By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 3 Human Settlements and Land Use students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 3 Human Settlements and Land Use
→ Man being a social animal, likes living in groups.
→ Due to social bonding and social needs many people come together and construct houses, which is known as settlement.
→ Development of settlement have co-relation between man and environment.
→ Type and spacing of settlements depend upon many physical factors like relief, soil, climate, drainage, groundwater level etc.
→ Social factors, sometimes are responsible for fragmentation of settlements.
![]()
Types of Settlement:
→ Settlements vary in their size and types ranging from hamlets to metropolitan city.
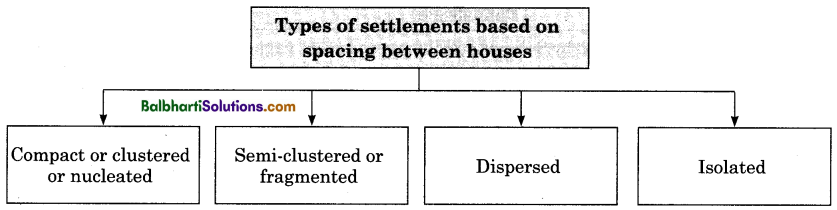
→ Type of settlement refers to some common features of the settlement.
→ Pattern of settlements refers to regular form in which series of things occur.
→ The term settlement pattern is strictly applied to the spatial arrangement or distribution of settlement within the given area.
→ On the basis of functions, there are two types of settlement – rural and urban.
→ Cities can be divided on the basis of their function.
→ Some cities specialise in certain functions, activities, products or services.
→ On the basis of specialisation of some important functions, Indian cities can be classified as follows:
Pimpri – Chinchwad as industrial town, Khadki as cantonment town, Pune as educational centre and Kolhapur, Pandharpur as religious town etc.
→ As town becomes city and city becomes metro cities, lots of changes can be seen in them in their form, land uses and structure.
→ As cities grow in their size, there is change in their skyline.
![]()
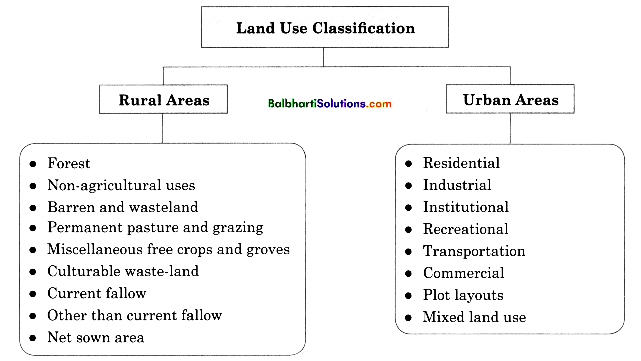
Land Use Classification:
→ Land use in rural areas is different from urban areas.
Land use and Landcover:
→ Land cover describes the physical surface covering the land like forest, water, sand, ice, rocks, etc.
→ Land use describes the use of the land; use might be recreational, but land cover might be forest or vegetation.
→ Land cover can be determined by analysis of satellite imagery, but the land use cannot be determined from the satellite imagery.
Urban-Rural Fringe:
→ The area between urban and rural area is called urban-rural fringe. It has both the urban and rural characteristics.
→ It is a transition zone between urban and rural area.
→ People from this area daily travel to central area for their work.
→ Here, we have a mixture of rural and urban land use.
→ The city and the surrounding areas consist of two administrative areas – Municipal Councils and Gram Panchayats.
→ Smaller municipal towns lose their identity, though they are geographical part of the city.
→ Town far from the main city maintain its distinct identity and have problems relating to the urban amenities and transportation.
→ The quality of available services is generally inferior.
→ Agricultural land may have been converted to residential or industrial areas or entire area may be rural.
→ Beyond urban fringe, there is a rural fringe. Rural fringe consists of only villages partly affected by the urbanisation.
![]()
Suburbs:
→ Outside metropolitan cities, there might be small towns or number of well-developed cities or towns. Such cities or towns are suburbs of Mumbai.
→ Andheri, Goregaon, Bhandup, Mulund, Thane, Kalyan etc., are suburbs of Mumbai.
→ All these suburbs developed as a result of the growth and development of Mumbai.