Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 8 Introduction to Economics Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 8 Introduction to Economics
Class 9 Geography Chapter 8 Introduction to Economics Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Explain the types of economies by filling correct information in the place of questions in the circle.
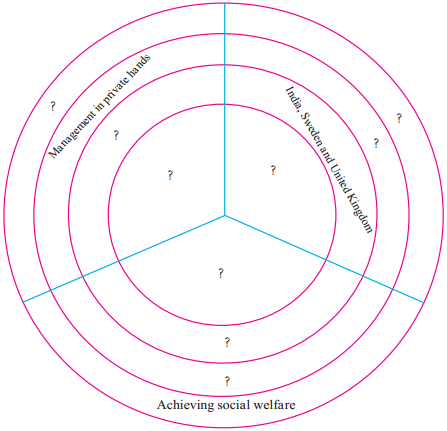
Answer:
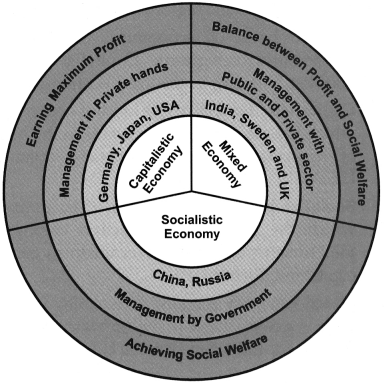
![]()
2. Give an explanation:
Question 1.
The economy begins at home.
Answer:
- Household finance is related to income and expenditure.
- Every household has unlimited expenditure and the income earned is limited.
- The household has to make a choice regarding how it has to spend its limited resources.
- Management of this limited income to meet the unlimited expenses is Economics.
- As we manage the finance of our family, similarly the villages/cities, states, countries and the whole world needs to have economic management. So we say Economy begins at home.
Question 2.
India’s economy is of mixed type.
Answer:
- Mixed economy is a combination of Capitalism and Socialism.
- India is said to be a Mixed economy because there is a co-existence of both public and the private sectors.
- The private sector undertakes production for the profit motive, whereas the state tries to achieve social welfare.
- India, therefore, tries to achieve a balance between maximum social welfare for its citizens on one hand and profit on the other. Therefore, India’s economy is of Mixed type.
Question 3.
On the basis of economies, we can divide countries into three groups.
Answer:
The activities related to the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services in a specific region is called economy. On the basis of economies, countries are divided into three groups. Capitalist Economy, Socialist Economy and Mixed Economy.
- Capitalistic Economy is a kind of economy in which the means of production is in the hands of the private sector, e.g. Germany, Japan, the U.S.A.

- Socialist Economy is a kind of economy in which the means of production belongs to the society i.e. the government’s control, e.g. China, Russia.
- Mixed Economy is a kind of economy in which there is a co-existence of both private and public sectors, e.g. India, Sweden, the U.K.
3. Write the following questions in one line:
Question 1.
To which economic factor is the management of individual or family finances related?
Answer:
Management of individual or family finances is related to the economic factor of ‘income and expenditure.
Question 2.
From which Greek word is the term ‘Economics’ derived?
Answer:
The word ‘Economics’ is derived from the Greek word ‘Oikonomia’ which means family management.
Question 3.
In a capitalistic economy, to whom does the ownership and management of means of production belong?
Answer:
In a Capitalistic Economy, the ownership and management of means of production belong to the private sector.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you mean by globalisation?
Answer:
Globalisation means aligning the country’s economy with the world economy.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 8 Introduction to Economics Intext Questions and Answers
Can you tell?
Suppose this is your expenditure this month and your monthly income is? 20,000. To strike a balance between your income and your expenditure, decide that will be your preferences for expenditure.
Rewrite the table according to your preferences and discuss in class.
| Sr.No. | — | Estimated Expenditure (₹) |
| 1. | Daily food | 6,000 |
| 2. | Buying two sets of Uniform | 2,000 |
| 3. | School Stationery | 500 |
| 4. | Medical expenditure | 450 |
| 5. | Recreation | 500 |
| 6. | Mobile Bill | 1,000 |
| 7. | Vegetables, Fruits, etc. | 1,000 |
| 8. | Public transport (bus, railway, rick-shaw, etc.) | 2,600 |
| 9. | Electricity Bill | 1,500 |
| 10. | Tourism | 4,000 |
| 11. | Bank Installment | 3,000 |
| Total Expenditure | 22,550 |
Answer:
Income And Expenditure Statement
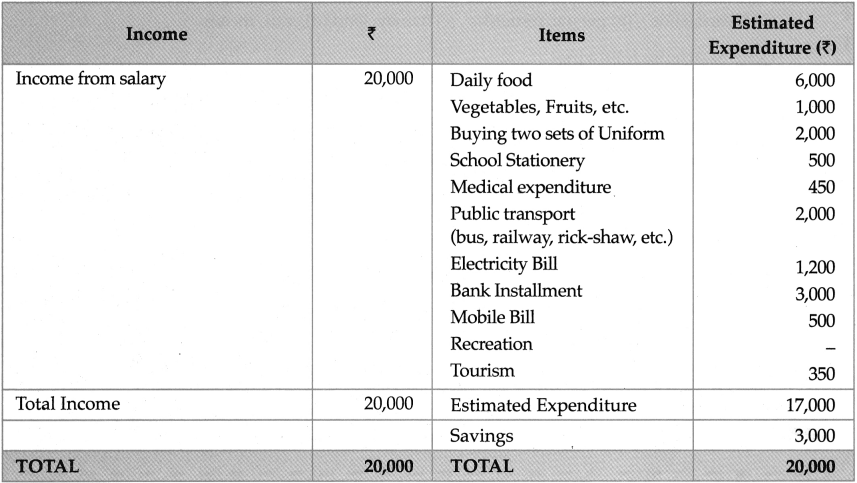
- Preferences have been rearranged to their urgency.
- Most urgent wants are placed on the top. Least urgent wants are placed at the bottom.
- Expenses have been cut down wherever possible.
- Money spent on tourism is nil.
- Mobile bill has been reduced to? 500 from? 1000.
- And Savings equals? 3000.
![]()
Can you do it?
Question 1.
Suppose you are the finance minister of an agrarian country. Giving priority to the overall development of the country, make a five-point program.
Answer:
As a Finance Minister of an Agrarian country like India, I would focus on transforming India in five areas:
- Modernization of agriculture, encouragement to export-oriented agro-processing industries.
- Education, skill-building, and healthcare.
- Information and communication technology.
- Infrastructure development for rural industrialization.
- Spirit of Entrepreneurship.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 8 Introduction to Economics Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the statements choosing the correct option:
Question 1.
The term economics’ is derived from Greek word
(a) oikomonia
(b) oikonomica
(c) oikonomia
(d) oikonomics
Answer:
(c) oikonomia
Question 2.
China and Russia have adopted type of economy.
(a) Socialistic
(b) Capitalistic
(c) Mixed
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Socialistic
![]()
Question 3.
The main motive of a economy is to earn profit.
(a) Mixed
(b) Capitalistic
(c) Simple
(d) Socialistic
Answer:
(b) Capitalistic
Question 4.
The main aim of Socialistic economy is to achieve
(a) social welfare
(b) profit
(c) injustice
(d) tolerance
Answer:
(a) social welfare
Question 5.
Germany is an example of a country which has adopted economy.
(a) Simple
(b) Socialistic
(c) Mixed
(d) Capitalistic
Answer:
(d) Capitalistic
Question 6.
Adam Smith has defined economics as the
(a) science of knowledge
(b) science of wealth
(c) science of peace
(d) science of needs
Answer:
(b) science of wealth
Question 7.
means making the country’s economy aligned with world economy.
(a) Liberalisation
(b) Privatisation
(c) Globalisation
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Globalisation
![]()
Question 8.
Economics is an important science.
(a) social
(b) political
(c) physical
(d) alternative
Answer:
(a) social
Question 9.
One of the main functions of the economy is to the production cost
(a) maximize
(b) inflate
(c) increase
(d) minimize
Answer:
(d) minimize
Question 10.
An economy strives to create a balance between resources and needs.
(a) unlimited, limited
(b) limited, unlimited
(c) plentiful, limited
(d) limited, scarce
Answer:
(b) limited, unlimited
Question 11.
is known as the Father of Economics.
(a) Lionel Robbins
(b) Prof. Samuelson
(c) Amartya Sen
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(d) Adam Smith
Question 12.
Economics is a science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between and scarce which have alternative uses.
(a) means, ends
(b) people, resources
(c) money, land
(d) ends, means
Answer:
(d) ends, means
![]()
Question 13.
We understand from economics, how to use, money, land and effectively.
(a) minerals, factory
(b) time, labour
(c) food grains, machines
(d) people, power
Answer:
(b) time, labour
Question 14.
On a global level, there are types of economies.
(a) four
(b) two
(c) three
(d) five
Answer:
(c) three
Question 15.
economy is a borderless economy.
(a) State
(b) Town
(c) Village
(d) World
Answer:
(d) World
Question 16.
In Globalisation, there is trade and all restrictions on are set aside.
(a) restricted, economy
(b) free, investments
(c) no, activity
(d) zero, labour
Answer:
(b) free, investments
Match the column
| Group A | Group B | |
| (1) Capitalist economy | (a) India | |
| (2) Socialist economy | (b) USA | |
| (3) Mixed economy | (c) Russia | |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – a)
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
Define Economics.
Answer:
According to Lionel Robbins, “Economics is a science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”.
![]()
Question 2.
What is an Economy?
Answer:
The activities related to the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services in a specific region is called an economy.
Question 3.
What is a Capitalistic Economy?
Answer:
The economy in which the ownership and management of the means of production is in the hands of private individuals is called as a Capitalistic Economy.
Question 4.
What is the main aim of a Capitalistic Economy?
Answer:
The main aim of a Capitalistic Economy is to earn maximum profit.
Question 5.
Which countries have adopted Capitalistic Economy?
Answer:
Germany, Japan and USA are the examples of countries which have adopted Capitalistic economy.
Question 6.
What do you mean by Socialistic economy?
Answer:
The economy in which the means of production belong to the society as a whole i.e. the government’s control is known as a Socialistic economy.
Question 7.
What is the main aim of a Socialistic economy?
Answer:
The main aim of a Socialistic economy is to achieve social welfare.
![]()
Question 8.
Name Adam Smith’s book and year of publication.
Answer:
Adam Smith’s book is titled ‘Wealth of Nations/ and was published in 1776.
Question 9.
What are the types of economy at the global level?
Answer:
Capitalist, Socialist and Mixed Economy are the types of economy at the global level
Question 10.
Which economist is known as Father of Economics?
Answer:
Adam Smith is known as Father of Economics.
Question 11.
How does Adam Smith describe Economics in his ‘Wealth of Nations’?
Answer:
In the book ‘Wealth of Nations’ Adam Smith describes Economics as ‘the science of wealth’.
Question 12.
What is the World Economy?
Answer:
World Economy is a borderless economy in which natural resources, profit, services, capital, labour and technology flow freely across the countries.
Distinguish between Capitalist Economy and Socialist Economy.
Answer:
| Capitalist Economy | Socialist Economy |
| (i) Ownership and management of means of production is in the hands of the private individuals. (ii) To earn maximum profit is the main aim of the Capitalist Economy. (iii) The USA, Germany and Japan have Capitalist Economy. | The means of production belong to the society as a whole and are under the control of the government. To achieve social welfare is the main aim of the Socialist Economy. Russia and China have Socialist Economy. |
Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the functions of an economy.
Answer:
Every country has a different economy. But the main functions of an economy are similar. Some of the main functions of an economy are:
- Deciding the product and quantity of its production.
- Deciding for whom will the goods be produced.
- Minimising the production costs as much as possible.
- Distributing national income1 according to social and economic justice2.
- Making appropriate provisions3 for the economic needs of the future.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the importance of Economics.
Answer:
Economics is an important Social Science Subject.
- We use Economics on a large scale in agriculture, trade, finance, administration, law and in our daily life.
- Economics holds a paramount4 importance in the overall social development of humans.
Question 3.
Name the factors affecting an economy.
Answer:
The factors affecting an economy are:
- Geographical area and natural resources.
- Population
- Occupations
- Political Sovereignty
Question 4.
Write a description of Economics given by Lionel Robbins.
Answer:
- According to Lionel Robbins, “Economics is a science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”.
- Since human wants are unlimited their priority is determined.
- The satisfaction of the basic needs are given priority.
- A scarce resource like land can be used either for agriculture or industries or development of infrastructure.
- In this way, Economics studies human behaviour related to unlimited wants with limited resources that have alternative uses.
Question 5.
Explain the nature of the Capitalist Economy.
Answer:
- The ownership and control of means of production is in the hands of the private individuals in the Capitalist Economy.
- There is no control of the government over economic activities in their ‘Free Market Economy’.
- The objective of economic activities is to earn maximum profit.
- The capitalist economy exists in Germany, Japan and the USA.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the nature of the Socialist Economy.
Answer:
- There is no private ownership of the means of production as these belong to the society as a whole.
- There is total control of the State over the economy.
- The objective of the economic activities is the fulfilment of social needs (social welfare).
- Socialist economy exists in Russia and China.
Question 7.
What are the main features (components) of the economy?
Answer:
- The economy is a system related to the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services in a specific region.
- The main features of an economy are :
- Well defined geographical area.
- Population, i.e. the people living within that geographical area and undertaking various economic activities.
- Natural resources to undertake economic activities.
- Political sovereignty that exercises control over the economy.
Question 8.
Explain the nature of globalisation.
Answer:
- Globalisation means aligning the economy of the country with the world economy.
- There is free trade and all restrictions on (foreign) investments are set aside.
- There is free flow of natural resources, profit, services, capital, labour and technology across the world.
- The aim is to establish a borderless economy.

- The recent economic policies of the government are leading the economy towards globalisation.