consumer to Consumer (C2C): The transactions such as buying and selling of variety of goods under C2C are between consumer and other consumers. Internet offers lot of scope for this activity. Payment modes for transactions are secured through advanced technology. The website do the job of intermediaries i.e. to match the consumers. Example of such a website is eBay.
5) Business to Administration (B2A): All transactions conducted online between business and public administration come under B2A, e.g. registration of companies, payment of taxes, obtaining various types of licences and permits, etc.
6) Consumer to Administration (C2A): All transactions conducted online between consumers (individuals) and public administration are j included in C2A. e.g. getting passport, aadhaar card, Pan card, licences, etc.
![]()
Benefits of E-business-
Internet has become fourth channel for trade. It has many advantages:
- Ease of formation: As compared to traditional business, e-business is relatively easy 5 to start and operate.
- Lower investment requirements: Investment requirements of e-business is very low in comparison to traditional business. It does not require large store and large manpower to conduct business. More contacts and effective communication can do huge business.
- Convenience: E-business of any thing can be done anytime and anywhere. It offers j convenience of 24 x 7 x 365 days a year.
- Speed: All aspects of business transactions such as buying or selling, making payments, etc. j can be done quickly and speedily at the click of mouse.
- Global access: Internet is boundryless. It allows the seller to have access to global market and also offers freedom to the buyer to choose products from any part of the world. For e-business face to face interaction between buyer and seller is not required.
- Movement towards a paperless society: Use of internet has reduced the dependence on paperwork to great extent. Recording and referencing of information has become easy.
- Government support: Government favours and supports e-business. It ensures maximum transparency.
- Easy payment: In e-business transactions, the payment is done by fund transfer, credit card, etc. Such payment can be made anytime, quickly and round the clock.
Limitations of e-business-
- Lack of personal touch: Lack of physical inspection and personal touch affect its sale adversely. The consumer cannot check the quality of product.
- Delivery time: In e-business, delivery of products is considerably delayed in comparison to traditional business. Time lag always discourages consumers to buy products online.
- Security issues: Scam and cheating through online business by the people or hackers cannot be denied. It lacks adequate security and integrity. It also disturbs the entry of potential buyers.
- Government interference: Government interference sometimes puts hurdles on its growth and expansion.
- High risk: E-business involves high risk because of absence of direct contact between the buyer and seller. In case of fraud, it is difficult to take legal action against the wrongdoer.
Online Transaction-
Meaning: Business transactions which are carried out and completed between seller and buyer with the help of internet are called online business transactions. In this, placing an order, selection of goods, execution of order, transfer of funds, etc. are completed via internet by using websites and e-mail addresses of buyer and seller.
Procedure of online Transaction: In online transaction, there are three stages, viz. pre-purchase/sale stage, actual purchase/sale stage and delivery stage.
Online transaction involves the following steps:
1) Registration: Registration is required for online transactions. One who wants to do online shopping is required to login on a website and fill relevant details with the online vendor. The customer’s email id, name, address and other details are saved by the website for future use.
2) Placing an order: The online customer or shopper can select, pick up and drop the items or things in the shopping cart. The shopping cart keeps the systematic and detail record of what items or things have been picked up and dropped in the shopping cart and the price of each. The buyer then needs to make payment.
3) Payments: The payment system, is fully secured. Payment can be made in one of the following ways:
- Cash on Delivery (COD): According to this mode of payment, after receiving physical delivery of goods at the door step, payments for the online goods ordered is effected by cash payment or by debit or credit card.
- Cheque: Under this mode of payment, the vendor collects the cheque from the customer and after realisation of the cheque, delivery of the goods is given to the buyer.
- Net banking transfer: Under this mode, the payment is made by buyer to vendor by transfer of funds through the internet. The buyer transfers the agreed purchase amount to the online vendor’s account. After receiving the amount, the vendor delivers the goods to the buyer.
- Credit or Debit Cards: The credit card or debit card is used by the cardholder for making payment of purchases online. The vendor gets the amount from the buyer through credit or debit Con’d. The amount gets immediately transferred to Vendor’s Bank Account. After the successful transfer of funds, goods are delivered by the vendor to buyer.
- Digital cash: This facility of electronic currency exists only in cyberspace. For making payment of purchases, online digital cash offers the ability to use real currency in an electronic format.
![]()
Buying Selling Process: Information relating to buying and selling is exchanged in traditional business and also in online (internet) business. In comparison to traditional, business, online business is more easier. In traditional business, time is required to visit the shop, to negotiate, to convince and the presence of buyer and seller is required for face to face interaction. So, to complete the deal lot of time is wasted. However, in online transactions all information is provided with terms and conditions and it is free from most of the problems as that of traditional business. Hence online transactions are result oriented and more easier than traditional business.
Outsourcing-
Meaning: Outsourcing is a process of an allocation of specific business processes or functions, mostly the non-core, to a specialised agency for certain monetary consideration. Usually, establishment, firms, corporate organisations, hospitals, malls, housing societies etc. outsource their non-core business areas such as security service, sanitation, household pantry, etc.
In outsourcing, the company benefits in two ways, viz. (i) It helps to reduce the company’s own cost and (ii) The company uses expertise of the specialised agencies to perform its business processes in a better way. Nowadays some functions like wedding, anniversary, birthday celebration, etc. are also outsourced to specialised agencies.
Need for Outsourcing:
- Some services require finely tuned skills which organisation cannot provide.
- Non-core business areas are outsourced to concentrate on improvement of quality of their products and services.
- Sometimes an organisation cannot handle all the functions internally.
- Some processes are required to perform once in several years.
Advantages of Outsourcing:
- Overall cost advantages: Outsourcing reduces its own overall cost. It saves cost of training, saves time and efforts on training.
- Stimulates entrepreneurship, employment and expertness: Outsourcing encourages and stimulates entrepreneurship, employment and expertness in the country from where outsourcing is done.
- Low manpower cost: Manpower through j outsourcing is available at much lower cost.
- Access to professional, expert and high quality services: The tasks are outsourced to the vendors who are specialised in their fields. They have deep knowledge, experience, specific equipment and technical expertise. They give better j performance and commit less errors.
- Emphasis on core process rather than the supporting ones: Outsourcing facilitates the organisation to spend more time to strengthen ; their core business processes. The organisations ! can easily focus their attention on improving the quality of their products and services.
- Investment requirements are reduced: When some areas of business are outsourced to specialised agencies, the parent organisation is not required to invest in latest technology, software and infrastructure. Hence investment requirement of the parent organisation is very less.
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Outsourcing increases efficiency and productivity j in the non-core area of an organisation.
- Knowledge sharing: While working in the organisation outsourced partners and employees of parent organisation share their knowledge, experience, technical expertise, etc. with each other.
- This is one of the prime advantages of outsourcing, This in turn develop both the companies and: enhance goodwill in the industry.
Disadvantages of Outsourcing:
- Lack of customer focus: An outsourced vendor may be catering to the expertise needs of several companies at a time. In such cases, he may lack focus and concentration on the parent company’s need or task. As a result, the quality of service given may not remain up to the mark.
- A threat to security and confidentiality: Outsourcing involves a risk of exposing confidential and secret information of the organisation to a third party. So, there is also danger of the misuse of company’s confidential information by the contractors.
- Dissatisfactory services: Some common problems of outsourcing include delayed (stretched) delivery and sub-standard (dissatisfactory) quality.
- Ethical issues: When some functions are outsourced to the foreign company, the unemployment problem of parent company and country gets worse. This is one of the ethical issues related to outsourcing.
- Other disadvantages: When business functions are outsourced, the parent company has to suffer disadvantages like misunderstanding of contracts, lack of communication, poor quality and delayed services.
Different Forms of Outsourcing-
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO):
Meaning: BPO implies outsourcing of peripheral or non-primary business functions of the organisation to an external organisation (service provider) to minimise cost and increase efficiency. It means to give contracts or responsibilities of specific business process to third party e.g. customer care centres of various banks.
Advantages of BPO:
- Productivity improvement: Outsourced business processes are performed by educated or skilled people more efficiently and hence productivity of the organisation improves.
- Optimum utilisation: BPO facilitates the parent organisation to utilise its available scarce resources up to their optimum level possible.
- Reduction in cost: BPO is more important to any organisation as it helps in reducing cost, increasing productivity and revenues of an organisation.
- Improved human resources: Outsourcing helps the parent organisation to get skilled and trained personnel (manpower) at low rates.
![]()
Disadvantages of BPO:
- Communication problems: The misunder¬standing and miscommunication between parent company and vendor company may lead to communication gap.
- Different time zones: Sometimes, the parent company and vendor company function in two different time zones. This may create many problems during online meeting, communication, etc.
- Loss of Control: On account of time differences and communication errors, the parent company may sometimes lose control over its project.
Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)-
Meaning: KPO is form of outsourcing in which knowledge related and information related work is outsourced to third party service providers. KPO is sub segment of BPO in which outsource service provider is hired to perform particular business function and to provide expertise around it. In KPO advanced analytical and technical skills and high degree of specialist expertise are required. The processes of specialised and knowledge based are outsourced to KPO which help in value additions.
KPO may be in the same country or at an off shore location.
Advantages:
- Cost reduction: In KPO, cost reduction is possible as parent company gets professional services at a cost effective price.
- Skilled personnel: The company can easily hired skilled employees from KPO service providers.
- Reduction in unemployment: Skilled and high end services are available at lower cost, reduce unemployment and provide benefits to the economy.
- Flexibility: KPO provides flexibility in terms of Human Resource Management (HRM) and Time Management.
Disadvantages:
- Security Problem: Many a time client organisation may have to face security problems because of leakage of secret information by the service providers.
- No assurance of quality work: The character of outsourced workers and the quality of work cannot be assured.
- Time consuming: KPO is time consuming process and cannot provide quick solution to the
company who need immediate results. - Complication: Communication gap due to legal, cultural and language barriers may lead to complications.
- Language barrier: Language barrier creates communication problem.
Legal Process Outsourcing (LPO)-
Meaning: LPO is a form of outsourcing in which legal services ranging from drafting legal documents, performing legal research to offering legal advices are provided by law firm for certain consideration in money term. In this, in-house legal departments outsource legal work which can S be done at lesser cost. LPO has gained tremendous i ground in India in recent years. It has been giving | services like document review, legal research, writing, drafting, briefing, etc.
Advantages:
- Cost savings: Considerable cost is saved by outsourcing legal functions to specialised law firm.
- Access to high talent: Outsourcing the | legal work to law form allows the client company | to get high talent and niche expertise that does not j exist in its own company.
- Division of workload: Utilisation of external and in-house talent permits the law firm and parent organisation to divide their liabilities in response to workload and client demands. Firm’s overhead reduces due to flexible staffing.
![]()
Disadvantages:
- Problem of authenticity: The client organisation is required to share some important document with legal firms. This creates the problem of authenticity (trustworthy).
- Problem of in-depth knowledge: There may be a problem of detail or thorough knowledge of all relevant laws.
- Communication problem: The cultural and language barriers hinder effective communication between domestic organisation and international team.
- Geographical problem: LPO affects adversely by geographical distance (hurdles) between client organisation and law firms.