By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 Biomolecules students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Biomolecules: Biomolecules are lifeless molecules that combine in a specific manner to produce life or control biological reactions. Examples: They are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. They play
an important role in the functions of organisms.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds that can be hydrolyzed to polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones.
![]()
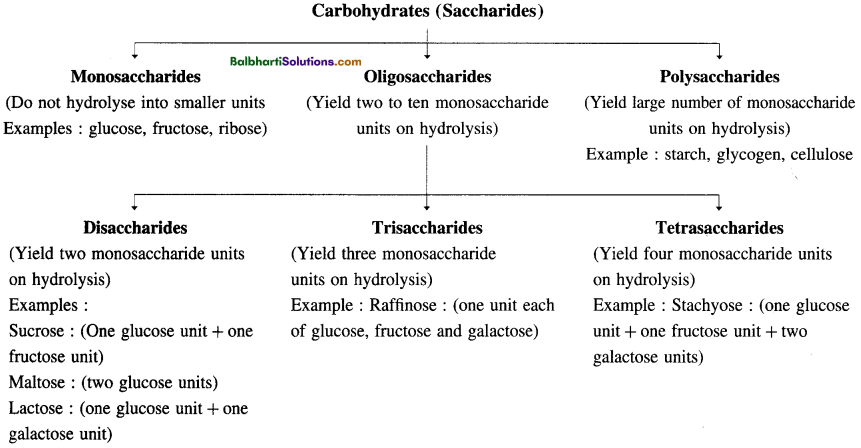
Classification of Carbohydrates:
Preparation of glucose: Glucose is prepared either from cane sugar or from starch.
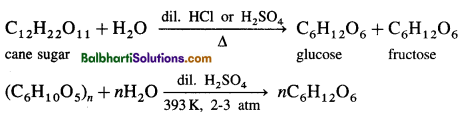
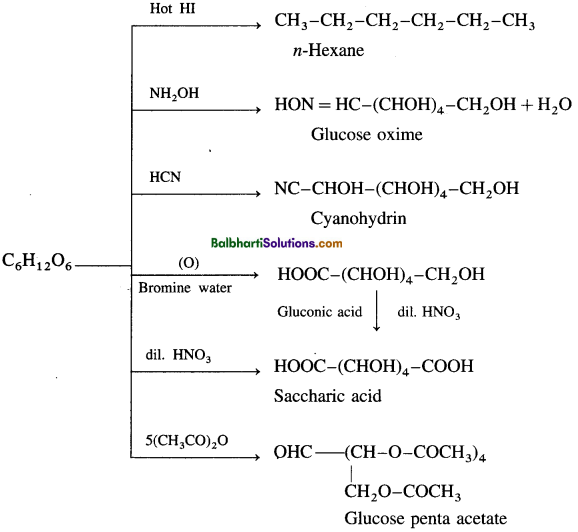
Reactions:
Glucose can be represented by Fischer projection formulae and cyclic structure by Haworth projection formulae. Fructose is ketohexose and is made by the isomerization of glucose. It is laevorotatory and belongs to the D series. Fructose can be represented by Fischer projection formulae and cyclic structure by Haworth projection formulae. Disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, cellobiose, lactose, etc. Polysaccharides are starch, cellulose, glycogen, etc.
![]()
Proteins: Proteins are naturally occurring polymeric nitrogenous organic compounds containing 16% nitrogen and peptide linkages. Proteins are classified into fibrous proteins (keratin, hair, skin, nails) and globular proteins (hemoglobin, thyroglobulin). The structure of a protein can be studied at different levels called primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Proteins on hydrolysis give a mixture of α-amino acids 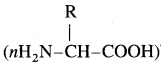 .
.
Amino acids are classified into three types-basic, acidic, and neutral amino acids.
Peptide linkage (-CONH) in an amide formed between -COOH and -NH2 group by elimination of water molecule.
Enzymes: Enzymes are biological catalysts for various chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes are required in small quantities. They act as catalysts and reduce the activation energy for a particular reaction. In many industrial processes, specific reactions are carried with the use of enzymes extracted from organisms.
Nucleic acids: Nucleic acids are esters of phosphoric acid with sugar. They control the synthesis of proteins and are also responsible for storing the genetic information of living organisms and passing the information from one generation to another.
Chromosomes contain two types of nucleic acids: Ribonucleic acid RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Nucleoside: A base-sugar unit
Nucleotide: A base-sugar-phosphoric acid unit. Nucleotides are monophosphates of nucleosides.