By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
Coordination compound : It consists of a central metal atom or ion surrounded by atoms, molecules or anions called ligands bonded by coordinate bonds, e.g. cisplatin, Pt(NH3)2Cl2, [Cu(NH3)4]S04.
According to Werner’s theory, metal atom or ion in the complex has primary valence (outer sphere) and secondary valence (inner sphere).
Coordination number (C.N.) : The number of ligand donor atoms directly bonded to the central metal atom or ion by coordination bonds or number of electron pairs involved in the coordinate bonds is coordination number (C.N.).
![]()
Ligands:
- Monodentate ligands (Cl–, OH–, NH3, H2O, etc.)
- Bidentate (en, C2O42- etc.)
- Tridentate (dien)
- Tetiadentate (trien)
- Hexadentate (EDTA)
Classification of complexes on the basis of types of ligands :
- Homoleptic complexes Ni(CO)4, [CO(NH3)6]Cl3
- Heterleptic complexes [CO(NH3)4Cl2H2O]Cl
Classification of complexes on the basis of charge :
- Cationic sphere complexes, [Zn(NH3)4]2+ , [CO(NH3)5Cl]2+
- Anionic sphere complexes, [Ni(CN)4]2-, [Fe(CN)6]3-
- Neutral sphere complexes, [Pt(NH3)2Cl2], [Ni(C0)4]
Effective atomic number : EAN = Z – X + Y
Isomerism in complexes :
(1) Stereoisomerism :
- Geometrical isomerism
- Optical isomerism
(2) Structural isomerism :
- Ionisation isomerism
- Linkage isomerism
- Coordination isomerism
- Solvate isomerism
![]()
Bonding in complexes:
- Valence bond theory (VBT)
- Crystal field theory (CFT)
- Ligand field theory (LFT)
- Molecular orbital theory (MOT)
Valence bond theory (VBT) : A central.metal atom or ion undergoes hybridisation like sp3, dsp2, d2sp3, etc. forming hybridised orbitals to accommodate the lone pairs of electrons from the ligands.
Inner complex : (n — 1)d orbitals of metal are used.
Outer complex: nd orbitals of metal are used.
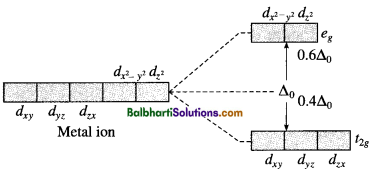
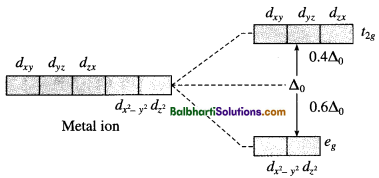
Crystal field theory (CFT) :
Degenerate d-orbitals: dxy, dyz, dzx, d(x2 – y2) and dz2
Crystal field splitting:
(1) For octahedral complex:
(2) For tetrahedral complex :
Factors affecting the stability of the complex :
- Charge to size ratio of the metal ion
- Nature of ligands
![]()
Applications of the coordination compounds:
- In biology
- In medicines
- To estimate the hardness of water
- In electroplating