By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 Solid State students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 Solid State
Solids-
- Crystalline
- Amorphous
Crystalline solids-
- Ionic crystals
- Covalent network crystals
- Molecular crystals
- Metallic crystals
Crystal systems-
- Cubic
- Orthorhombic
- Tetragonal
- Monoclinic
- Rhombohedral
- Triclinic
- Hexagonal
Classification of crystal systems (Bravais lattices) :
Cubic lattice –
- Simple cubic or primitive
- Body centred cubic
- Face centred cubic
Number of atoms in the unit cell :
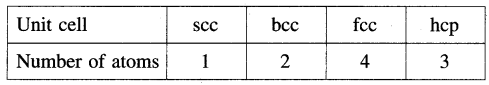
![]()
Packing efficiency :
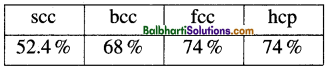
Number of tetrahedral voids = 2 Number of atoms
Number of octahedral voids = Number of atoms
Relation between radius (r) of an atom and edge length (a) of cubic unit cell
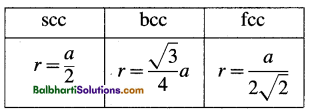
Density of the crystal: p = \(=\frac{n \times M}{a^{3} \times N_{\mathrm{A}}}\)
Defects in solids-
(1) Point defects-
- Vacancy defects (Schottky defects)
- Interstitial defects (Frenkel defects)
- Impurity defects-
- Substitutional impurity defects
- Interstitial impurity defects
(2) Nonstoichiometric defects
- Metal deficiency defect
- Metal excess defect
![]()
Conducting solids-
- Conductors
- Semiconductors
- Insulators
Semiconductors –
- Intrinsic
- Extrinsic
- n-type
- p-type
Magnetic properties-
- Diamagnetic
- Paramagnetic
- Ferromagnetic
(1) Diamagnetism is due to the presence of all paired electrons in the substance.
(2) Paramagnetism is due to the presence of one or more unpaired electrons in the substance.