9th Standard Maths 2 Practice Set 1.2 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 1.2 Geometry 9th Class Maths Part 2 Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry.
Class 9 Maths Part 2 Practice Set 1.2 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Geometry Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
The following table shows points on a number line and their co-ordinates. Decide whether the pair of segments given below the table are congruent or not.

i. seg DE and seg AB
ii. seg BC and seg AD
iii. seg BE and seg AD
Solution:
i. Co-ordinate of the point E is 9.
Co-ordinate of the point D is -7.
Since, 9 > -7
∴ d(D, E) = 9 – (-7) = 9 + 7 = 16
∴ l(DE) = 16 …(i)
Co-ordinate of the point A is -3.
Co-ordinate of the point B is 5.
Since, 5 > -3
∴ d(A, B) = 5 – (-3) = 5 + 3 = 8
∴ l(AB) = 8 …(ii)
∴ l(DE) ≠ l(AB) …[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ seg DE and seg AB are not congruent.
ii. Co-ordinate of the point B is 5.
Co-ordinate of the point C is 2.
Since, 5 > 2
∴ d(B, C) = 5 – 2 = 3
∴ l(BC) = 3 …(i)
Co-ordinate of the point A is -3.
Co-ordinate of the point D is -7.
Since, -3 > -7
∴ d(A, D) = -3 – (-7) = -3 + 7 = 4
∴ l(AD) = 4 . ..(ii)
∴ l(BC) ≠ l(AD) … [From (i) and (ii)]
∴ seg BC and seg AD are not congruent.
iii. Co-ordinate of the point E is 9.
Co-ordinate of the point B is 5.
Since, 9 > 5
∴ d(B, E) = 9 – 5 = 4
∴ l(BE) = 4 …(i)
Co-ordinate of the point A is -3.
Co-ordinate of the point D is -7.
Since, -3 > -7
∴ d(A, D) = -3 – (-7) = 4
∴ l(AD) = 4 …(ii)
∴ l(BE) =l(AD) …[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ seg BE and seg AD are congruent.
i.e, seg BE ≅ seg AD
Question 2.
Point M is the midpoint of seg AB. If AB = 8, then find the length of AM.
Solution:
Point M is the midpoint of seg AB and l(AB) = 8. …[Given]

Question 3.
Point P is the midpoint of seg CD. If CP = 2.5, find l(CD).
Solution:
Point P is the midpoint of seg CD and l(CP) = 2.5 …[Given]
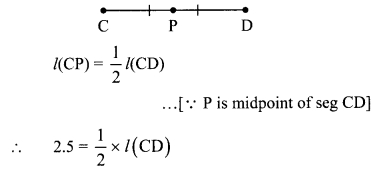
∴ l(CD) = 2.5 x 2
∴ l(CD) = 5
Question 4.
If AB = 5 cm, BP = 2 cm and AP = 3.4 cm, compare the segments.
Solution:
Given, l(AB) = 5 cm, l(BP) = 2 cm,
l(AP) = 3.4 cm … [Given]
r Since, 2 < 3.4 < 5
∴ l(BP) < l(AP) < l(AB)
i.e., seg BP < seg AP < seg AB
Question 5.
Write the answers to the following questions with reference to the figure given below:
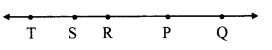
i. Write the name of the opposite ray of ray RP
ii. Write the intersection set of ray PQ and ray RP.
iii. Write the union set of ray PQ and ray QR.
iv. State the rays of which seg QR is a subset.
v. Write the pair of opposite rays with common end point R.
vi. Write any two rays with common end point S.
vii. Write the intersection set of ray SP and ray ST.
Answer:
i. Ray RS or ray RT
ii. Ray PQ
iii. Line QR
iv. Ray QR, ray QS, ray QT, ray RQ, ray SQ, ray TQ
v. Ray RP and ray RS, ray RQ and ray RT vi. Ray ST, ray SR
vii. Point S
Question 6.
Answer the questions with the help of figure given below.
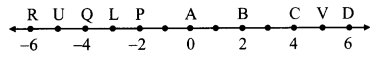
i. State the points which are equidistant from point B.
ii. Write a pair of points equidistant from point iii. Find d(U,V), d(P,C), d(V,B), d(U, L).
Answer:
i. Points equidistant from point B are a. A and C, because d(B, A) = d(B, C) = 2 b. D and P, because d(B, D) = d(B, P) = 4
ii. Points equidistant from point Q are a. L and U, because d(Q, L) = d(Q, U) = 1 b. P and R, because d(P, Q) = d(Q, R) = 2
iii. a. Co-ordinate of the point U is -5. Co-ordinate of the point V is 5. Since, 5 > -5
∴ d(U, V) = 5 – (-5)
= 5 + 5
∴ d(U, V) = 10
b. Co-ordinate of the point P is -2.
Co-ordinate of the point C is 4.
Since, 4 > -2
∴ d(P, C) = 4 – (-2)
= 4 + 2
∴ d(P, C) = 6
c. Co-ordinate of the point V is 5.
Co-ordinate of the point B is 2.
Since, 5 > 2
∴ d(V, B) = 5 – 2
∴ d(V, B) = 3
d. Co-ordinate of the point U is -5.
Co-ordinate of the point L is -3.
Since, -3 > -5
∴ d(U, L) = -3 – (-5)
= -3 + 5
∴ d(U, L) = 2
Std 9 Maths Solutions Maharashtra State Board