By going through these Maharashtra State Board Bookkeeping and Accountancy 11th Notes Chapter 8 Rectification of Errors students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Accounts Notes Chapter 8 Rectification of Errors
Meaning of Accounting Errors-
In simple words error means mistake or omission. Accounting error refers to mistakes committed in recording business transactions in the books of accounts, carrying forward amount to next page, posting the amount on the wrong side of ledger account, failing to record transactions in the books of accounts. Omission of writing accounts in the books of accounts is also considered as accounting error. Accounting errors are committed without any intention. If mistakes are committed with some intention, it is not considered as an accounting error but is cheating or fraud.
Accounting errors if at all committed, are required to be corrected as soon as they are detected. Some accounting errors are traced out by checking or verifying the ledger accounts systematically whereas others can be found out through preparation of trial balance. When total of debit column of the trial balance does not tally with the total of credit column of trial balance, it is confirmed that some type of accounting errors have been committed in writing the accounts in the books of accounts. For instance, instead of debiting Vishwanath’s A/c. for amount paid, wrongly debited Vishwasrao’s A/c. is considered as accounting error.
Effects of Accounting Errors-
Some accounting errors if committed do not allow the total of trial balance to agree with each other. Accounting errors affect the net result and financial position of the business. They also affect the arithmetical accuracy of the business. Accounting errors may occur at any one of the following stages viz. (1) Preparation of documents (2) Preparation of Primary books (3) Preparation of ledger accounts (4) Preparation of trial balance and (5) Preparation of final accounts.
![]()
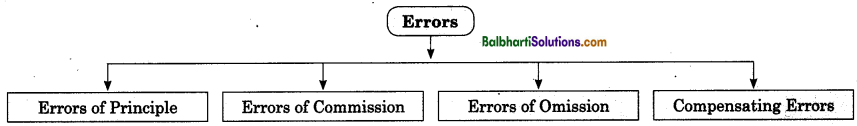
Types of Accounting Errors-
The different types of accounting errors are shown in the following chart:
Each of the above accounting errors is explained in detail:
(i) Errors of Principle : Error of principle is said to be committed if accounting entries are not made as per fundamental rules, of accountancy. Errors of principle refers to mistake committed by accountant by not following accounting principles properly. Error of principle is said to be committed when an accounting principles relating to proper distinction between capital and revenue items is violated. These errors are not disclosed by the trial balance.
Examples :
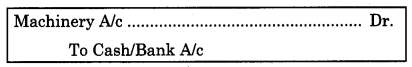
- Wages paid for installation of machinery, debited to Wages Account is an error of principle. Wages paid for installation of machinery is a capital expenditure and it supposed to be added to the cost of machinery. Correct entry for wages paid for installation of machinery is:
- Repair charges of building paid are debited to Building A/c
- Payment of rent debited to Landlord’s A/c.
(ii) Error of Commission : Errors of commission occur when incorrect entries are passed in the journal, wrong posting is done in the ledger, wrong casting is done, wrong calculations are done, mistake made in carrying forward the amount to next page etc. This type of error is disclosed by trial balance. If error of commission takes place, trial balance will not tally. Error of commission is detected by preparing a trial balance.
For instance, in credit purchase of goods worth ₹ 1,850 from M/s. Shanti General Stores is entered in the purchase book as ₹ 1,850 and in the ledger account of M/s. Shanti General Stores as ₹ 1,580. This is error ‘
of commission. In this case M/s. Shanti General Stores Account is given less debit by ₹ 270. This error is rectified by giving additional debit of ₹ 270 to M/s. Shanti General Stores Account. ‘
(iii) Errors of Omission : Errors of omission are said to occur if the accountant or clerk has failed completely to record a particular business transaction in the books of account. In other words, if business transactions are not at all recorded in the books of account, errors of omission are said to be committed.
For example, failure on part of the clerk to record credit sales in the sales book, is an error of omission. Error committed due to entire omission will not affect the agreement of totals of trial balance, but error committed due to partial omission will definitely affect the agreement of totals of trial balance.
(iv) Compensating Errors : Compensating error is said to be committed if error committed on one side of
ledger account compensate an error committed on the other side of some other ledger account. Errors which are committed on one side of account remove or nullify the effect of errors committed on the other side of account, is called a compensating error. This type of error may be different in nature but they are similar in amount. Compensating errors are committed exactly on opposite side of same account or different account.
Even compensating errors are committed on same side of different account, by giving over debit to one account and under debit of same amount to.other account. This type of error cannot be detected by preparing trial v balance.
For instance, if purchase book is overcast by ₹ 1,500 and sales book is also overcast by ₹ 1,500 than such ‘
errors are called compensating errors because one error removes the effect of other error. ;
Errors Affecting And Not Affecting The Trial Balance-
The classification of error on the basis of trial balance is shown in the following chart:
Trial Balance Basis:
(A) Errors not affecting the trial balance (Two sided Errors)
- Complete omission of transaction.
- Posting wrong amount on both the sides of an account.
- Posting wrong heads of account.
- Compensating Errors. BoIbhartSoIution5com
- Recording wrong amount in original books.
(B) Errors affecting the trial balance (One sided errors)
- Partial omission of a transaction.
- Posting of Wrong amount on one side of an account.
- Posting entry on wrong side of an account.
- Wrong totalling or balancing of an account.
- Omission of transferring the balance of an account to Trial Balance.
(A) Errors not affecting the trial balance (Two sided errors):
An accounting error which affects or does not affect debit side of one account as well as credit side of another account is called two sided error. This type of error cannot be detected by preparing a trial balance. These types of errors are explained below.
(i) Complete omission of a transaction: For the explanation please refer to point 3 (iii) of this chapter.
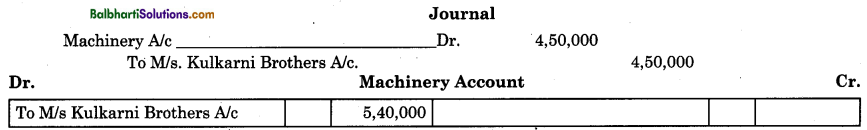
(ii) Posting or recording wrong amount on both the sides of an account: This type of error is said to be committed when accountant enters wrong amount in both affected accounts. Such error will not be disclosed by the trial balance.
This is explained as follows:
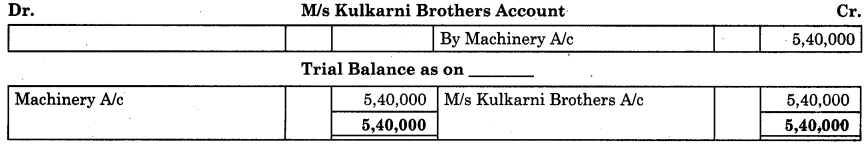
![]()
(iii) Posting to wrong head of account: This type of error is said to be committed when a transaction is recorded correctly in the original books of account, but ledger posting is done to wrong heads of account, e.g. Furniture purchased from M/s Salgaonkar is posted to Machinery A/c. In this case M/s Salgaonkar’s A/c is correctly credited but Machinery A/c is wrongly debited instead of Furniture A/c.
(iv) Compensating errors : For the detail information, refer point No. 3 (iv) from the Subject Matter.
(v) Wrong amount in the original books: This type of error is said to be committed when a transaction is wrongly recorded in the original books and is subsequently carried through to the ledger account, e.g. Sales of goods ₹ 854 on credit recorded in the sales books as ₹ 584 and subsequently posted to ledger the same wrong amount of ₹ 584. This error does not affect the trial balance.
(vi) Errors of principle :
Errors of Omission : Errors of omission are said to occur if the accountant or clerk has failed completely to record a particular business transaction in the books of account. In other words, if business transactions are not at all recorded in the books of account, errors of omission are said to be committed.
For example, failure on part of the clerk to record credit sales in the sales book, is an error of omission. Error committed due to entire omission will not affect the agreement of totals of trial balance, but error committed due to partial omission will definitely affect the agreement of totals of trial balance.
(vii) Recording twice : This type of error is said to be committed when transaction is recorded twice in the original book. e.g. Paid salaries ₹ 5,000 recorded twice in the cash book. Since excess debit and credit given to both the account, such error does not affect the trial balance.
(B) Errors affecting the trial balance (One sided errors)’:
Some accounting errors bring out the difference in debit total and credit total of trial balance. Such errors are called errors affecting the trial balance or one sides errors. The different types of errors affecting trial balance are explained below.
(i) Partial omission of a transaction : When a transaction is recorded correctly in the original books of accounts, but due to mistake one of the ledger accounts remains to be posted, then such a error is called error of partial omission of transaction. e.g. Cash ₹ 6,000 received from Mr. Kishor not posted to Mr. Kishor’s A/c. In this case trial balance will not agree.
(ii) Posting of wrong amount to one account: Error of posting of wrong amount to one account is said . to be omitted when wrong amount is posted to one of the ledger accounts from the original books. In
‘this case trial balance will not get tallied.
(iii) Posting on the wrong side of an account: This type of error is said to be committed when entry
is posted to wrong side of the ledger account from the original book. In this case trial balance will not agree.
(iv) Wrong totalling and balancing: When any ledger account is totalled wrongly or balanced wrongly, this type of error is said to be committed. Because of wrong totalling or wrong balancing, the trial balance will not agree.
(v) Omission of balance of an account in trial balance : If balance of any one or more account are omitted to transfer to the trial balance, this type of error get committed. As a result trial balance will not agree.
(vi) Errors of double posting to one account : When entry for accounting transaction is correctly recorded in the original book but it is posted or recorded two times in one of the ledger accounts, then such error is called error of double posting to one account.
Steps to locate Accounting errors :
The following steps are taken to locate the errors :
- Verification of trial balance: The total of debit column and credit column should be checked once again. Accounts that are grouped together and shown under one head of account should be checked minutely and carefully, e.g. Total of sundry debtors and sundry creditors.
- Verification of cash book: The total of debit column and credit column of cash book should be rechecked. Closing balance of cash and bank balance must be verified.
- Verification of ledger accounts: All the posting made to various ledger accounts must be checked once again. The total of amount column on debit side and credit side of each ledger account should be checked. Similarly balancing figures and carry forward of each ledger account should be checked once again. Any discrepancy, if noticed, it should be corrected at once.
- Verification of trial balance: After verification of ledger accounts, if difference still arises in the totals of the trial balance, the accountant has to find out exact difference in the totals of the trial balance. This will help to locate the errors.
- The accountant should confirm whether closing balance of each ledger account is transferred to trial balance or not. There is possibility that balance of one or two accounts may be omitted or recorded twice.
- The accountant should also go through the journal to find out if any entry is passed with unequal amount specially of compound entries.
- The totals of subsidiary books such as Purchase Book, Sales book, Purchase Return book, Sales Return book etc. should be verified once again and posting to various ledger accounts there from should be verified.
- The accountant should check whether closing balances of various accounts of last year are brought forward to the respective ledger accounts correctly or not.
![]()
Suspense’Account:
Final account is prepared on the basis of the trial balance. Trial balance is supposed to be tallied then only final account can be prepared. Sometimes the trial balance does not tally eveti after repeated efforts. In such circumstances preparation of the final accounts cannot be postponed indefinitely till the errors are disclosed and rectified. In such a case difference of trial balance is usually placed or transferred to a separate account known as suspense account, and the trial balance is made to tally for the purpose of preparation of final accounts. If debit column of trial balance cast short, difference of trial balance is transferred and posted to debit side of suspense account.
Similarly if credit column of trial balance cast short, the difference of trial balance is transferred and posted to credit column of suspense account. If errors are not detected and rectified, balance of suspense account is transferred to balance sheet. Debit balance of Suspense A/c should be shown on asset side of Balance Sheet and Credit balance of Suspense account should be shown on the liabilities in suspense account. When all errors are detected, rectified and adjusted, suspense account will automatically stand balanced. Rectification of errors which affect trial balance are only adjusted in suspense account.
Rectification Entry-
An accounting entry which is drafted to cancel the effects of wrong entry and to give the correct effect of the entry is called rectification entry.
(a) Rectification of Errors of Principle : To rectify errors of principle, the following procedure is to be followed.
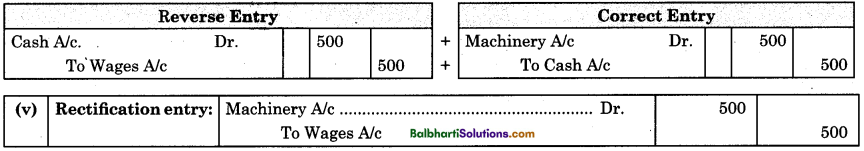
First draft a wrong entry of given transaction and then pass reverse entry of wrong entry. After this, draft ‘ correct entry which we are suppose to pass. Then reconcile reverse entry and correct entry so drafted, to get rectification entry. In short, ;
Reverse entry of wrong entry + Correct entry = Rectification entry
Example : Rent of ₹ 1,200 paid to land lady Mrs. Anuradha has been debited to her personal account. Rectification entry is composed by following procedure :
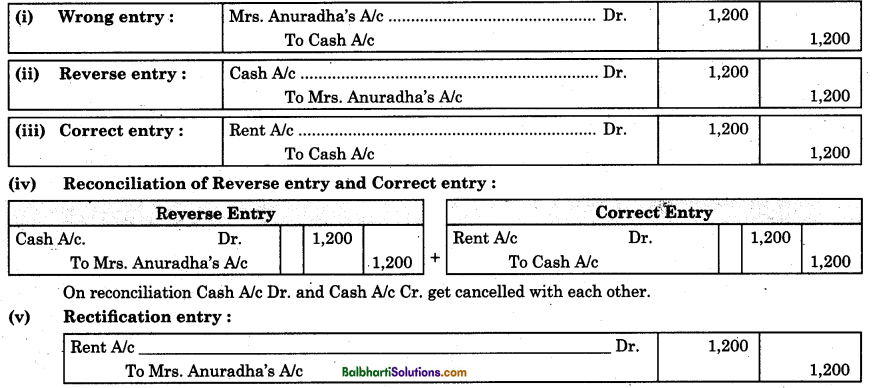
(b) Error of Commission : Procedure of rectification of error of commission is stated as below : Example : Paid general expenses of ₹ 18, were posted in the ledger as ₹ 81.
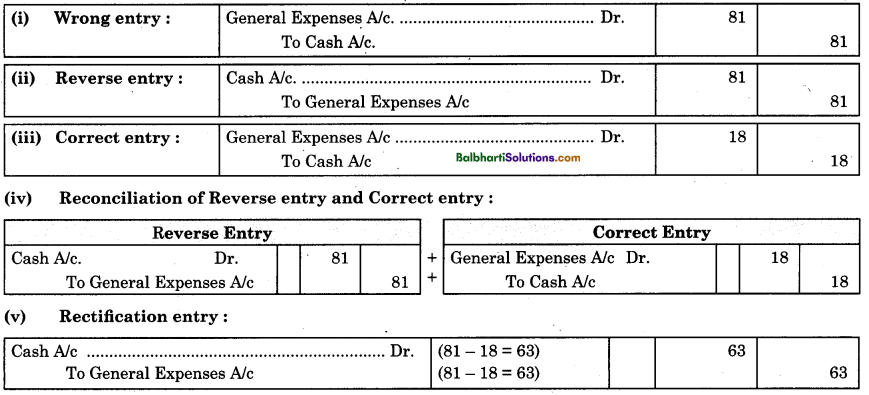
(c) Error of Omission: Procedure of rectification of omission is given be1ov:
Example: Credit purchase of goods worth Z 2,000 from Kishor remained to be recorded in the books of
accounts.
(i) Wrong entry: Not passed
(ii) Reverse entry: NIL
(iii) Correct entry:

Since no wrong entry is passed, correct entry is itself a rectification entry.
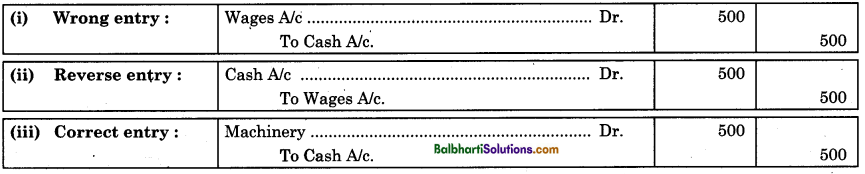
(d) Two-sided Errors: The procedure of rectification of two-sided errors is stated as below:
Examples: Wages ₹ 500 paid for the installation of machinery, debited to wages account.
![]()