By going through these Maharashtra State Board Secretarial Practice 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 1 Secretary students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Secretarial Practice Notes Chapter 1 Secretary
Origin of Secretary

![]()
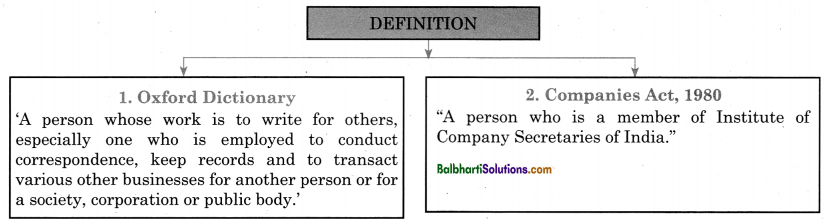
Meaning and Definition
1. Oxford Dictionary:
‘A person whose work is to write for others, especially one who is employed to conduct correspondence, keep records and to transact various other businesses for another person or for a society, corporation or public body.’
2. Companies Act, 1980: “A person who is a member of Institute of Company Secretaries of India.”
Features of Secretary:
- Individual – Only an individual can be as a Secretary
- Duties – Perform routine and administrative duties O Day to day duties
Ensure legal compliances - Qualification – Prescribed qualification according to Companies Act, 2013
- Appointment – Can be appointed by individuals, professionals, society corporation, etc.
- Paid Employee – Paid either by salary or paid an honorarium.
- Confidential Officer – Acts as a custodian of secret and confidential information of the organization.
- Representative – Personal secretaries – represent their employers.
Institutional secretaries who is appointed by societies, companies, government departments – represent their organizations. - Qualities – o Concentration, intelligence, tact, loyalty, co-operation, courtesy, etc.
![]()
Importance of a Secretary:
1. Expert advice and guidance –
- opinion of secretary valuable.
- advices the superiors in the matter of policy decisions.
- guides to the management for business growth.
2. Administrator-
- routine office administration
- office management, documentation of important issues
- executive duties : like assisting policy formulation, preparation of plans, supervision on execution of plans
3. Custodian of secret information-
- access to confidential and crucial information related to the organization.
- making and executing important decisions
- guards the secrets of the organization as ‘confidential officer’.
4. Correspondent –
- responsible for inward and outward correspondence.
- correspondence with members, directors, banks, insurance companies, etc.
5. Legal compliance officer –
- ensure proper and timely legal compliances.
- perform various statutory duties.
- file returns, documents with proper authorities within the stipulated time.
6. Conducting meetings-
- formalities required to be undertaken before, during and after the meeting.
- includes preparation of agenda. sending notices, preparing minutes etc.
7. Link between management and staff –
link between management and staff. helping in effective communication.
8. Fulfillment of Secretarial Standards and Secretarial Audit-
to check whether the company is adhering to legal and procedural requirements.
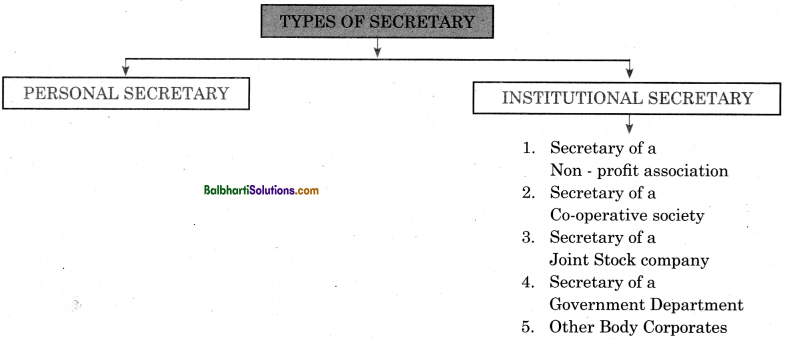
Types of Secretary:
- Personal Secretary
- Institutional Secretary
Institutional Secretary-
- Secretary of a Non – profit association
- Secretary of a Co-operative
- Secretary of a Joint Stock company
- Secretary of a Government Department
- Other Body Corporates
![]()
Personal Secretary-
- Appointment
- Qualifications
1. Appointment –
Individuals appoint personal
secretary to look after other or daily routine work.
E.g. → (1) Doctors (2) Lawyers (3) Engineers (4) CA (5) Actors (6) Politicians, etc.
Qualifications-
- No specific qualifications
- Depends on the requirement of employer’s profession

Institutional Secretary-
1. Secretary of a Non – Profit Association
Example: Secretary — Rotary club — Lions club. etc.
Appointment:
may be a full time or part time person working on salary basis or on honorarium basis.
Qualification:
- no prescribed qualification
- should be acquainted with the objects and basic functioning of the organization.
2. Secretary of a Co operative Society
Example:
3ecretary – Co-op. Bank – Co-op. Housing ociety. etc.
Appointment:
- one member of managing committee is appointed as a Secretary.
- works on honorary basis.
- for large scale co-operative organisation; he/she may be appointed as a
full time employee on salary basis.
Qualification:
- no specific qualification.
- good knowledge of the Co-operative Societies Act with at least
graduate qualification.
3. Secretary of a Joint
Stock Company
Example:
Reliance Industries Ltd, Tata Motors Ltd, etc.
Appointment:
Company Secretary is appointed and works under the control of Board of Directors.
Qualification: As per Section 2O3 of Companies Act 2013, Company Secretary must be a member of the Institute of Company Secretaries of India (ICSI).
![]()
4. Secretary of Government Department
Example:
Finance Secretary, Defence Secretary, etc.
Appointment:
Acts as an administrative head of a Ministry or Department for Government of India or State government.
Qualification:
- requires graduation degree.
- should have passed the Civil Services Examination and should be an TAS.
Functions of a Secretary-
1. Correspondence
- to look after inward and outward mail.
- to reply to inquiries from outsiders, government department.
- to look after the various records of the organization.
2. Office management
- to supervise and control the staff.
- to look after smooth functioning of the company.
- to look after training, promotion and transfer of the office staff.
3. Reception function
- to attend to telephone calls and visitors.
- to attend to inquiries, fixing appointments, etc.
4. Financial functions
- to handle banking transactions and maintain books of accounts.
- to keep watch on receipts and payments.
- to provide information to employer, management, banks and Govt.
5. Arrange meetings
- between employer and other parties.
- to arrange general meetings and board meetings as per Act.
- to draft notices, agenda and minutes of the meeting.
6. Statutory functions
to comply the provisions of the Companies Act, Income Tax Act, Stamp Act, etc.
7. Assistance in formulating policies
- to collect statistical data and information.
- to assist the management in formulating policies
8. Providing information
to provide Information related to various departments to management, banks, government departments, shareholders and employees.
9. Administrative functions
- to assist in appointing employees,
- to distribute office work, to supervise, to train and to promote.
- to maintain all statutory books and keep under proper custody.
![]()
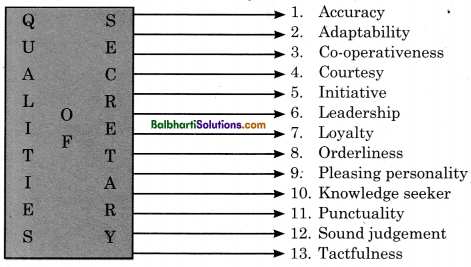
Qualities of a Secretary-
- Accuracy
- Adaptability
- Co-operativeness
- Courtesy
- Initiative
- Leadership
- Loyalty
- Orderliness
- Pleasing personality
- Knowledge seeker
- Punctuality
- Sound judgement
- Tactfulness
Word Meaning:
emerged – to come out / to rise up; assist – to help someone; employer – one who keep the worker against remuneration (salary, wages); employees- one who works for someone against remuneration (salary or wages) / a person who works for somebody for salary; compliance – to follow rules / to abide; prescribed – to advice / to suggest; honorarium- payment made to professionals for their services; custodian – a person who is officially charged for something; personal- one’s own property / belonging; institutional – large organization; concentration- to focus on some work; courtesy – polite behavior towards other people; orderliness – neat and tidy / proper placement; seeker – needy person; able- guidance – valuable suggestion; executive – person at top level; formulation – creation of a plan or policy; stipulated – fixed / desired time; agenda – points to be discussed in meeting; minutes – written record of points discussed in meeting; co-ordinate – to work together; adhering – to follow; procedural – formal way to do something; acquainted – habitual; vital- important; relevant – important / needed; promotion – to lift up; voluntarily – by one’s own wish; accomplish – to achieve / to get; pleasing – good looking personality; implies – without saying directly; mannerism – behave respectfully, statutory – compulsory; appropriate – proper; effectiveness – productiveness; determined – firmly / fixed; perks – additional benefits.