By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 4 Social Institutions students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 4 Social Institutions
→ Social institutions refer to a system of well-defined, stable patterns of behaviour. It depends upon the collective activities of people. Institutions are formed to satisfy the primary needs of individuals.
→ The Functionalist perspective looks at social institutions as playing a number of specific roles in
facilitating human social life.
→ The Marxist or Conflict perspective holds that all individuals are not placed equally in society.
→ The society comprises various social institutions like family, marriage, education, religion, economy, etc.
→ Family is the most important primary unit of human society. A family is a group of people related by blood.
![]()
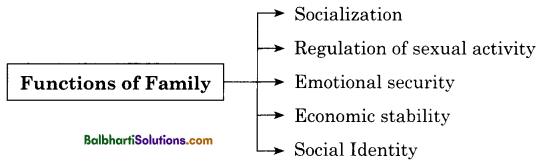
Functions of Family :
- Socialization
- Regulation of sexual activity
- Emotional security
- Economic stability
- Social Identity
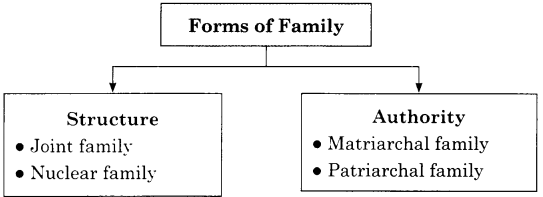
Forms of Family:
Structure
Authority
1. Structure:
- joint family
- Nuclear vamily
2. Authority
- Matriarcha1 family
- Patriarchal family
Twenty first century families:
Family as an institution is significantly changing and many new forms are in the making.
- Single parent fami’y
- Cohabitation
- Step-parenting

Marriage:
- Marriage is a social institution through which family relations are formed. It refers, to a pattern sanctioned by society to enter into sex relations and to procreate.
- Today the concept of marriage is enlarged to include homosexual relations.
- In 1989, Denmark became the first country to formally recognize homosexual marriages.
![]()
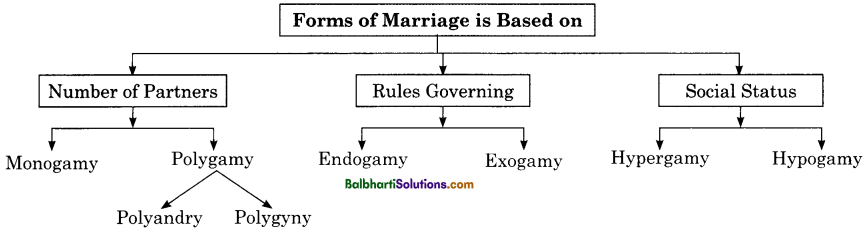
Forms of Marriage –
Forms of Marriage is Bases on:
- Number of Partners
- Rules Governing
- Social Status
1. Number of Partners:
- Monogamy
- polygamy
- polyandry
- Polygyny
2. Rules Governing:
- Endogamy
- Exogamy
3. Social Status
- Hypergamy
- Hypogamy
![]()
Family, Kinship and Marriage:
- A family is a group of persons directly linked by kin relations.
- Kinship ties are connections between individuals, established either through marriage or through the lines of descent that connect blood relatives.
Economy and Work :
- Economy is a basis social institution which organises production distribution and consumption of goods and services.
- Every society has to fulfil material needs in order to maintain itself.
- Human society has evolved through various stages, depending upon the way it evolved mechanisms to adapt to changing material needs.
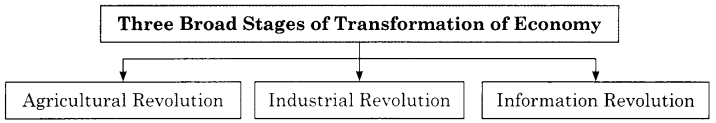
Three Broad Stages of Transformation of Economy:
- Agricultural Revolution
- Industrial Revolution
- Information Revolution
Changing Nature of Work :
- With advanced industrialization, the proportion of population engaged in agriculture is declining.
- There is also an expansion of service sector in India. One of the main features of modern societies is an enormous expansion of economic interdependence.
- Growing competition between firms and countries make it essential to keep production flexible.
Education :
Modern societies have evolved a distinct institution of education to fulfill basic goals like disseminate ideas and knowledge and to develop skills to use existing knowledge for the betterment of society.
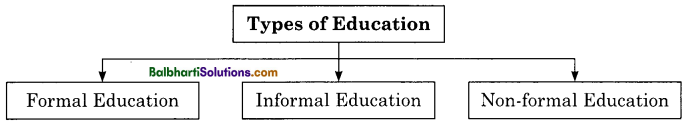
Types of Education:
- Formal Education
- Informal Education
- Non-formal Education
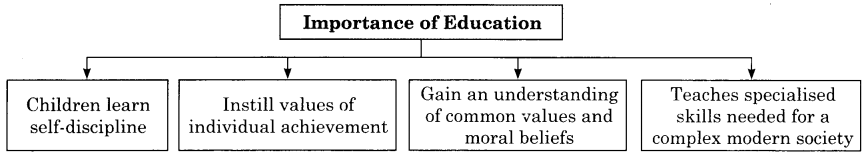
Importance of Education:
- Children learn self-discipline
- Instill values of individual achievement
- Gain an understanding of common values and moral beliefs
- Teaches specialised skills needed for a complex modern society
![]()
Education and Social Division :
Scholars like Bowles and Gintis argue that workplace inequalities are mirrored in the organization of schools and that the education system reproduces these inequalities. Many studies have pointed out that education as a system also perpetrates gender differences.