By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 8 Introduction to Management students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 8 Introduction to Management
Management-
Managerial → Derived from Italian words
- Manus – hand
- agere – to act
Meaning and Definition:
- Mary Parker Follet: “ Management is an art of getting things done through others”.
- Henry Fayol : “ To manage is to forecast and plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control”.
- Fedrick Winslow Taylor : “ Management is knowing exactly what is to be done and seeing that it is done in the best possible manner*’.
- George Terry : “Management is the process consisting of planning, organizing, actuating and controlling, performed to determine and accomplish the objectives by the use of people and resources. ”
![]()
Characteristics of Management-
- Management is Dynamic
- Management is Inborn Quality
- Management is a Social Process
- Management is a Continuous Process
- Management is Different from Ownership
- Management is Intangible
- Management is Situational
- Management is Goal Oriented
- Management is Universal
- Management is a Group Activity
Level of Management-
- Top – Board of Directors, President, Chief Executive Officer, Managing Directors, etc.
- Middle – Functional Managers i.e. Finance Manage, Production Manager, Sales Manager, etc.
- Lower – Superintendents, Supervisors, Foremen, etc

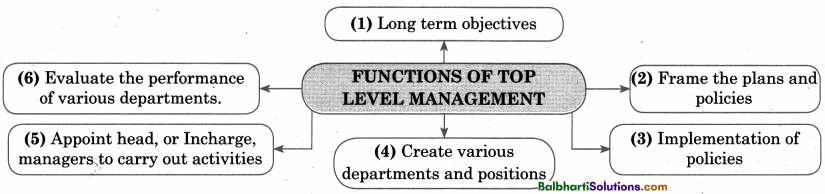
Functions of Top Level Management-
- Long term objectives
- Frame the plans and policies
- Implementation of policies
- Create various epartments and positions
- Appoint head, or Incharge, managers to carry out activities
- Evaluate the performance of various departments.
- Implementation of policies Functions of Middle Level Management
![]()
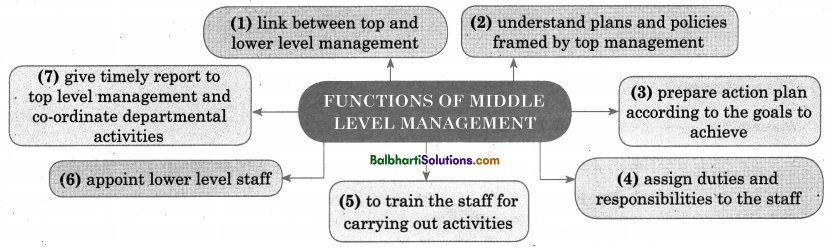
Functions of Middle Level Management-
- link between top and lower level management
- understand plans and policies framed by top management
- prepare action plan according to the goals to achieve
- assign duties and responsibilities to the staff
- to train the staff for carrying out activities
- appoint lower level staff
- give timely report to top level management and co-ordinate departmental activities
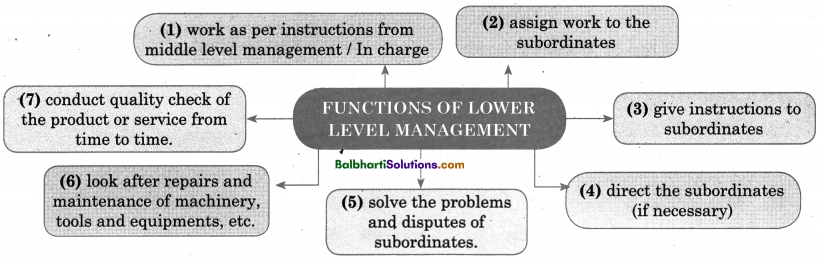
Functions of Lower Level Management-
- work as per instructions from middle level management /In charge
- assign work to the subordinates
- give instructions to subordinates
- direct the subordinate (if necessary)
- solve the Problems and disputes of subordinates.
- look after repairs and maintenance of machinery, tools and equipments, etc.
- conduct quality check of the product or service from time to time.
Management as an Art
- “Art is the bringing about a desired result through the application of skills”
Relation Between Art And Management
- Personal Skills: Solve the resource problems by individual way
- Creativity: Ability to find new ideas, according to changes in business situation.
- Regular Practice: Use of different techniques and skills to deal with different people, different situations, different organizations.
- Personal Abilities: Ability to co-ordinates the activities and guide people.
Management as a Science-
- Science refers to a systematically organized body of knowledge based on proper findings and
exact principles and is capable of verification.
Relation Between Science And Management
- Systematic body of Knowledge: Management Principles are based on experiments conducted through management theories and approaches
- Use of Scientific Method of Observation: Management uses systematic methods of data collections, verification, analysis, interpretation and on this basis taking decisions.
- Cause and Effect relationship: Management theories are also based on Cause and Effect relationship
- Universal Applicability of Principles: Principles of Management are universal applied in any condition and situation
Management as a Profession-
A profession may be defined as an occupation backed by specialised knowledge and training and to which entry is regulated by a representative body and duly recognized by the society.
![]()
Relation between profession and Management
- Formal Education: Formal management diploma or degree with training from management from school to work professionally
- Code of Conduct: Managers have to follow code of conduct based on customs and traditions
- Expertise: Manager is an expert in practicing his or her knowledge and skill
- Registration: Managers can take the membership of Chambers of Commerce
- Restricted Entry: No such compulsion for a manager
Word Meaning:
ancient – in early time; essential – necessary; indispensable – necessary; never ending – endless; creative
– having good imagination; optimum – maximise; techniques – method; exhaustive – complete; character – nature / personality; universal – in general; adaptation – accept tq change; procurement – to obtain; dynamic
– constant change; evaluation – to assess / to judge; static – fixed; forecast – to predict; systematic – in order / well arranged; vision – planning about future goals; utilization – effective use of something; mission – assignment; synchronization – activity of two or more things at same time; evaluate – to assess; purposeful – determined; implementation – to execute; guidance – to instruct / to direct; supervisory – to direct someone; intangible – not physically seen or touched; inherent – built in; continuity – in progression / without a break; context – with reference to topic; innovativeness – new ideas; qualitative – relating with quality; inborn – from birth; backed by – supported; skill – capability; regulated – to control; consistent – stable; practice – to use; organized – arranged in proper way; irrespective – no matter what; findings – to discover; formal education – process of education completed in school and colleges; verification – to find validity of something; stimulate – to encourage; principles – essential; functions – results; theories – judgement / beliefs; approaches – method; conclusions – opinion / judgement; analysis – to investigate / to inspect; interpretation – to review; motivate – to inspire; quantitative – related with numbers.