By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Economics students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 1 Basic Concepts in Economics
→ Types Of Sciences :
Natural Sciences:
- Called as exact sciences
- E.g. Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry
Social Sciences:
- Called as abstract / behavioural /inexact sciences
- Eg. Psychology, Sociology, Economics

![]()
→ Origin of the term ‘Economics’ lies in the Greek word ‘Oikonomia’ meaning management of the household.
→ Economics → ‘Queen of Social Sciences’ — Paul Samuelson.
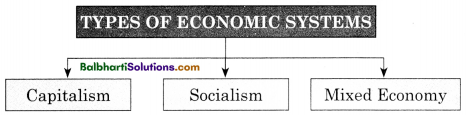
→ Types of Economic Systems:
- Capitalism
- Socialism
- Mixed Economy
→ ‘Artha’ means Wealth’ and ‘Shastra’ means ‘Science’
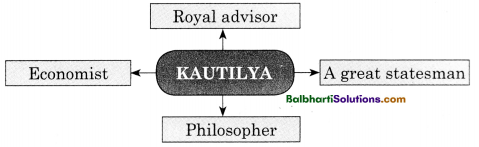
→ Kautilya:
- Royal advisor
- A great statesman
- Philosopher
- Economist
→ Kautilya was also known by the names ‘Chanakya’ or ‘Vishnugupta’
→ Kautilya was an author of book Arthashastra’.
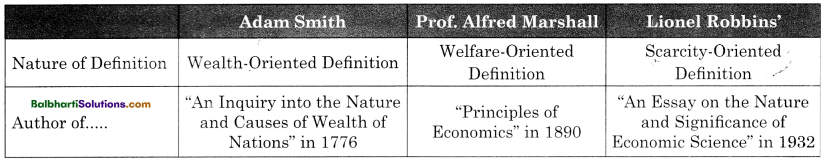
→ Adam Smith is called as “Father of Economics”
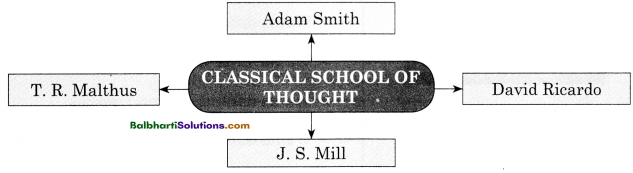
→ Classical School Of Thought:
- Adam Smith
- T. R. Malthus
- David Ricardo
- J.S Mill
→ Neo-Classical School Of Thought:
- Irving Fisher
- A.C Pigou
- Alfred Marshall
![]()
→ Modern School Of Thought
- J.M. Keynes
- Lionel Robbins
- Paul Samuelson
→ Branches Of Economics:
Micro Economics
- Greek word – ‘Mikros’
- means small
Macro Economics:
- Greek word – ‘Makros’
- means large / aggregate / total
→ Basic Concepts Of Micro Economics
- Wants
- Goods and Services
- Utility
- Value
- Wealth
- Personal Income
- Personal Disposable Income (PDI)
- Economic Activity
→ Characteristics Of Wants:
- Wants are unlimited
- Wants are recurring in nature
- Wants differ with age
- Wants differ with gender
- Wants differ due to preferences
- Wants differ with seasons
- Wants differ due to culture
→ Classification Of Wants:
(1) Economic & Non-economic Wants
E.g.
- Economic wants : food, medicines, etc.
- Non-economic wants : air, sun shine, etc.
(2) Individual Wants and Collective Wants
E.g.
- Individual wants : a doctor using stethoscope, a judge wearing his coat, a teacher using his duster
- Collective wants : travelling by train, bus, aeroplane, etc.
(3) Necessities, Comforts and Luxuries
E.g.
- Necessities : food, clothing, shelter, health and education
- Comforts : washing machine, mixer, pressure cooker, geyser, etc.
- Luxuries : AC-car, Air conditioner, diamond necklace, etc.
→ Goods and Services :
- Goods : Any commodity which satisfies human wants is called as goods. Eg. chalk, toothbrush, tooth paste, pen, pencil, eraser, etc.
- Services : Any kind of services which satisfy human wants is called as services. Eg. service of a doctor, teacher, lawyer, carpenter, cobbler, tailor, etc.
→ Utility : A power in a commodity or service to satisfy a human want is called as utility.
![]()
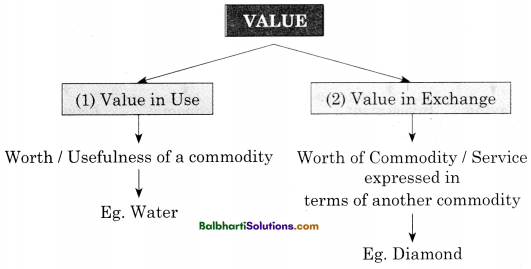
→ Values:
(1) Value in use:
- Worth / Usefulness of a commodity
- Eg. Water
(2) Value in Exchange:
- Worth of Commodity / Service expressed in terms of another commodity
- Eg. Diamond
→ Characteristics of Wealth:
- Utility
- Scarity
- Externality
- Transferability
→ Personal Income : Income received from all the sources is called Personal Income.
→ Personal Disposal Income : It is a part of Personal Income which is left behind after payment of taxes.
→Types Of Income
- Fixed Income
- Fluctuating income
- Unearned income
- Money income
- Earned income
- Real income
- Residual income
- Contractual income
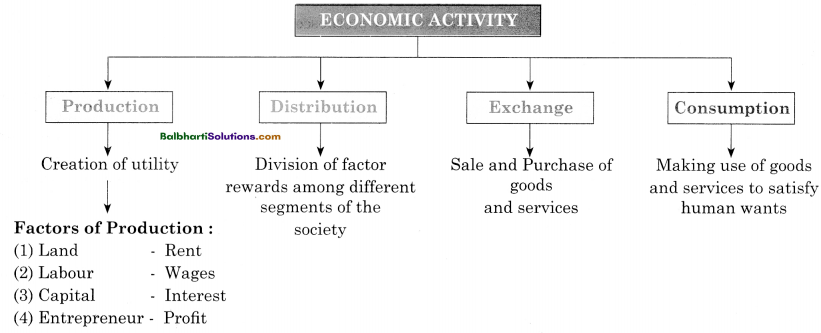
Economic Activity:
Production:
Creation of utility
Factors of Production :
- Land – Rent
- Labour – Wages
- Capital – Interest
- Entrepreneur – Profit
Distribution:
Division of factor rewards among different segments of the society
Exchange:
Sale and Purchase of goods and services
![]()
Consumption:
Making use of goods and services to satisfy human wants
→ Concept Of Macro Economics
- National Income
- Saving
- Investment
- Trade Cycles
- Economic Growth
- Economic Development
Economic Growth:
- indicates increase in the real national income of the country
- narrow and quantitative concept
- possible without economic development
- uni-dimensional concept
- it is spontaneous and reversible
- measured in terms of national income and per capita income
Economic Development:
- indicates economic growth plus progressive changes
- broader and qualitative concept
- not possible without economic growth
- multi-dimensional concept
- it is deliberate and irreversible
- measured in terms of agricultural productivity, industrial productivity, quality of human life, etc.
![]()
Word Meaning:
inventions – to create, empirical approach – method of inquiry and observation by experiments, psychology- study of mental behaviour of human being, abstract – ideas without any physical or concrete existence, sociology – study of social behaviour of human being, tendencies – behaviour, acquiring – to obtain, treatise – study of, broadest – large, crucial – important, compilation – list of something, statesman – political leader, literacy – written, Laissez faire – without any interference of Government, Neo-classical – time period between 1660 – 1798, attainment – a thing to achieve, requisites – necessary, material welfare – to get all the basic needs for well being, scarce – limited, alternative – many, comparatively – in compare of something, priority – importance, coined – create. Micro – small, variables – factor which changes, desire – strong feeling to have something, unending – something which has no ends, occasional – sometime, chronological – in order, preferences – choices, influence – effect, monetary – exchange of goods transaction and services in which money is involved, value – importance, well-furnished – well decorated, capacity – the total amount of something contains, immense – importance, utility – useful, transferability – to pass something from one person to another, tangible – physically can be touched, Notional – assumed, efficiency – productivity, earnings – income, stable – fixed, fluctuating – changing, contractual – as per the agreement, residual – leftover, unearned – earning without actual working, entrepreneur – a person who sets and runs the business, charity – to help other in form of money/material, reward – returns/ benefits, labour – do work physically, macro – large, aggregate – total, estimate – to calculate, foregoing- sacrificing, mobilization – moving, inflation – continuous rise in price (increase in price), depression – Continuous fall in price (decrease in price), quantitative – measured by quantity of something, progressive – continuous, multi-dimensional – in several measuring ways, narrow – small, spontaneous – immediate, reversible – moving in backward direction, deliberate – for long time, per capita income – each person income, paradox – opposite statement, qualitative – measured in terms of quality of something.