By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 1 Introduction of Commerce and Business students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 1 Introduction of Commerce and Business
Human Activities –
Non-Economic Activities
- Done without monetary reward.
- Done to satisfy personal social or religious requirements.
- Examples
- Teacher teaching her son.
- Serving people.
- Cooking by mother, etc.
Economic Activities:
- Involves production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
- Done for monetary reward
- Examples
- Teacher teaching in a school.
- Worker working in a factory.
- Doctor working for a hospital.
- Further divided into 3
- Business
- Profession
- Employment
![]()
Definition of Business-
By Prof. L. H. Haney
“Business activities are all those human activities which are directed towards the prod uction and processing of wealth”
By Pride, Hughes and Kapoor “The organised efforts of individuals to produce and sell for a profit, the goods and services that satisfy society’s needs”
Characteristics / Features of Business-
- Continuity in Dealings: Every business requires regularity in transactions.
- Uncertain Returns: Returns are never predictable or guaranteed, it may earn profit or suffer a loss.
- Risk Element: Exposure to loss due to some unfavorable or undesirable event. Intensity of risk can be minimized but can’t be avoided.
- Satisfaction: Satisfying the customers by providing quality products and services at a reasonable price.
- Two Parties: Minimum two parties are required for exchange i.e. the seller and the buyer.
- Economic Activity : To earn money or livelihood.
- Profit Motive :
- Basic purpose of business is to earn the profit.
- It is spine of business which keeps the business growth till long term.
- Production of Goods and Services : Goods are either manufactured or procured from the supplier with aim of selling to consumers for profit.
- Exchange of Goods and Services :
- Transfer of goods and services directly or indirectly with money or money’s worth.
- e.g. Buying clothes against cash.
- Dealings in Goods and Services :
- Every business is involved either with Goods or Services.
- Goods-
- Consumer Goods (Tea, Milk, Pencil, etc.)
- Capital Goods (Machinery, Plant, Furniture, etc.)
Profession-
Part of economic activities under which a person uses his educational knowledge and special skill to
render services for earning some income.
e.g. Doctor, Lawyer, Chartered Accountant, Professor, etc.
Features of Profession-
(i) Qualification : Practiced after acquiring required qualifications.
(ii) Returns :
- Professional gets fees in exchange of service rendered.
- Can be employed in an organization or self employed.
(iii) Capital:
- Either can be practiced independently or professionals can work under someone.
- Independent practiced professional requires huge capital for setup.
(iv) Work Nature :
Professionals hold special knowledge and do skillful work like Doctors , Lawyers, etc.
(v) Aim:
- Practiced for earning money.
- Render service to their clients and solve their problems.
(vi) Registration and Membership : Professionals have to register them with their respective council and get certificate for practice.
(vii) Non-transferability : Profession cannot be transferred to other person on the will of professional.
![]()
Employment-
- It is an economic activity in which people work for others for remuneration.
- Term and conditions are agreed by both employer and employee.
Features of Employment-
(i) Qualifications:
Skilled Job
- Requires specific qualifications,
- E.g. Job of Accountant or Nurse
Unskilled
- Requires specific qualifications,
- E.g. Office boy or Clerk.
(ii) Monetary Returns :
Wages
- Decided in advance before appointment.
- Paid daily or weekly.
Salary
- Paid monthly
- Other benefits are also provided.
Capital: No capital is required for employment.
Nature of Work : The nature of job decide the nature of work.
Aim: To earn money for meeting needs of employer and employee.
Registration:
- No registration is required.
- Has to follow rules and regulation as mentioned in the terms and conditions of the employment- contract.
Non-transferability : Employment cannot be transferred from one person to another.
![]()
Business Objectives-
- Economic Objectives
- Social Objectives
Economic Objectives
- Searching New Customers
- Earning Profit
- Best Possible use of Resources
- Innovations
Social Objectives
- Contributing to the welfare of the society
- Avoiding unfair trade practices
- Supplying quality Products
- Help to solve social problems
- Employment generation
- Welfare of employees
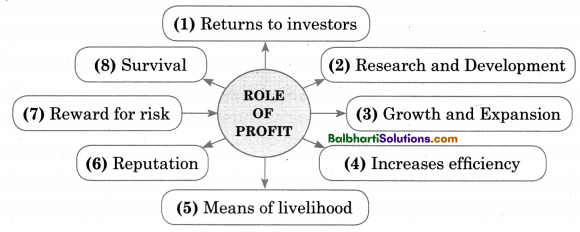
Role of Profit in Business
Profit = Revenue – Total Cost
Role of Profit
- Returns to investor
- Research and Deve1opmen
- Growth and Expansion
- Increases efficiency
- Means of livelihood.
- Reputation .
- Reward for risk
- Survival
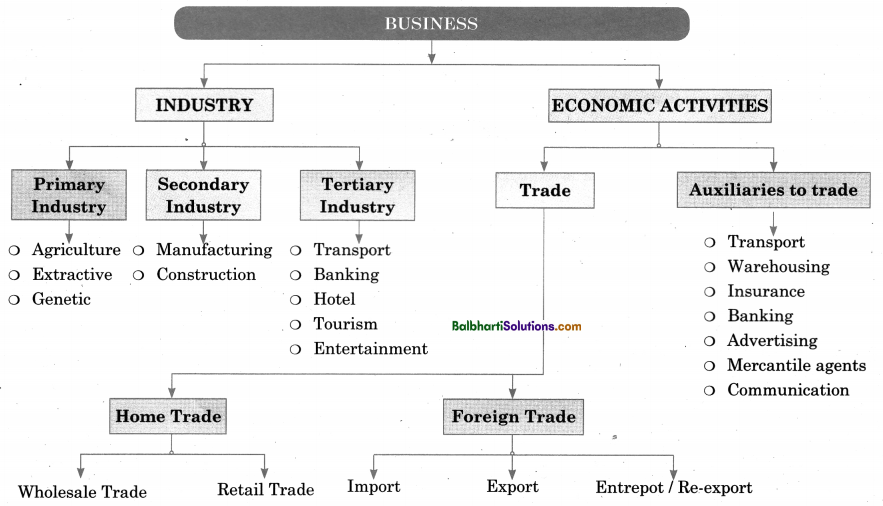
Classification of Business Activities-
- Industry
- Economic Activities-
Industry:
- Primary Industry
- Secondary Industry
- Tertiary Industry
Primary Industry
- Industry
- Agriculture
- Extractive
- Genetic
Secondary Industry
- Manufacturing
- Construction
Tertiary Industry
- Transport
- Banking
- Hotel
- Tourism
- Entertainment
Economic Activities-
- Trade
- Auxiliaries to trade-
Trade
- Home Trade
- Foreign Trade
Home Trade
- Wholesale Trade
- Retail Trade
Foreign Trade
- Import
- Export
- Entrepot/ Re-export
Auxiliaries to trade-
- Transport
- Warehousing
- Insurance
- Banking
- Advertising
- Mercantile agents
- Communication
![]()
Word Meaning:
monetary – related to money; consumption – using; livelihood – to get basic needs of life; systematic – properly arranged; reward – returns; multiple – many; complex – difficult; manpower – human; cultivating – a process in farming; warehousing – place where goods are stored; spine – backbone; intangible – can’t be seen physically; continuity – regularly; predictable – expected; intensity – force; render – provide; acquiring – obtaining; code of conduct – set of rules; expert – person knowledgeable in a particular area; remuneration – salary; quarters – place to stay provided by company to his employees; subsidized – in low cost; bulk – in large quantity; survival – continuing to live; scarce – short in supply; unfair trade – wrong business practice; black marketing – illegal trade; misleading – false information; divyang – physically challenged; welfare – wellbeing; impartial – equal treatment; incentives – benefits in terms of money; retention – continuation; volume – size; diversification – process of enlarging the business; adverse – unfavorable; utility – useful; crude – raw material; tertiary – service; uninterrupted – continuation; auxiliaries – assistant; hindrances – problems; reasonable – low cost; rescue – save; desire – strong wish to have something; prominent – important; scattered – found in various location; information explosion – increased amount of information; broader – large; narrow – limited.