Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 8 Company Accounts – Issue of Shares Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 8 Company Accounts – Issue of Shares
1. Objective Questions:
A. Select the appropriate answer from the alternative given below and rewrite the sentence.
Question 1.
The balance of Share Forfeiture A/c is transferred to ______________ Account after re-issue of these share.
(a) Reserve Capital
(b) Capital Reserve
(c) Profit & Loss
(d) Share Capital
Answer:
(b) Capital Reserve
Question 2.
Premium received on issue of shares is shown to ______________
(a) Liability side of Balance Sheet
(b) Asset side of Balance Sheet
(c) Profit & Loss A/c debit side
(d) Profit & Loss A/c credit side
Answer:
(a) Liability side of Balance Sheet
Question 3.
Shareholders get ______________ on shares.
(a) interest
(b) commission
(c) rent
(d) dividends
Answer:
(d) dividends
![]()
Question 4.
The document inviting to subscribe the shares of a company is ______________
(a) Prospectus
(b) Memorandum of Association
(c) Articles of Association
(d) Share certificate
Answer:
(a) Prospectus
Question 5.
As per SEBI guidelines, minimum amount payable on share application should be ______________ Nominal Value of shares.
(a) 10%
(b) 15%
(c) 2%
(d) 5%
Answer:
(d) 5%
Question 6.
When shares are forfeited the Share Capital Account is ______________
(a) credited
(b) debited
(c) neither debited nor credited
(d) None of the given
Answer:
(b) debited
Question 7.
The liability of shareholder in Joint Stock Company is ______________
(a) joint and several
(b) limited
(c) unlimited
(d) huge
Answer:
(b) limited
![]()
Question 8.
The Share Capital which a company is authorized to issue by its Memorandum of Association is ______________
(a) Nominal Capital/Authorised Capital
(b) Issued Capital
(c) Paid-up Capital
(d) Reserve Capital
Answer:
(a) Nominal Capital/Authorised Capital
Question 9.
The unpaid amount on allotment and calls may be transferred to ______________ Account.
(a) Calls-in-Advance
(b) Calls
(c) Calls-in-Arrears
(d) Allotment
Answer:
(c) Calls-in-Arrears
Question 10.
There must be provision in ______________ for forfeiture of shares.
(a) Articles of Association
(b) Memorandum of Association
(c) Prospectus
(d) Balance Sheet
Answer:
(a) Articles of Association
B. Give one word/term/phrase for each of the following statements.
Question 1.
Amount called up on shares by the company but not received.
Answer:
Calls-in-Arrears
Question 2.
Issue of share at its face value.
Answer:
Issue at par
Question 3.
The person who purchases the shares of a company.
Answer:
Shareholder
![]()
Question 4.
The form of business organisation where a huge amount of capital can be raised.
Answer:
Joint-stock company
Question 5.
The capital is subscribed by the public.
Answer:
Subscribed capital
Question 6.
The shares having preferential rights at the time of winding up of the company.
Answer:
Preference shares
Question 7.
The shares on which dividend is not fixed.
Answer:
Equity shares
Question 8.
The part of subscribed capital is not called up by the company.
Answer:
Uncalled capital
C. State true or false with reasons.
Question 1.
Directors can forfeit the shares for any reason.
Answer:
This statement is False.
After paying money on share application, When share applicant fails to pay the call money or premium on shares in spite of repeated reminders and warnings directors/company can forfeit the shares.
Question 2.
Once the application money is received, directors can immediately proceed with the allotment of shares.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Directors can proceed for allotment of shares only after receiving the minimum subscription amount of the issued amount by cheque or other instrument complying with all legal requirements.
![]()
Question 3.
Joint-stock company forms of business organisations came into existence after the industrial revolution.
Answer:
This statement is True.
As the volume and scale of trade and industry expanded, especially after the industrial revolution, a very large unit of the commercial organisation requiring large capital and greater managerial skill, called Joint-stock company came into existence.
Question 4.
Equity shareholders get a guaranteed rate of dividend every year.
Answer:
This statement is False.
One of the features of equity shares is the rate of dividend payable on equity shares keeps on changing from one year to another. So, there is no question of guaranteed dividend every year for equity shareholders.
Question 5.
The face value of shares and market value of shares is always the same.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Face value of shares means the issue price of shares while the market value of shares means the trading price of shares at the stock exchange. The face value of shares remains the same and fixed. However, market price changes as per the performance of the company. Hence face value and market value of shares is not the same.
Question 6.
Sweat shares are issued to the public.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Sweat shares are issued by a company to its directors or employees at a discount or for consideration other than cash. Sweat shares are not issued to the public.
D. State whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Question 1.
In the case of Pro-rata allotment the excess application money received must be refunded.
Answer:
Disagree
![]()
Question 2.
Calls-in-Advance account is shown on the asset side of the Balance Sheet.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 3.
The Authorised Capital is also known as Nominal Capital.
Answer:
Agree
Question 4.
Paid-up capital can be more than Called-up Capital.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 5.
The joint-stock company can raise a huge amount of capital.
Answer:
Agree
Question 6.
When shares are Forfeited Shares Capital Account is credited.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 7.
Directors can re-issue forfeited shares.
Answer:
Agree
![]()
Question 8.
When the issued price of a share is ₹ 12 and face value is ₹ 10, the share is said to be issued at a premium.
Answer:
Agree
Question 9.
A public limited company can issue its share without issuing its prospectus.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 10.
Shares can be issued for consideration other than cash.
Answer:
Agree
E. Answer in one sentence only.
Question 1.
What are Preference Shares?
Answer:
Preference Shares are a type of share which enjoys priority or preference over equity share for the repayment of dividends at a predetermined fixed rate and for the repayment of capital.
Question 2.
What is Registered Capital?
Answer:
Registered Capital or Authorised Capital means the maximum limit up to which a company is authorized to raise share capital.
Question 3.
What is Reserve Capital?
Answer:
Reserve Capital is that part of the subscribed capital which is reserved to be called up only at the time of winding up or liquidation of the company.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Over Subscription of Shares?
Answer:
When a company received more applications of shares than those actually offered or issued to the public, known as Over Subscription of Shares.
Question 5.
Which account is debited when share first call money is received?
Answer:
The bank account will be debited when share first call money is received.
Question 6.
When are shares allotted on a pro-rata basis?
Answer:
Shares are said to be allotted on a pro-rata basis when the applications are received for more shares than the number of shares issued and shares are allotted in the proportion to the number of shares applied for.
Question 7.
What is Forfeiture of Shares?
Answer:
When a shareholder fails to pay the call money or premium on the shares in spite of repeated reminders and warnings, the company forfeits the shares of such defaulters known as forfeiture of shares.
Question 8.
What is Calls-in-Arrears?
Answer:
Non-payment of allotment or call money by the applicants in spite of repeated reminders are called Calls-in-Arrears.
![]()
Question 9.
What do you mean by Shares Issued at Premium?
Answer:
When shareholders are supposed to pay a price higher than the face value of the shares, their shares are said to be issued at a premium.
Question 10.
What is Paid-up Capital?
Answer:
Part of the called-up capital which is actually paid by the shareholders is called Paid-up Share Capital.
F. Complete the following sentences.
Question 1.
When the face value of the share is ₹ 100 and the issued price is ₹ 120, then it is said that the shares are issued at ______________
Answer:
premium
Question 2.
______________ Capital is the capital which a company is authorized to issue by its Memorandum of Association.
Answer:
Authorized
Question 3.
The difference between Called-up Capital and Paid-up Capital is known as ______________
Answer:
Calls-in-Arrears
![]()
Question 4.
______________ shareholders get fixed rate of dividend.
Answer:
Preference
Question 5.
______________ shareholders are the real owners of the company.
Answer:
Equity
Question 6.
______________ form of business organisation in which capital is raised through the issue of shares.
Answer:
Joint-stock company
Question 7.
______________ Capital is the part of Issued capital which is subscribed by the public.
Answer:
Subscribed
![]()
Question 8.
The part of Authorised Capital which is not issued to the public is known as ______________ Capital.
Answer:
Unissued
G. Calculate the following.
Question 1.
One shareholder holding 500 equity shares paid share application money @ ₹ 3, Allotment money @ ₹ 4 per share and failed to pay a final call of ₹ 3 per share his share was forfeited calculate the amount of forfeiture.
Solution:
Amount of forfeiture = Amount received by the company (In case of non-payment of ‘calls’)
Here, shareholders paid ₹ 3 per share on application and ₹ 4 per share on the allotment on 500 shares.
So, total amount received by company = 500 × ₹ 3 + 500 × ₹ 4
= 1,500 + 2,000
= ₹ 3,500
∴ Amount of share forfeiture = ₹ 3,500.
Question 2.
10,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each issued at a 10% premium. Calculate the total amount of share premium.
Solution:
Equity shares = 10,000
Face value = ₹ 10 per share
Premium @ 10% = 10,000 × 10 × \(\frac{10}{100}\) = ₹ 10,000
So, premium 10,000 shares of ₹ 10 each at 10% = ₹ 10,000
Question 3.
The company received excess applications for 5000 shares @ ₹ 4 per share. The application of 1000 shares was rejected and a pro-rata allotment was made. Calculate the amount of application money adjusted with allotment.
Solution:
Excess application money received for 5000 shares @ ₹ 4 per share = ₹ 20,000
Less: Application of 1000 shares rejected and money refunded = ₹ 4,000
Excess money received to be adjusted with allotment = ₹ 16,000
![]()
Question 4.
80,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each issued and fully subscribed and called up at 20% premium. Calculate the amount of Equity Share capital.
Answer:
Equity Share capital = No. of equity shares × face value of each share
= 80,000 × ₹ 10
= ₹ 8,00,000
Note: Equity Share capital has no concern with premium or discount amount.
Question 5.
Directors issued 20,000 equity shares of ₹ 100 each at par. These were fully subscribed and called up. All money was received except one shareholder holding 100 equity shares failed to pay a final call of ₹ 20 per share. Calculate the amount of Paid-up capital of the company.
Solution:
Fully subscribed and called-up amount = 20,000 equity shares × ₹ 100 each share
= ₹ 20,00,000
But one share holder failed to pay final call of ₹ 20 per share of 100 equity shares means
Non-payment of shares = 100 equity shares × ₹ 20 per share = ₹ 2,000
∴ Total Paid-up capital amount = ₹ 20,00,000 – ₹ 2,000 = ₹ 19,98,000
Question 6.
The company sends a regret letter for 100 shares and an Allotment letter to 25,000 shareholders. Application money per ₹ 20 per share. Calculate the amount of application money that the company is refunding.
Solution:
The company sends a Regret letter for 100 shares for ₹ 20 per share application money received i.e. only that much amount the company will refund.
Amount of refund = No. of shares × Value of per share
= 100 × ₹ 20
= ₹ 2,000
Practical Problems
Question 1.
Vijay Ltd. was registered with an authorized capital of ₹ 15,00,000 divided into 1,50,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each.
The company issued 1,00,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each at a premium of ₹ 2 per share. The company received applications for 80,000 equity shares and was allotted the shares.
The company received application money ₹ 3 per share, allotment money ₹ 4 per share
(Including premium) and first, call money ₹ 3 per share.
The Directors have not made the final call of ₹ 2 per share. All money was received except one shareholder holding 500 shares did not pay the first call.
Show Authorised Capital, Issued Capital, Subscribed Capital, Called-up Capital,
Paid-up Capital, Calls in Arrears, and Share Premium amount in the company balance sheet.
Solution:
In the books of Vijay Ltd.
Balance Sheet as on ______________
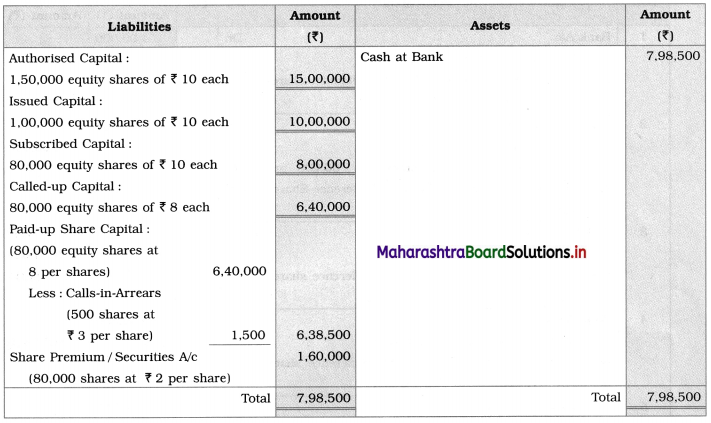
Working Notes:
1. Bank balance at the end = Amount received on application + Amount received on allotment + Amount received on 1st call + Premium amount received
= 80,000 × 3 + 80,000 × 2 × 79,500 × 3 + 80,000 × 2
= 2,40,000 + 1,60,000 + 2,38,500 + 1,60,000
= ₹ 7,98,500
2. Directors have not made the final call of ₹ 2 per share means total called-up amount = ₹ 10 – ₹ 2 = ₹ 8
3. Calls-in-Arrears on 500 shares at ₹ 3 = ₹ 1,500 of the first call
4. Share premium on 80,000 shares @ ₹ 2 received at allotment stage i.e. share premium amount = 80,000 x ₹ 2 = ₹ 1,60,000
![]()
Question 2.
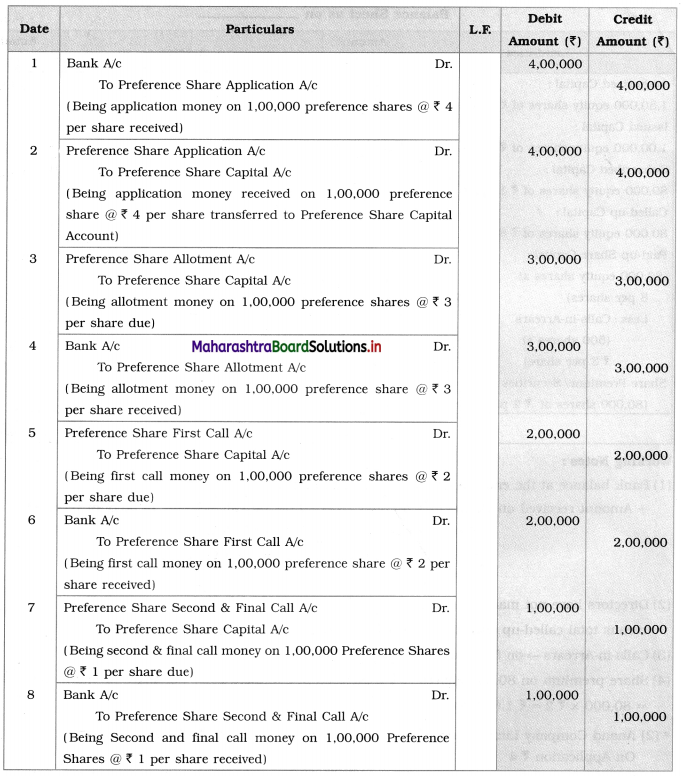
Anand Company Limited issued 1,00,000 preference shares of ₹ 10 each payable as-
On Application ₹ 4
On Allotment ₹ 3
On First call ₹ 2
On Second & Final call?
The company received applications for all these shares and received all money.
Pass Journal Entries in the books of Anand Company Ltd.
Solution:
Journal Entries in the books of Anand Company Ltd.
Question 3.
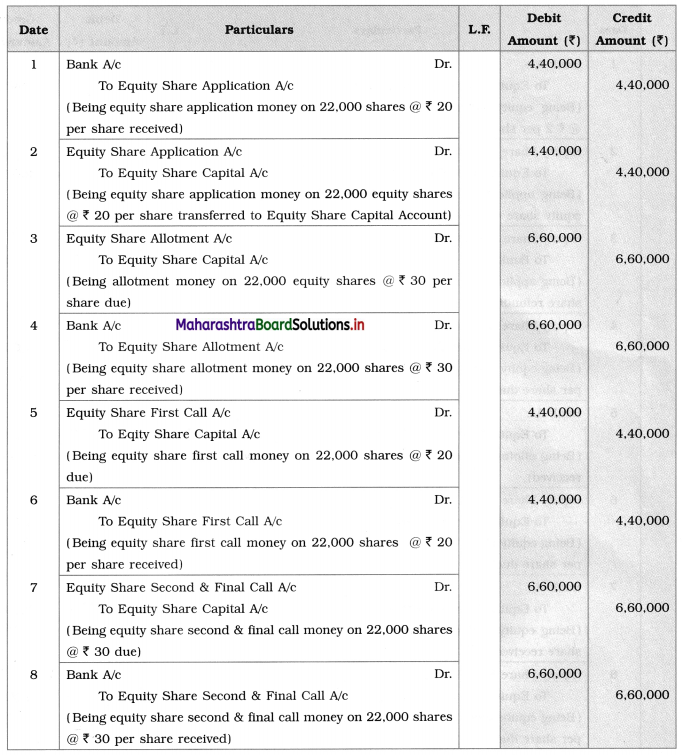
Rohini Company Limited issued 25,000 equity shares of ₹ 100 each payable as follows:
On Application ₹ 20
On Allotment ₹ 30
On First call ₹ 20
On the Second & Final call ₹ 30
The application was received for 22,000 equity shares and allotment of shares was made to them. All money was received by the company.
Pass Journal Entries in the books of Rohini Co. Ltd.
Solution:
Journal Entries in the books of Rohini Company Limited
![]()
Question 4.
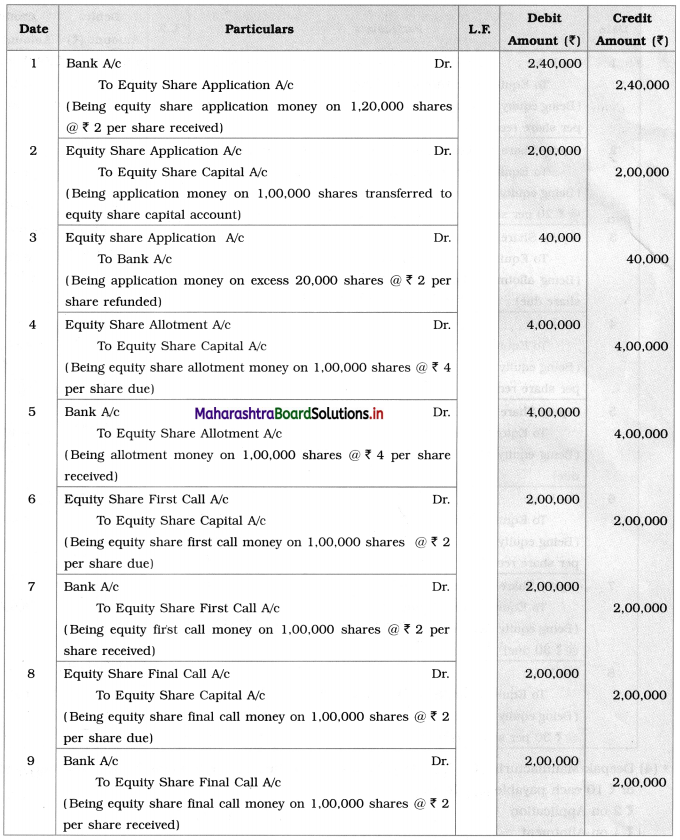
Deepak Manufacturing Co. Ltd. issued a prospectus inviting applications for 1,00,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each payable as follows :
₹ 2 on Application
₹ 4 on Allotment
₹ 2 on the First call
₹ 2 on Final call
The application was received for 1,20,000 equity shares. The Directors decided to reject excess applications and refunded application money on that. The company received all money.
Pass Journal Entries in the books of a company.
Solution:
Journal Entries in the books of Deepak Manufacturing Co.Ltd
Question 5.
Sucheta Company Limited issued ₹ 20,00,000 new capital divided into ₹ 100 equity shares at a premium of ₹ 20 per share payable as ₹ 10 on Application, ₹ 40 on Allotment and ₹ 10 premium ₹ 50 on Final call and ₹ 10 premium.
The issue was oversubscribed to the extent of 26,000 equity shares. The applicants on 2,000 shares were sent a letter of regret and their application money was refunded.
The remaining applicants were allotted shares on a Pro-rata basis. All the money due on Allotment and Final call was only received.
Make necessary Journal Entries in the books of Sucheta Company Ltd.
Answer:
Solution:
Journal Entries in the books of Sucheta Company Limited
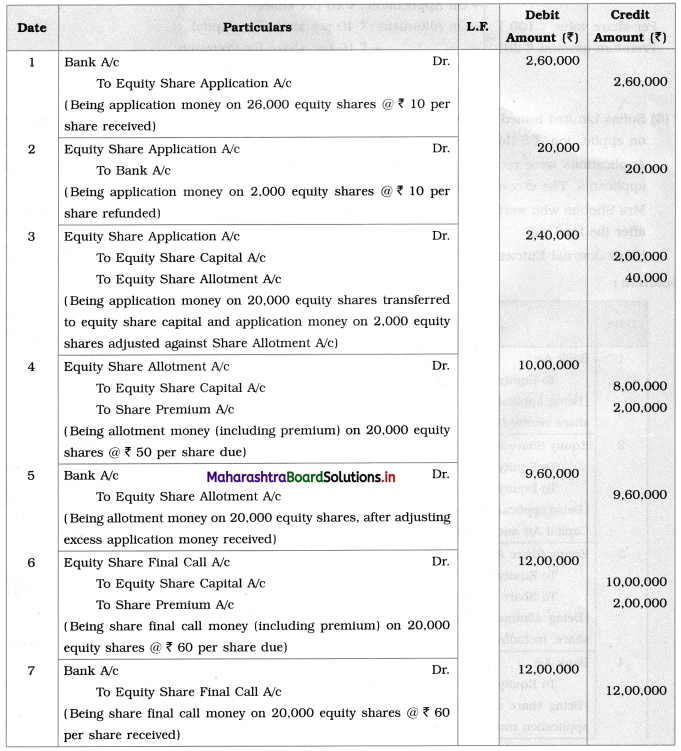
Working Note:
Calculation of Application money transferred to Share Allotment:
Application money received (26,000 × 10) = 2,60,000
Less: Application money refunded (2,000 × 10) = 20,000
Less: Application money transferred to Share Capital: (20,000 × 10) = 2,00,000
Excess money received on application transferred to Share Allotment = 40,000
Bifurcation of calls amount:

![]()
Question 6.
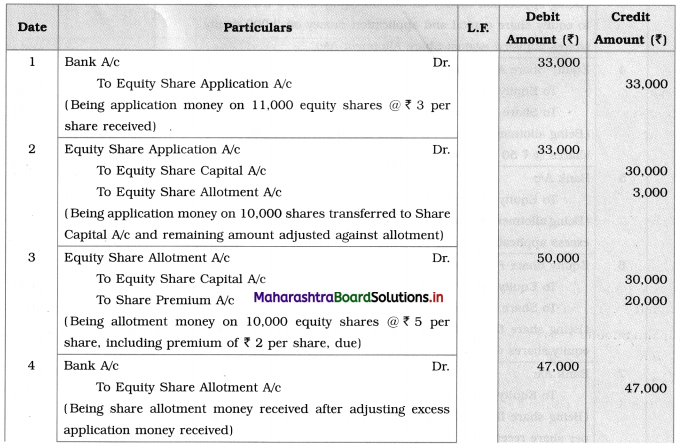
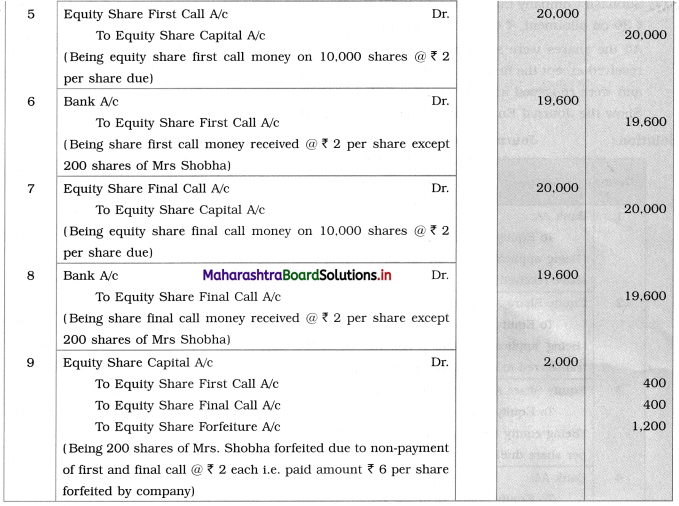
Suhas Limited issued 10,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each at a premium of ₹ 2 per share payable ₹ 3 on application, ₹ 5 (including premium) on the allotment, and the balance in two calls of an equal amount. Applications were received for 11,000 equity shares and pro-rata allotment was made for all the applicants. The excess application money was adjusted towards allotment.
Mrs. Shobha who was allowed 200 equity shares failed to pay F/F/C and her shares were forfeited after the final call.
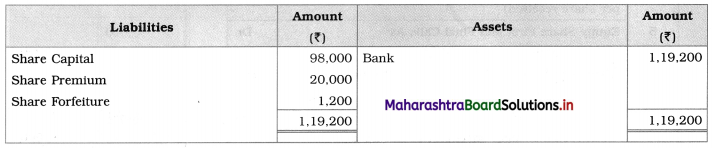
Show Journal Entries in the books of Suhas Ltd. and also show its presence in Balance Sheet.
Solution:
Journal Entries in the books of Suhas Limited
Balance Sheet of Suhas Limited
Working Notes:
1. Excess amount received at the time of application ₹ 3,000 adjusted at allotment stage, so allotment amount received in the bank is ₹ 47,000.
2. Amount called-up per share: ₹ 3 on application, ₹ 5 (including premium) on allotment i.e. ₹ 2 premium + ₹ 3 capital and balance amount ₹ 4 in two calls of the equal amount i.e. ₹ 2 on the first call and ₹ 2 on final call.
3. Mrs. Shobha was not able to pay F/F/C i.e. first and final call means 200 × ₹ 2 first call money = ₹ 400 and 200 × ₹ 2 final call money = ₹ 400.
Mrs. Shobha paid ₹ 6 per share towards capital which the company received and the company has the right to forfeit only paid amount means the company forfeited ₹ 1,200 of Mrs. Shobha.
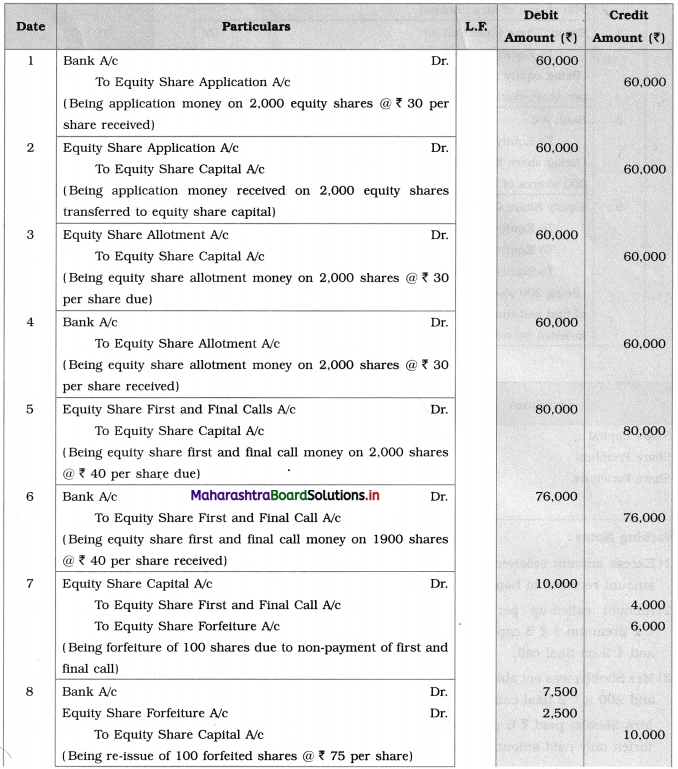
Question 7.
Subhash Company Limited issues 2000 Equity shares of ₹ 100 each payable as ₹ 30 on application, ₹ 30 on the allotment, ₹ 40 on first and final call.
All the shares were subscribed and duly allotted. The company made all the calls. All cash was duly received except the first and final call on 100 equity shares. These shares were forfeited by the company and were re-issued as fully paid for ₹ 75 per share.
Show the Journal Entries in the books of Subhash Company Ltd.
Solution:
Journal Entries in the books of Subhash Company Limited

Working Notes:
1. Amount forfeited by the company on 100 shares forfeited = 100 × (30 + 30)
= 100 × 60
= ₹ 6,000
2. Calls-in-Arrears = 100 × 40 = ₹ 4,000.
3. Amount received on re-issue of 100 forfeited shares = 100 × 75 = ₹ 7,500.
Balance of ₹ 2,500 (i.e. loss 25 × 100) is transferred to Share Forfeiture A/c.
4. Amount transfer from Share Forfeiture A/c to Capital Reserve is ascertained by preparing Share Forfeiture A/c.
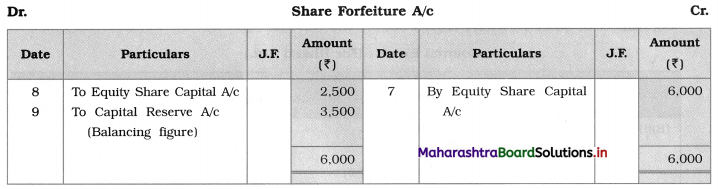
![]()
Question 8.
Pass Journal Entries for the forfeiture and re-issue of shares in the following cases:
(A) Asha Ltd. forfeited 100 equity shares of ₹ 20 each fully called-up for non-payment of the first call of ₹ 3 per share and final call of ₹ 5 per share. 80 shares of these were re-issued at ₹ 15 per share as fully paid.
(B) Bhakti Ltd. forfeited 100 equity shares of ₹ 10 each, ₹ 6 called-upon which the shareholder paid application and allotment of ₹ 5 per share. Of these 80 shares were re-issued as fully paid-up for ₹ 16 per share.
(C) Konark Ltd. forfeited 50 shares of ₹ 10 each, ₹ 8 called-up. The shareholder failed to pay the first call of ₹ 3 per share. Later on, 30 shares of these were re-issued at ₹ 7 per share.
Solution:
Journal Entries [For Asha Ltd.]
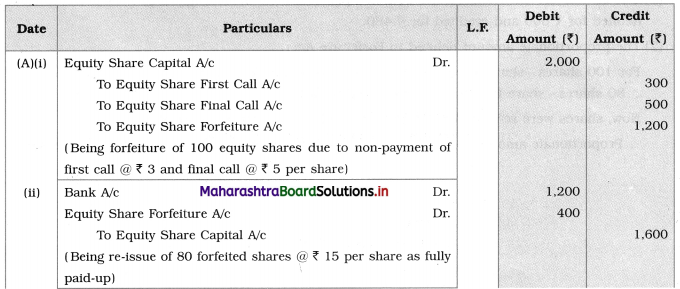

Working Notes for A:
1. Out of 100 forfeited shares, 80 shares were re-issued accordingly Equity Share Capital A/c is debited and credited.
2. To find the proportionate amount for Forfeiture A/c:
For 100 shares-share forfeiture amount = ₹ 1,200
∴ 80 shares – share forfeiture amount = ₹ 960
Now, out of this ₹ 960 we used ₹ 400 from Share Forfeiture A/c at the time of re-issue of shares.
So, balance of Share Forfeiture A/c = ₹ 960 – ₹ 400 = ₹ 560
Journal Entries [For Bhakti Ltd.]
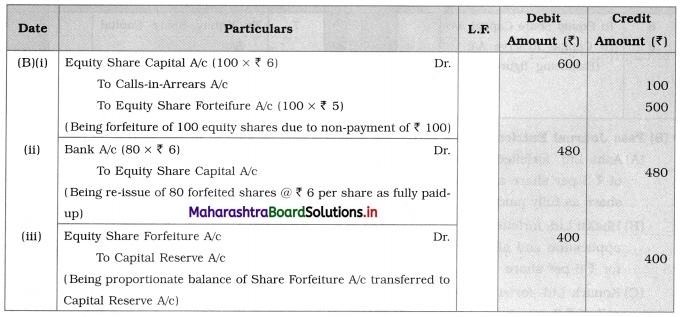
Working Notes for B:
1. Out of 100 forfeited shares, 80 shares were re-issued accordingly Equity Share Capital A/c is debited for ₹ 600 and credited for ₹ 480.
2. The proportionate amount debited to Forfeiture A/c:
For 100 shares-share forfeiture amount debited = ₹ 500 1 Qn
∴ 80 shares – share forfeiture amount = ₹ \(\frac{80}{100} \times \frac{500}{1}\) = ₹ 400
Now, shares were re-issued at ₹ 6 per share which is a called-up amount.
∴ The proportionate amount for Forfeiture A/c ₹ 400 will be transferred to Capital Reserve A/c.
![]()
Journal Entries (For Konark Ltd.)
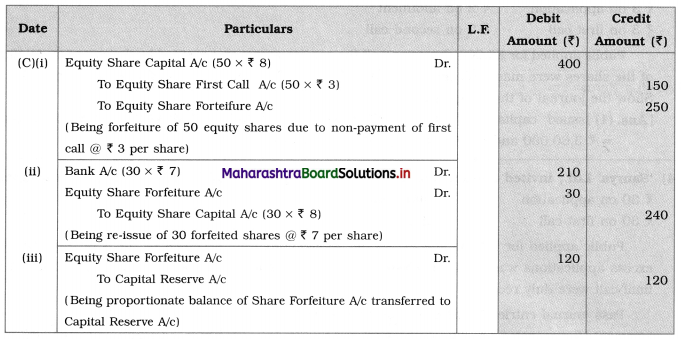
Working Note for C:
The proportionate amount debited to Forfeiture A/c:
For 50 shares – share forfeiture amount debited is ₹ 250
∴ 30 shares-share forfeiture amount = ₹ \(\frac{30}{50} \times 250\) = ₹ 150
Out of this ₹ 30 used for re-issue of forfeited shares.
∴ Balance of Share Forfeiture A/c = ₹ 150 – ₹ 30 = ₹ 120.