By going through these Maharashtra State Board Secretarial Practice 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 6 Directors and Key Managerial Personnel of a Company students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Secretarial Practice Notes Chapter 6 Directors and Key Managerial Personnel of a Company
Reasons leading to separation of ownership and management in the Company-
- Large business organization
- Large shareholders are scattered all over
- Disinterest on part of most of the shareholders
- Incapability in terms of qualification
- Inability on part of most shareholders to manage company.
Hierarchy of Company Management-
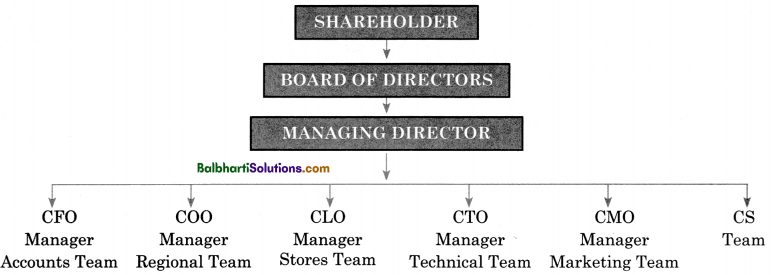

- CEO — Chief Executive Officer
- CFO — Chief Financial Officer
- COO — Chief Operating Officer
- CLO — Chief Law Officer
- CTO — Chief Technology Officer
- CMO — Chief Marketing Officer
- CS — Company Secretary
![]()
Director-
Meaning:
- As per Section 2(34) of the Act, Director \means a director appointed to the Board of the company.
- Director is a person appointed to manage, direct and supervise the affairs of a company.
Provisions and Rules with respect to appointment of a Director-
Section 149 of the Companies Act
1. Only an Individual can be appointed as Director.
2. Minimum number of directors:
- Public Company :— 03
- Private Company :— 02
- One-Person Company (OPC)
3. Maximum Number of Directors:
15 Directors are allowed. If a company requires more than fifteen, a special resolution should be passed.
4. Prescribed classes of company
At least one woman director.
5. At least one director who stay in India for at least 182 days during the financial year.
6. Listed public company should have l/3rd of its Board as an Independent Director.
7. Allowed to hold directorship of maximum Twenty (20) companies at the same time.
8. Maximum number of public companies in which a person can act as a director is Ten (10) only.
Director Identification Number (DIN)-
- Unique identification number for existing director or person desiring to be the director of company.
- Compulsory to acquire DIN
- Only single DIN is needed, irrespective of number of directorship
- On resignation of a director of a company, DIN does not get cancelled.
- DIN can be obtained through an online process
- Pre-requisite for e-filing of company’s documents
- Document authorised by a director should mention his DIN with his name.
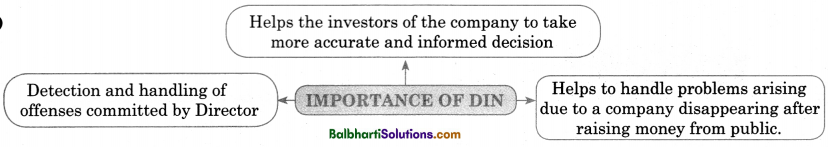
Importance Of Din-
- Helps the investors of the company to take more accurate and informed decision
- Detection and handling of offenses committed by Director
- Helps to handle problems arising due to a company disappearing after raising money from public.
Qualification of a Director-
- No prescribed academic or professional qualifications
- If any provision in Articles of company is mentioned for a minimum share qualification shares.
![]()
Types of Directors
- First Directors
- Rotational Directors
- Additional Directors
- Alternate Director
- Woman Director
- Nominee Director
- Executive Director
- Non-Executive Director
- Independent Director
- Small Shareholders’ Director
Appointment of Director-
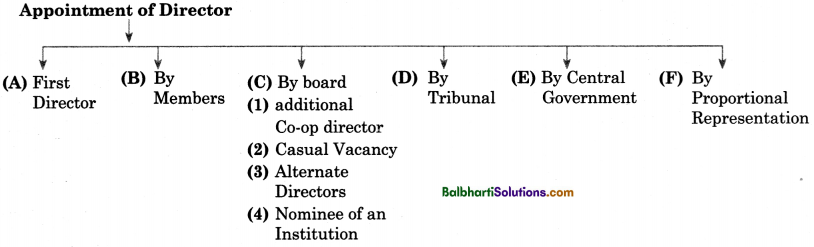
(A) First Director
(B) By Members
(C) By board
- additional Co-op director
- Casual Vacancy
- Alternate Directors
- Nominee of an Institution
(D) By Tribunal
(E) By Central Government
(F) By Proportional Representation
Powers of the Directors-
- Works as a team
- Cannot exercise the powers which are exercised by shareholders
- Exercise the powers — (i) by passing a Resolution (ii) by Delegation to different committees created by Board
- Exercise of powers — subject to provision of Act, Memorandum of Association, Articles of Association
Duties of a Director-
(1) Statutory Duties:
- To file Return of Allotments
- Act accordance of Articles of company
- Disclose interest in a transaction
- Attend Board Meetings.
- Appoint first auditors
(2) General Duties:
- Duty of good faith
- Duty of Care
- Duty not to delegate his function to others
Liabilitird of Directors –
- Liability to the company
- Liability to the third party
- Liability for breach of statutory duties
- Liability for the acts of Co-directors
- Criminal Liability
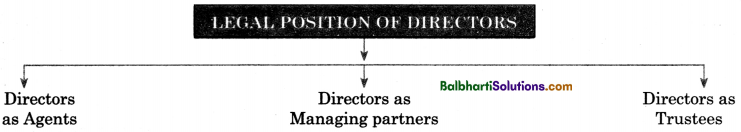
Legal Position of Directors-
- Directors as Agents
- Directors as Managing partners
- Directors as Trustees
Remuneration of Directors and Managing Director u/s 197-
Entitle in form of
- Salary
- Specified percentage of net profits / commission and sitting fees for attending board meetings
Public Company Director’s Salary
Should not exceed 11% of net profit in a financial year.
(Excludes sitting fees paid or to be paid for meeting)

Removal of a Director-
- Shareholders u/s 169
- Tribunal u/s 402
Vacation of office by a Directors: u/s 167 of the Act
- Any disqualification u/s 164
- Absentee at Board Meaning u/s 167.
- Contravention of Provision of Act
- Failure to Disclose Personal Interest
- Disqualification by Court or Tribunal
- Imprisonment for an offence
- Provision of the Act
![]()
Key Managerial Personnel (KMP) of the Company-
Meaning:
u/s 2(51) KMP means the following :
- The CEO or the Managing Director or the Manage
- The Company Secretary
- The Whole Time Director
- The Chief Financial Officer
- Any other officer as may be prescribed
u/s 203 of Act: Stated that every listed company and public company with a share capital of Rs. 10 crores or more should have following Whole Time KMP
- The Managing Director / The Chief Executive Officer/The Manager and in the absence a Whole-time Director
- A Company Secretary
- A Chief Finance Officer
The Managing Director: u/s 2(54)-
1. Appointment:
- An agreement with company
- A Resolution passed by company in General Meeting
- A Resolution passed by Board of Directors
- A clause in the Articles of Association of the company
2. Term of Appointment: Term of 5 years
Disqualification for post of Managing Director
- Any person less than 21 years of age and more than 70 years of age
- Undischarged insolvent person or at any time been adjudged as an insolvent
- Suspended payment to his creditors at any time
- Convicted by a court of law of an offence with a sentence of more than six months period.
Powers and Duties of Managing Director-
- Appointed to manage the affairs of the company.
- By Agreement made with company, by Memorandum and Articles of Association, Resolutions passed by board and members.
- Substantial powers of management.
- Relate to particular divisions of the business.
- May be more than one Managing Director in business / company.
- Superintendence control and directions of the Board of Directors.
- Must be a Director of the company.
- Fulfill his duties, responsibilities and liabilities as an ordinary director of the company.
The Whole Time Director of the Company (WTD) u/s 2(94)-
- whole time employment.
- whole / full time to work.
- employee director.
- does not exercise substantial powers.
- perform important administration functions.
The Manager: u/s 2(53)-
- Superintendence, control and direction of the Board.
- To manage whole or substantially whole affairs of the company.
- Occupies the position of a manager (or known by in any name). .
- Need not be the director of the company.
- Company cannot have more than one manager.
Appointment of different categories of managerial personnel (u/s 196) :
- It is prohibited to appoint both Managing Director and Manager simultaneously.
- There is no prohibition on having whole time director and manager simultaneously.
- There is no prohibition on having managing director and whole time director simultaneously. —
- There is no prohibition on having more than one Managing Director in a company.
![]()
Company Secretary-
Meaning:
Section 2(24)
- Company Secretary is appointed to perform functions of Company Secretary under the Act.
- Person should be a member of the Institute of Company Secretaries of India (ICSI).
- Appointment a whole-time company Secretary -(a) Listed companies (b) All other companies with a paid-up share capital of five crores or more.
- Appointment a whole time Company by a resolution of the Board
- Cannot hold office in more than one company.
- Can be director of a company with the permission of the Board.
- Appointed by the Promoters of the company is the first Secretary is called as ‘Pro-tem Secretary’ for fulfilling different formalities during formation of the company
- Must be recorded in the Register of Directors and key managerial personnel and their shareholdings.
Dut’iks of Company Secretary-
(i) Statutory Duties
- Organize and present at all meetings
- Make minutes of all meetings
- Correspondence with the shareholder
- Issuing notices and circular
- Maintain and update different Registers and books
- Filing all necessary returns with the Registrar of companies
(ii) General Duties
- Provide guidance to the Board and Director
- Represent before different authorities and regulators
- Assist board in the conduct of the affairs of the company.
- Assist and advise the Board ensuring corporate governance.
- Perform all the duties time to time.
Rights of Company Scretary –
- Control and supervise his department
- Indemnified by company if any loss is suffered by Secretary
- Right to sign a document as Principal officer
- Get remuneration as employee of the company

Role Of Company-
- As a Statutory Officer
- As a Coordinator
(a) Internal
(b) External - As an Administrative Officer

![]()
Secretarial Audit: u/s 204-
Meaning:
- This is an audit which checks the compliance of various legislations including Companies Act and other corporate and economic laws applicable to the company.
- In order to prevent risk and losses.
- Gives confidence to regulators, Management, Stockholders.
The Chief Financial (finance) Officer (CFO)-
- Responsible for company’s finances.
- Analyzing company’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Taking timely corrective measures.
- Timely and reporting accurate financial information of the company.
- May be full time employee or contractual.
- Need not be Director.
- Compulsorily requires to sign audited financial statements.
Word Meaning:
incapability – unable applied to a person; elaborately – in detailed; statutory – required as per the law; inability – unable to do something; vastness – very great in ; hierarchy – order in which members of organization are placed; extensive – large; composition – formation; indicative – certain examples set for something; Detection- observation; indicative – certain examples set for something; eligently – in simple manner; academic – formal education in school and colleges; entrusted – the responsibility given to someone; impose – to force; parameters – measurable set of condition; mandatory – compulsory; entitlement – right; tribunal – a body establish to solve the disputes; imprisonment – jail; obedience – act as given order; superintendence – management; prudence – common sense; virtue – merit/principles; delegate – a person authorised to represent others; substantial – important; undischarged – not officially removed; legislations -law; adjudge – to consider; devotes – to give; simultaneous – at a time; prohibition – restricted/ stop; authentication – originality; manifolds – many in numbers; mouthpiece – speaker; amalgamation – Union of two or more companies; reor ganization – rearranging; diverse – various; standardizing – systematic arrangement; harmonizing – to go together; varied – various; non-compliances – not working as per the law.