By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 2 Utility Analysis students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 2 Utility Analysis
Meaning of Utility:
Utility means want satisfying power of a commodity. It is a capacity of a good to satisfy human want.
Features of Utility:
- Utility is a subjective concept.
- Utility is a relative concept.
- Utility differs from usefulness.
- Utility differs from pleasure.
- Utility and Satisfaction are interrelated but they are not same.
- Utility depends upon intensity (urgency) of want.
- Utility is the basis of Demand.
- Utility is morally colourless.
- Utility is multi-purpose.
- Utility is not cardinally measurable.
Types of Utility:
| Types of Utility | Example |
| (1) Form Utility | Furniture made of wood, toys from clay |
| (2) Place Utility | Woollen clothes in cold regions |
| (3) Service Utility | Teacher teaches to student, lawyer’s advice to client |
| (4) Knowledge Utility | Getting or acquiring knowledge about functions |
| (5) Possession Utility | Transfer of goods from sellers, to buyers. |
| (6) Time Utility | Books during examination |
![]()
Concepts of Utility:
→ Marginal Utility (M.U.): It refers to an additional utility derived by a consumer from each unit of commodity consumed. It is the addition made by last unit.
→ Total Utility (T.U.): It refers to sum of utilities derived by a consumer from all units of commodity consumed. It is an aggregate of marginal utilities.
Relationship between M.U. & T.U.:
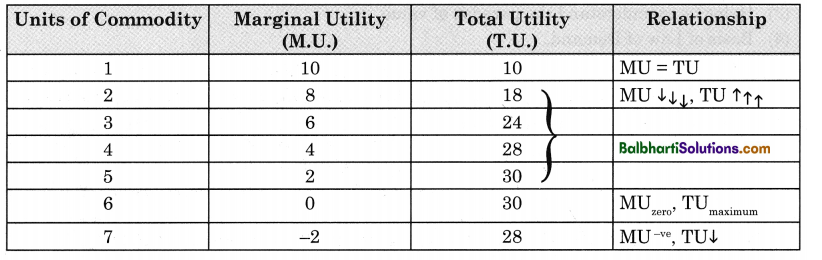
Law of Diminishing M.U:
It explains economic behaviour of a rational consumer. It was first proposed by Prof. Gossen, but later, it was explained in detail by Prof. Alfred Marshall in his book “Principles of economics” in 1890.
Statement of the Law of DMU:
“Other things remaining constant, the additional benefit, which a person derives from a given increase in his stock of a thing, diminishes with every increase in the stock that he already has.” In simple words, MU goes on diminishing with every successive unit of commodity consumed.
![]()
Assumptions of the Law:
- Cardinal measurement
- Homogeneity
- Rationality
- Continuity
- Reasonability
- Divisibility
- Constancy
- A single want
Tabular Presentation Schedule:
| Units of Commodity | Marginal Utility (M.U.) |
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 |
| 6 | 0 |
| 7 | -2 |
![]()
Graphical Presentation Diagram:
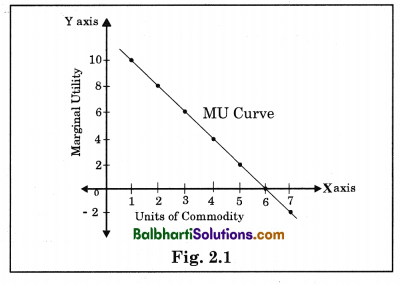
Exceptions to the Law of DMU :
- Hobbies
- Miser
- Money
- power
- money
- Reading
- music
![]()
Criticisms of the Law of DMU:
- Unrealistic assumptions
- Cardinal measurement – not possible
- Not applicable to indivisible goods
- Constant MU of money
- Restricted to a single want
Significance of the Law of DMU:
- Useful to consumers to maximise satisfaction.
- Useful to Government in framing various policies.
- Helps us to understand the paradox of value.
- Basis of Law of Demand.
Relationship between MU & Price:
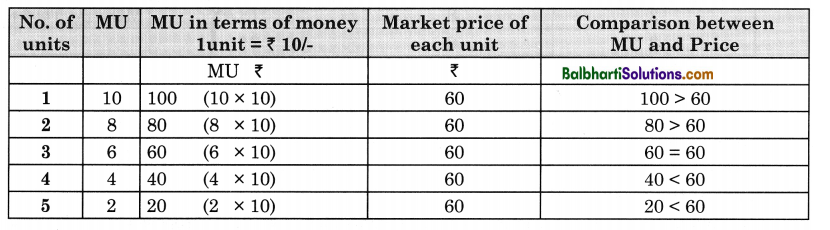
A rational consumer attains equilibrium where MUx = Px. So, a consumer will buy 3 units.
Two English Economists:
J. R . Hicks & R. G. D. Allen were the two main exponents of In difference Method. It adopts the concept of ordinal utility.