By going through these Maharashtra State Board Book Keeping & Accountancy Notes 12th Chapter 7 Bills of Exchange students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Accounts Notes Chapter 7 Bills of Exchange
Introduction-
When goods are sold on credit, there is an implied promise by the buyer to pay money to the seller on a future date. Similarly, in the case of borrowing or lending of money, borrower/debtor borrows money on oral or implied promise. Such credit sales or lending of money involves risk of recovery of debts in time. In spite of repeated reminders, some borrowers/debtors do not fulfil their promises. So in the interest of seller or creditor, the party to the credit transaction prepares a written document or undertaking giving the details of debts such as person liable to pay debts, person entitled to receive the payment, amount of debts, date of payments, signatures of the parties to the transaction, etc.
This written document or undertaking is called Credit Document or Negotiable Instrument. Bill of Exchange is one of the important credit instruments used to support credit transactions. In India, in ancient days, instrument of credit popularly known as Hundies were used on large extent. Bills of exchange if drafted in any one of the Indian languages such as Marathi, Gujarati, Urdu, Hindi, etc., is called Hundi. Hundies are classified into different types like Shahjog Hundi, Darshani Hundi, Muddati or Miadi Hundi, Namjog Hundi, Dhani-Jog Hundi, Jawabee Hundi, Hukhami Hundi, Firman-Jog Hundi, etc.
![]()
Necessity : The necessity of Bills of Exchange is summarised as follows :
- In the Bills of Exchange the debtor gives acknowledgement of the debts which automatically
creates evidence of debts. , - The seller or creditor is relieved from the tension or risk of recovery of the amount or debts.
- The seller or creditor comes to know the exact date of receiving the payment of the bill.
- It is a valuable document which can be discounted with the bank to raise needed finance.
- It can be used or endorsed by its owner in settlement of the debts owed by him / her.
Meaning and definition : Bill of Exchange is a written acknowledgement of debt given by the debtor to the creditor along with a written promise to pay that debt on demand or after a specified period to the creditor or any other person as per his order. Usually bill of exchange is drawn by the creditor on his debtor. It is accepted by debtor.
According to the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, Bill of Exchange is defined as, “ an instrument in writing containing an unconditional order signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay on demand, or on a certain future date, or after a certain period of time, a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument. ”
Salient features of a Bill of Exchange :
- A bill of exchange must be in writing.
- A stamp of proper value must be affixed on it as per the provisions of Stamp Duty Act, 1889.
- It must be dated.
- It should contain an unconditional order to pay certain sum of money only.
- Such order is given to make payment of certain or definite sum of money only.
- The order is to make payment to a certain person whose name is specified in it or to his order or the bearer.
- The maker of the bill signs the bill of exchange.
- It must be accepted by the drawee i.e. the person on whom it is drawn.
- It must clearly specify when payment is to be made.
Draft, Format of Bills of Exchange-
There are three parties to a bill of exchange viz., the drawer, the drawee and the payee.
(1) Drawer : The person who draws or prepares the bill, gives the order to pay money and signs on it is called Drawer. He is a creditor. He has to receive the amount specified on the bill. Accordingly drawer records all transactions relating to bills under the title or name called “Bill Receivable”.
(2) Drawee : The person on whom the bill is drawn is called Drawee. Every bill drawn by the drawer Is required to be accepted by the drawee. When drawee accepts the bill or agrees to make the payment, he becomes the Acceptor. Since, the amount of bill is payable on due date by drawee and hence for him it is “Bill Payable”.
(3) Payee : The person named in the instrument, to whom the amount of the bill is to be paid is called the Payee. Generally, drawer is the payee, but payee could also be a third person like a creditor to whom the amount is made payable by drawer.
Contents of format of B of Exchange :
- Date : At the top righ and corner below the address of the drawer, date on which bill is drawn is to be written, which is required to calculate maturity date.
- Term : Term of bill must be mentioned in months or in days.
- Amount: Below the stamp, amount of bill in figure should be mentioned and amount of bill in words are written in the body of bill.
- Stamp : Appropriate value of stamp should be affixed as per Indian Stamp Act 1889.
- Parties : in the bill of exchange names of drawer, drawee and payee and their address must be mentioned.
- For value received : The bill of exchange should be issued in exchange of some benefit received which is legally necessary.
- Acceptance : At per mutual understanding, drawer makes a draft for bills of exchange and sent it to drawee for acceptance. Drawee then signs that draft with his name along with date across the face of the bill with the words ‘Accepted’. On acceptance by drawee, that ‘draft’ becomes bill of exchange.
![]()
Pro Forma of a Bill of Exchange :
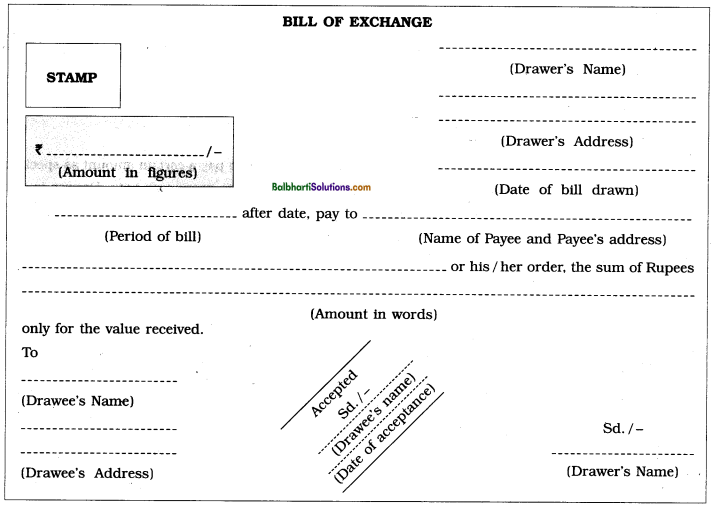
Acceptance of Bill of Exchange : Acceptance of a bill of exchange means signing the bill of exchange by drawee to give his assent to pay the amount of the bill. Unless the bill is accepted by drawee, he is not liable to pay an amount of the bill. A bill of exchange before its acceptance is called a Draft.
Types of Acceptance : Acceptance of bill of exchange can be of two types viz., (1) Unconditional or General Acceptance and (2) Conditional or Qualified Acceptance.
(1) General Acceptance :if the drawee accepts the bill without putting any condition or making any change in the original terms of the bill, such an acceptance is known as Unconditional or General Acceptance.
(2) Qualified Acceptance : If the drawee accepts the bill by making certain changes in the original terms regarding the time, amount of payment or place of payment, the acceptance is said to be Conditional or Qualified Acceptance.
A qualified or conditional acceptance may be of five types. They are explained below :
- Qualified as to Time : When drawee accepts the bill by making changes in the period of the bill, it is called Qualified as to Time.
- Qualified as to Place : When drawee is not ready to make payment at the place mentioned in the bill and suggests a different place where he is willing to pay the amount of the bill, it is called Qualified acceptance as to Place.
- Qualified as to Amount : When drawee accepts the bill not for entire amount specified on the bill but for part of the amount of the bill, it is called Qualified acceptance as to Amount.
- Qualified as to Parties : When drawee is not ready to pay the amount of bill to the payee as mentioned in the bill, it is called Qualified acceptance as to Parties.
- Qualified as to Condition : When drawee accepts the bill by putting his own conditions, it is called Qualified as to Condition.
![]()
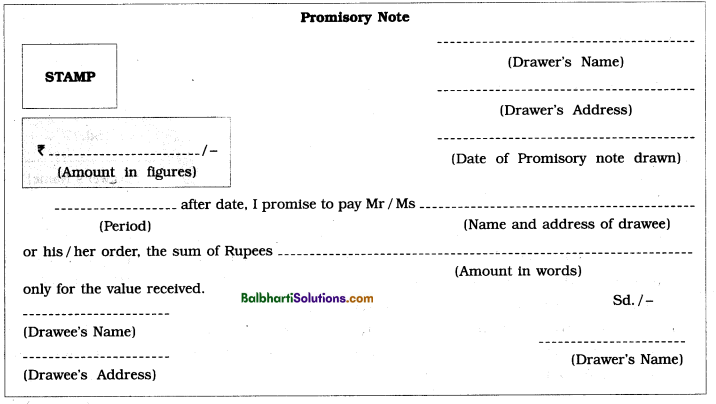
Promisory Note: Promisory note is one of the negotiable instrument payable either to order to bearer.
Parties to a Promisory Note :
- Drawer: A person who draws a promisory note, promises to pay a certain amount as specified
in the promisory note is known as Drawer or Maker of the promisory note. Drawer is also known as the Promiser. - Drawee : A person in whose favour the promisory note is drawn is known as Drawee or Payee of the promisory note. Drawee is aLIso known as Promisee.
Specimen of Promisory Note:
Terms of Bills of Exchange:
Tenor or Term : Tenor or Term of the bill of exchange refers to a period or duration for which bill of exchange is drawn. It is the period of the bill after which it becomes payable. It may be in number of months or in number of days. If the bill of exchange is drawn for 90 days, the term of the bill of exchange in that case is 90 days.
Draft: A bill which is prepared by drawer and not yet accepted by drawee, then it is called Draft.
Days of Grace : Days of grace refer to three extra days allowed by law to the drawee over and above the period of the bill to enable him to make payment. Legal due date is calculated by adding days of grace to the period of the bill. However, grace days are not allowed for the bill payable on ‘Demand’ or ‘At sight’.
Date of Maturity/Due Date of a Bill: The date of maturity or the due date of a bill is the date on which the amount of the bill is to be paid. In the case of a bills made payable, a specified period after date or after sight, the law allows three days of grace in addition to the period specified in the bill. Formulae to calculate the due dates are given below :
(i) If the bill is payable ‘on Demand’ or ‘At sight’, its due date is that date on which it is presented to the drawee for payment. It does not have definite period of time and grace days are not allowed for this type of bill.
(ii) If the bill is drawn ‘After date’
Due Date = Date of bill drawn + Period of the bill + 3 days of grace.
Period of the bill may be in number of months or in number of days.
(iii) If the bill is drawn ‘After sight’
Due Date = Date of bill accepted or date of bill presented for acceptance + Period of the bill + 3 days of grace.
Types of Due Date :
(a) Nominal Due Date : The date on which the term i.e. the period of a bill of exchange gets expired is called Nominal due date. It is calculated without adding days of grace to the period of the bill. .•. Nominal due date = Date of bill drawn / accepted + Period of the bill.
(b) Legal Due Date : Legal due date is that date which is arrived at after adding 3 days of grace in nominal due date.
∴ Legal due date = Nominal due date + 3 days of grace.
If the due date falls on public holiday or Sunday, the payment of the bill is required to be made on immediate preceding working day, e.g. if the due date falls on 15th August, payment must be made on 14th August. Similarly if the due date falls on 26th January, payment must be made on 25th January. According to the provisions made in the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, if in emergency, the Government of India declares a particular date as holiday, then all bills fall due for payment on that date will be paid on very next working date.
![]()
However, if due date of a bill falls due on 7th July, 2020 and this day, the Government of India declared emergency public holiday due to heavy rain and flood, then that bill would be paid on 8th July, 2020 provided it is not Sunday.
Holder : Any person who is entitled in his own name to the possession of the bill and to receive or recover the amount due thereon from the concerned parties thereon is called “holder of the bill”. He may be drawer himself or his creditor in favour of whom drawer has endorsed the bill. Somebody in possession of a stolen or a lost instrument i.e., bills of exchange cannot be a holder. The payee of the bill can be a holder. Any person who has received the instrument from the payee or any previous holder can be a holder.
Holder in due course : A person is said to be “holder in due course” if he satisfies the following conditions :
- He is a holder if it is payable to bearer or he is the payee or endorsee, if it is payble to or to the order of the payee.
- He became the holder before the amount mentioned in the instrument became payable i.e. before maturity.
- He became the holder for valid consideration.
- He became the holder without having sufficient cause to believe that any defect existed in the title of the person from whom he received it, though not of any prior party.
Types of Bills of Exchange : The bills of exchange may be classified as :
(1) Trade bill : A bill of exchange which is drawn by a creditor on his debtor for certain valuable consideration is called Trade bill. Only in case of credit and lending and borrowing, transactions Trade bills are used. The different types of trade bills are explained below :
- Inland bill of exchange : A bill of exchange drawn and accepted between the two parties from the same country is called Inland bill of exchange, e.g. a bill of exchange drawn and accepted at Mumbai and made payable at Kolkata, is known as Inland bill of exchange.
- Foreign bill of exchange : A bill of exchange drawn and accepted in one country and made payable in some other country is called a Foreign bill of exchange, e.g. a bill of exchange drawn in India and made payable in Japan is called a Foreign bill of exchange.
- Bills Payable on Demand or at Sight: A bill of exchange which does not have definite period of time and made payable whenever its payment is demanded, is called bill payable on Demand or at Sight. Grace period of 3 days is not allowed on these bills.
- Bills Payable After Date : A bill of exchange in which period of bill is counted from the date of bill drawn, is called Bills Payable after Date. Grace period of 3 days is allowed on these bills.
- Bills Payable After Sight: A bill of exchange in which period of a bill is counted from the date of presentation or date of acceptance whichever is earlier is called Bill Payable after Sight. Grace period of 3 days is allowed on these bills.
(2) Accommodation bill : A bill drawn not against value received, but to raise money on credit and thus meet the temporary financial needs of the parties thereto, is called Accommodation bill. In order to help a friend and for mutual benefits of the parties thereto, this type of bill is drafted and accepted without any consideration.
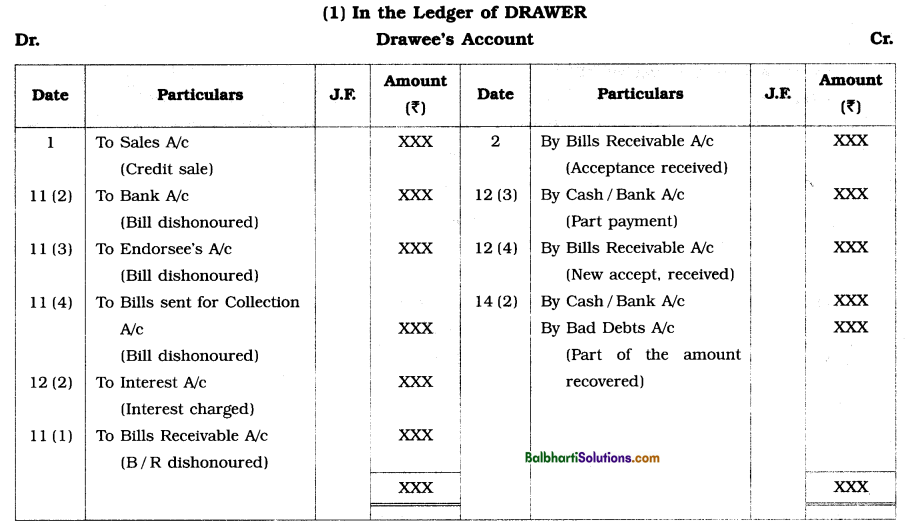
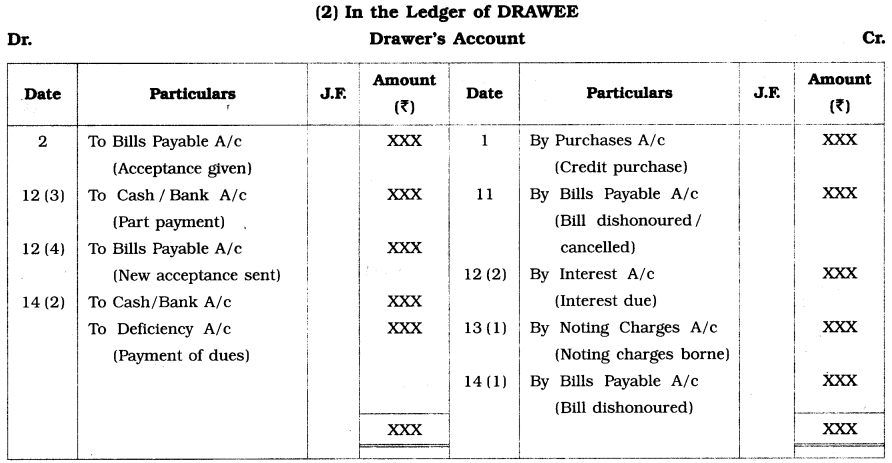
Classification of bills for Accounting : The two fundamental accounting rules for recording bill transactions are : first, to remember that for the acceptor or drawee, a bill is always a Bills payable as he is required to make payment, while for all other parties, it is a Bill receivable; and secondly, to treat both the Bills Receivable A/c and the Bills Payable A/c as Real accounts, debiting what comes in and crediting what goes out.
Thus, on accepting a bill of exchange, the acceptor will debit the Drawer’s A/c and credit the Bills Payable A/c, and on receipt of this acceptance, the drawer will debit the Bills Receivable A/c and credit the Acceptor’s or Drawee’s A/c.
How using of Bill :
If on the due date of a bill, its drawee or acceptor makes a full payment on it to its holder, the bill is said to be duly met or honoured.
Meeting or honouring a bill, thus, means making a full payemnt on it to the holder on the due date by its drawee. For honouring the bill, the drawer or holder of the bill must present the bill to the drawee on or before due date for payment.
Dishonour of a Bill : If the drawee or acceptor of a bill fails to make payment on it on the due date, the bill is said to be dishonoured. The bill may be dishonoured in two ways :
- When drawee does not accept bill, the bill is said to be dishonoured for non-acceptance.
- When drawee refuses or does not make payment on the due date of the bill, the bill is said to be dishonoured for non-payment.
![]()
Legal protection afforded by Bills of Exchange :
(i) Noting of Dishonour : On dishonour of a bill, the holder has to create official proof of dishonour by getting the bill noted. For this he has to approach a Notary Public. Noting of a bill of exchange means recording the facts of dishonour of bill of exchange, date of dishonour, reasons of dishonour, parties to bill, etc. by a Notary Public. The Notary Public also records the facts of dishonour in his official register. Thereafter, the holder generally gives a notice of dishonour to all parties to the bill and seeks to recover from any or all of them the value of the bill plus the noting charges.
(ii) Protesting : Protesting refers to issue of formal certificate bearing a Notary’s seal by notary public, certifying the facts of dishonour of bill of exchange based on noting. Protesting is absolutely necessary in respect of dishonour of foreign bill of exchange. The protest is accepted by the court as evidence of dishonour of a bill of exchange.
Notary Public : An officer appointed by the Government to certify dishonour of bills of exchange is called Notary Public. According to provisions made in the Notaries Act, 1952, he is a public officer whose function is to administer oaths, to attest and certify, by his hand and official seal, certain classes of documents, in order to give them credit and authenticity, to take acknowledgments of deeds and other to conveyances, and certify the same, and to perform certain official acts, chiefly in commercial matters such as the protesting of notes and bills, the noting of foreign drafts, and marine protests in cases of loss or damage. The Notaries Act is administered by the Central as well as State Governments.
Noting Charges : Noting charges refer to fees charged by Notary Public for establishing facts and causes of dishonour of the bill. Drawee or acceptor who is ultimately responsible for dishonour of the bill, has to bear noting charges.
Accounting treatment of Bills of Exchange-
(a) Retaining the bill till due date : Retaining the bill till due date means act of drawer or holder to keep the bill with himself till its due date. On the due date, the drawer or holder of it has to present the bill to the drawee for payment which may be honoured or dishonoured by drawee.
(b) Endorsement of a bill of exchange : When the holder or owner of a bill of exchange signs on its back with the object of transferring its title to somebody else, the signature or the act of signing is called an Endorsement and the bill is said to be Endorsed. The person so signing a note or bill is called the Endorser, while the person to whom it is endorsed is called the Endorsee. The act of endorsement of bill of exchange may continue till its due date.
(c) Discounting of a bill of exchange : A bill is said to be discounted, if before its due date, the holder of the bill, exchanges it for cash, giving away a small part of its face value by way of interest for the unexpired period. Bill is usually discounted with the bank.
While computing the amount of such discount, the students should remember that unless followed biy the words ‘per annum’, the given rate of discount is to be treated as straight or flat, irrespective of the period. Thus, if a three-month bill for ₹ 10,000 is discounted at 5%, the discount will be ₹ 500, but if it is discounted at 5% per annum, the discount will be ₹ 125.
On the due date of the discounted bill, the bank presents the bill before the drawee and recover the entire amount of the bill. In case the bill is dishonoured by the drawee, the bank returns the bill to the drawer and recovers the entire amount from drawer.
Formulae for calculation of discount :
(i) If flat rate of discount is given (i.e. when per annum rate is not given) :
![]()
(ii) If discount rate per annum and period in months are given :
![]()
(iii) If discount rate per annum and period in number of days are given :
![]()
in case of leap year number days will be 366 instead of 365.
(d) Sending the Bills of Exchange to the bank for collection : The drawer of a bill of exchange may deposit the bill with the bank with the instruction that the bill be kept till its maturity and present the same before the drawee on its due date to collect its amount. Accordingly on the due date the bank present the bill before the drawee and collects the amount of the bill. Then the bank credits the proceeds of the bill to the bank account of the depositor (drawer or holder). If bill is dishonoured, the bank will return bill to the depositor. For this service the bank debits the account of the depositor with certain amount of charges.
On depositing the bill with the bank for collection purpose, the drawer opens a separate Account called “Bill sent to Bank for collection Account,” in his books of accounts.
(e) Renewal of a bill of exchange : If the drawee or acceptor of a bill is not in a position to make full payment on it on its due date, he can approach the drawer on or before the due date and request him for an extension of time for payment.
Thus, renewal of a bill of exchange refers to drafting a new bill of exchange in cancellation of earlier bill of exchange by drawer at the request of drawee.
![]()
Note that in most cases, the drawer will not agree to a renewal unless a part payment of the amount due is made in cash and the interest on the unpaid balance for extension of time is also taken into consideration. (Such interest is either paid in cash immediately or is included in the amount of the new bill.)
(f) Ways to renew a bill of exchange :
(1) New bill is drawn without interest for extended credit period :
- A new bill is drafted and accepted equal to the amount of old bill for the extended period of credit.
- The drawer or holder of bill accepts the part payment and drafts a new bill for the balance amount for the extended credit period.
(2) New bill is drawn with interest for extended credit period :
- The drawer or holder receives the interest in cash and drafts a new bill for the amount equal to the amount of that old bill for the extended credit period.
- The drawer or holder receives the part payment along with interest on the balance amount in cash and drafts a new bill for the balance amount for the extended credit period.
- The drawer or holder receives only part of the bill amount of bill and drafts a new bill for the balance amount plus interest due thereon for the extended credit period.
The drawer may renew the bill even after its dishonour on maturity. In such a case, noting
charges may be recovered immediately or added to the amount of new bill.
(g) Insolvency of Acceptor / Drawee on or before due date of a bill :A person whose liabilities are greater than his assets and such liabilities he cannot pay in full, is called insolvent or bankrupt person. If the drawee or acceptor of a bill is declared insolvent, his acceptance is deemed to be dishonoured. Thus, as soon as the drawee or acceptor is declared insolvent, all parties to the bill will treat the bill as dishonoured and pass appropriate entries. If insolvent person owns and possesses any property, it is sold by a liquidator appointed by the court and proceeds so obtained is distributed among the creditors as per the ratio of their dues. Thus, drawer or holder recovers part of the amount due from insolvent drawee’s property. The unsatisfied balance which is not recovered is treated as Bad debts and debited to ‘Bad debts Account’ in the books of drawer and credited to ‘Deficiency Account’ in the books of drawee or acceptor.
(h) Retirement of a bill of exchange : If the drawee or acceptor desires to pay the amount of the bill before its due date, he may approach its holder and offer to make an early payment, generally in reborn for a discount or rebate. If the holder of the bill agrees to the proposal, and accordingly drawee makes payment before maturity, the bill is said to be retired.
Retirement of a bill, thus, means its payment by the drawee or acceptor before its due date, generally at a discount or rebate. Such rebate or discount is an expense to the party (i.e. drawer) receiving the payment and gain to the party (i.e. drawee) making the payment.
Pro Forma journal entries with respect to bills transactions in the books of Drawer and Drawee :
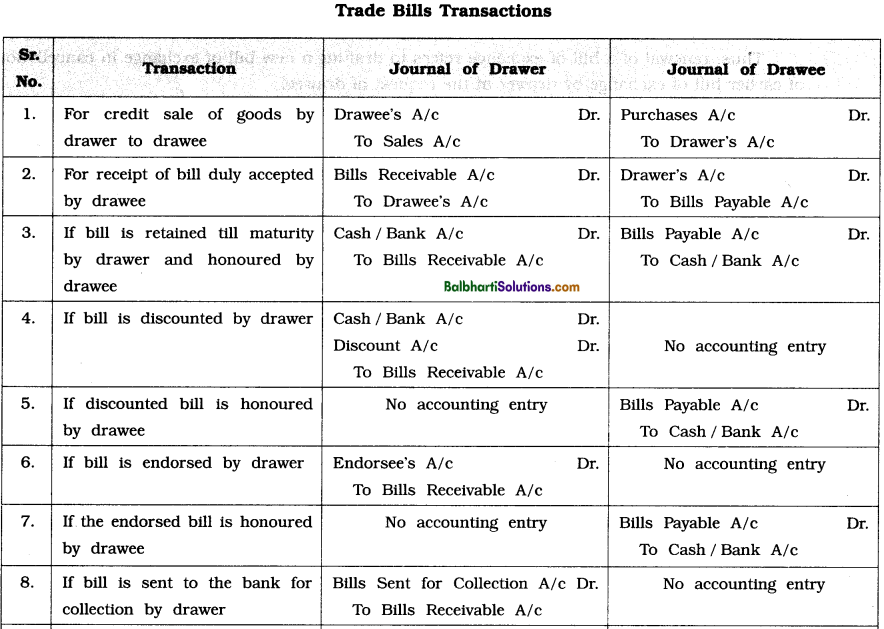
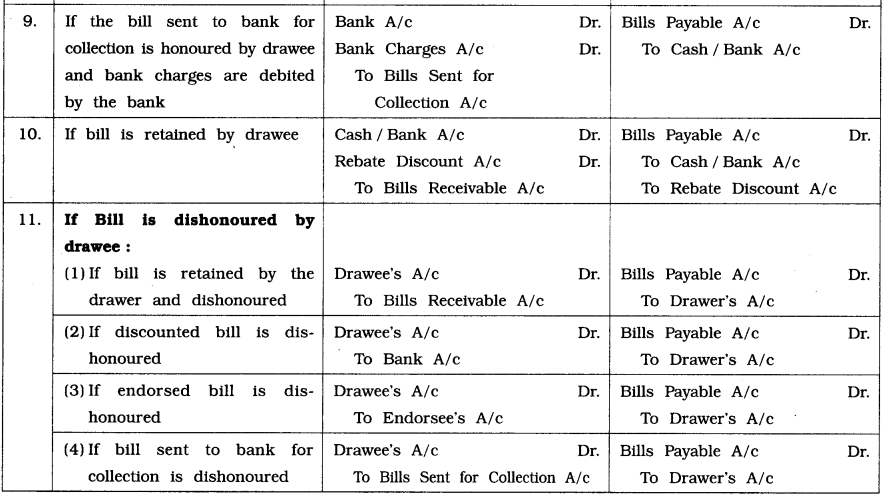
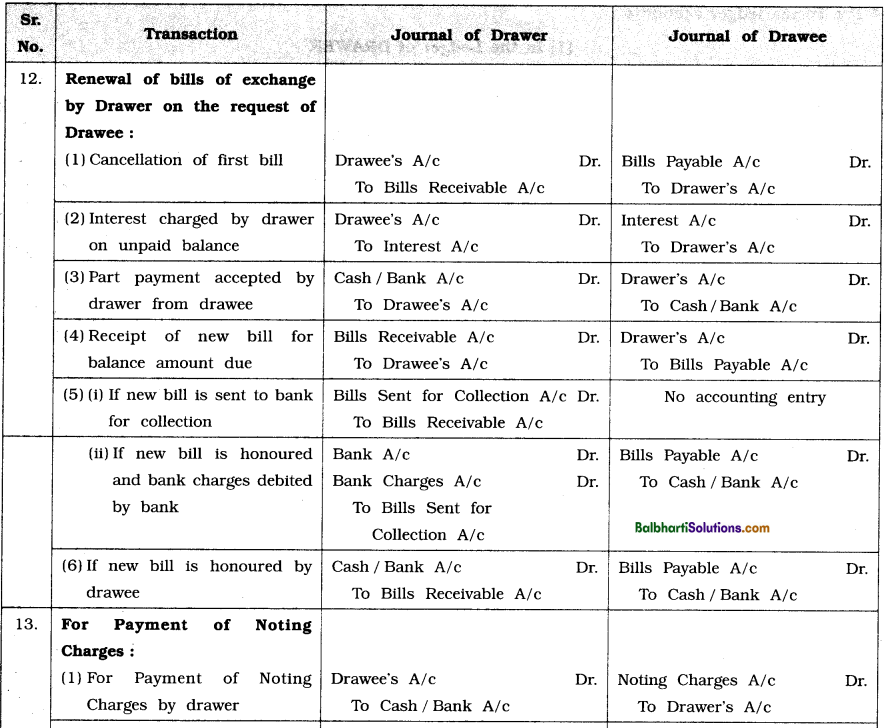
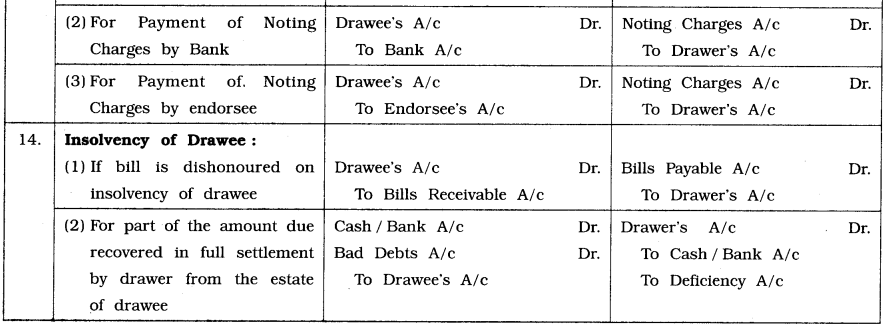
![]()
Pro Forma ledger accounts :