By going through these Maharashtra State Board Secretarial Practice 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 12 Correspondence with Statutory Authorities students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Secretarial Practice Notes Chapter 12 Correspondence with Statutory Authorities
Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)-
- Powers delegated by Central Government to regulate
- the functioning of the Corporate sector to MCA.
- MCA mainly concerned with
Administration of the following Acts-
- The Companies Act, 2013
- The Partnership Act, 1932
- The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008
- The Competition Act, 2002
- Societies Registration Act, 1860
Supervision of Professional Bodies like-
- Institute of Chartered Accountant of India (ICAI)
- Institute of Company Secretaries of India (ICSI)
- Institute of Cost Accountants of India
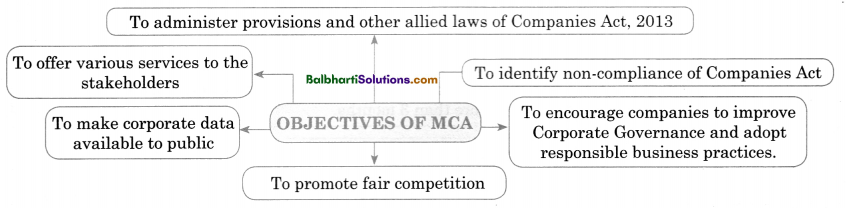
Objectives of MCA
- To administer provisions and other allied laws of Companies Act. 2O13
- To offer various services to the stakeholders
- T0 identify non-compliance of Companies Act
- To make corporate data available to public
- To encourage companies to improve Porate Governance and adopt responsible business practices
- To promote fair competition
![]()
Organizational set up to administer the Companies Act, 2013:
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (Head Quarters in New Delhi)
- 7 Regional Directors (Incharge of 7 regions in India) (Ahmedabad, Chennai, Hyderabad,
- Kolkata, Mumbai, New Delhi, Shillong)
- 22 Registrars of Companies
- 1 Central Registration Center
- 9 ROCs-cum- Official Liquidators
- Official Liquidators (Officers appointed by High Courts to assist in procedure of winding up of companies)

Registrar of Companies (ROC’s)-
- Appointed by Central Government
- To administer the Companies Act in the State under its jurisdiction
- To look after Registration of Companies falling under its jurisdiction
- Acts as full time field officers with wide powers and responsibilities

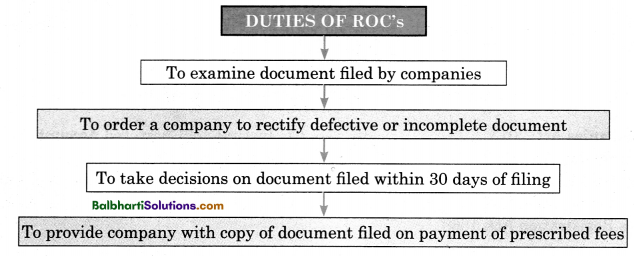
Duties of ROC’s-
- To examine document filed by companies
- To order a company to rectify defective or incomplete document
- To take decisions on document filed within 30 days of filing
- To provide company with copy of document filed on payment of prescribed fees
![]()
Powers of ROC’s-
- To extend the time of holding Annual General Meeting, by a period not more than 3 months.
- To inspect or call for books of accounts, other books and papers.
- To seek in writing an information or explanation relating to furnished.
- To get Special Court permission to is sue an order for seizure of books and papers of a Company, if such records are to be destroyed, altered or falsified.
- To strike off or remove the name of a company from the Register.
National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)-

Power of (NCLT)-
- To hear and give decisions on proceedings related to compromise, arrangement and reconstruction of a company.
- To hear and give decision on winding up petitions.
- To hear and give decisions on petition for extension of time for repayment of deposits.
- To make call for holding AGM or EOGM of a company
- To direct company to not dispose off funds of a company and to freeze the assets of a company used against the interest of the company.
- To hear and give decisions on grievances of rejection in transferring shares and securities
- To hear and give decisions on grievances of rejection in transferring shares and securities.
![]()
National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT)-
- Set by Central Government in June, 2016.
- To hear appeals against the orders of NCLT / National Financing Reporting Agency.
- To hear appeals against the order passed by Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India.
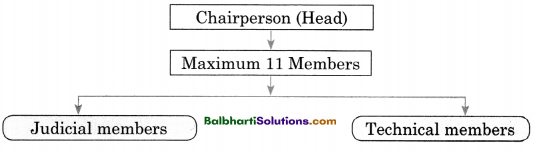
Structure of National Company Law Appellate Tribunal-
Chairperson (Head):
Maximum 11 Members:
- Judicial members
- Technical members
Operation of NCLAT
- Any person aggrieved by an order of the Tribunal, may within 45 days from the date of order may file an appeal to NCLAT.
- NCLAT may confirm, modify or set aside the order.
- An appeal against the NCLAT order may be filed to Supreme Court within 60 days from date of receipt of NCLAT order.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)-
- Statutory body
- Head office – Mumb
- Established in 1992

Objectives of SEBI-
- To regulate the functioning of securities markets and Stock Exchanges in India.
- To protect investors and safeguard their rights.
- To regulate the market intermediaries.
- To develop a code of conduct for fair practices for market intermediaries.
![]()
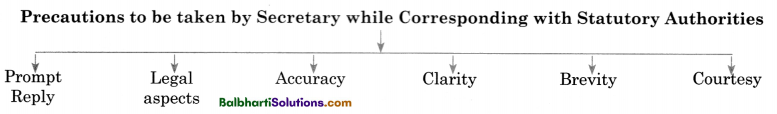
Precautions to be taken by Secretary while Corresponding with Statutory Authorities:
- Prompt Reply
- Legal aspects
- Clarity
- Brevity
- Courtesy
Word Meaning:
allied – joined / connected; fair – honest; stakeholder – a person having an interest in the business; liquidators – a person appoint to wind up the affairs of company; defective – wrong; prescribed -to advise; vested – given; delegated – to give responsibility of certain work; furnish – to provide; alter- to change; falsified – to alter wrong information; quasi – partly; jurisdiction – official power to make legal judgments or decisions; seizure – to take back; empowered – power to do something; oppression – ill treatment; dispose off – give it away; freeze – temporary stopping the rights; grievances – problems; rejection – to not approve; appeal – to request; bankruptcy – failure to run the business; aggrieved – a person who does not accepts the order passed by lower jurisdiction body; safeguard – to protect; code of conduct – set of rules; intermediaries – middle person to do certain work / agent; explicit – to state clearly; calamity – sudden damage; portal – a website; instances – example; challan – form to filled to pay taxes; petition – a formal written request; default – failure to pay; regulator – a person / organization supervise certain activity.