By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 Elements of Groups 16, 17 and 18 students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 Elements of Groups 16, 17 and 18
Atomic, physical and chemical properties of group 16,17 and 18 elements-
Group 16 elements-
O to Po:
- Atomic size, M.P., B.P., Density increase
- Ionisation enthalpy, electronegativity decrease
- Hydrides (H2X) : Bond angle, bond energy decrease Reducing power increases
- Oxides (EO2, EO3) (E = S, Se, Te, Po)
- Halides (EX6, EX4, EX2) (E = S, Se, Te)
- Reacts with metals to form compounds
Allotropes :
- O : O2, O3 (Ozone)
- S : Rhombic, monoclinic, cyclo-S6
- Se : red, grey
- Te : Crystalline, amorphous
- Po : α, β
Group 17 elements-
F to I (At):
- Atomic size, Density increase
- Ionisation enthalpy, electronegativity decrease
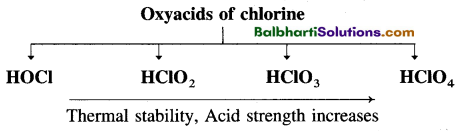
- (Haloacids, HX) : Acidity, reducing character increase Stability decrease
- Oxides of halogens (Most of them are unstable)
- Interhalogen compounds
- Metal halides
![]()
Group 18 elements-
He to Xe (Rn):
- Atomic size, density, M.P., B.P., increase
- Ionisation enthalpy, decreases
- Chemically inert towards hydrogen, oxygen
- krypton and Xenon form fluorides
Oxoacids of sulphur-

Oxoacids of halogens-
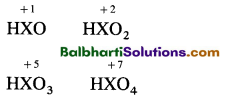
O2 – Preparation –
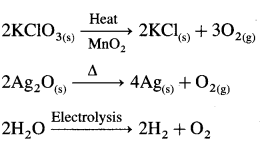
O2 –
2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
C + O2 → CO2
![]()
Simple oxides-
Acidic (CO2, SO2, etc.)
Basic (CaO, BaO, etc.)
Amphoteric (Al2O3, Zno, etc.)
Ozone –
Oxidising property: (i) PbS(S) + 4O3(g) → PbSO4 + 4O2(g)
(ii) 2KI + H2O +O3 →2KOH + I2 + O2
(iii) NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g)
Bleaching property O3 → O + O2
Reducing property : BaO2 + O3 → BaO + 2O2
H2O2 + O3 → H2O + 2O2
![]()
SO2 – preparation
S(S) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
Na2SO3 + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4 + H2O(I) + SO2(g)
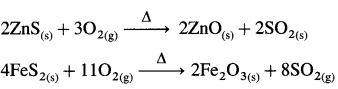
SO2 –
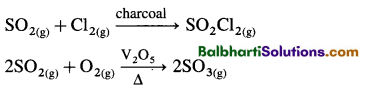
2NaoH + SO2 → Na2SO3 + H2O
Na2SO3 + H2O + SO2 → 2NaSO3
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO4 2- + 4H+
H2SO4 (Manufacture)—Contact process—(Catalyst V2O5)
H2SO4 –
C + 2H2SO4 → CO2 + 2H2O + 2SO2
S + 2H2SO4 → 3SO2 + 2H2O
Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
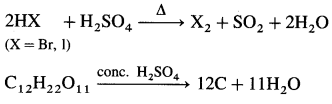
NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
KNO3 + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HNO3
CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
Chlorine Preparation –
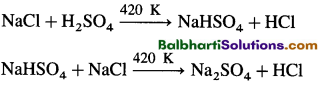
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
4NaCl + MnO2 + 4H2SO4 → 4NaHSO4 + MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
![]()
NaCl ⇌ Na+ + Cl–
Cl2 –
2Al + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3
P4 + 6Cl2 → 4PCl3
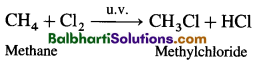
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
8NH3 (Excess) + 3Cl2 → 6NH4Cl + N2
2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 → Ca(OCl)2 + CaCl2 + 2H2O
2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + Cl2 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 2HCl
Cl2 + H2O → HCl + HOCl
HCl : Preparation –
HCl –
HCl(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+ + Cl–(aq)
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
Au + 4H+ + NO–3 + 4Cl– → AuCl–4 + NO + 2H2O
![]()
Interhalogen Compounds-

Compounds of Xenon-
| Compound | Hybridisation | Structure |
| (i) XeF2 | sp3d | linear |
| (ii) XeF4 | sp3d2 | square planar |
| (iii) XeF6 | sp3d3 | distorted octahedral |
| (iv) Xe03 | sp3 | pyramidal |