By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 8 Poverty in India students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 8 Poverty in India
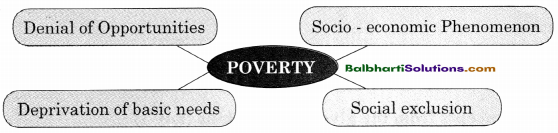
→ Poverty:
- Denial of Opportunities
- Socio – economic Phenomenon
- Deprivation of basic needs
- Social exclusion
![]()
→ Poverty in India During British Period:
- Economic drain of resources
- Recurrence of famines
- Decline of handicraft and cottage industries
- Oppressive economic policies

→ Policy Measures Undertaken By India Government:
- Economic Planning
- Economic Reforms
- Antipoverty Programme
→ (Garibi hatao)

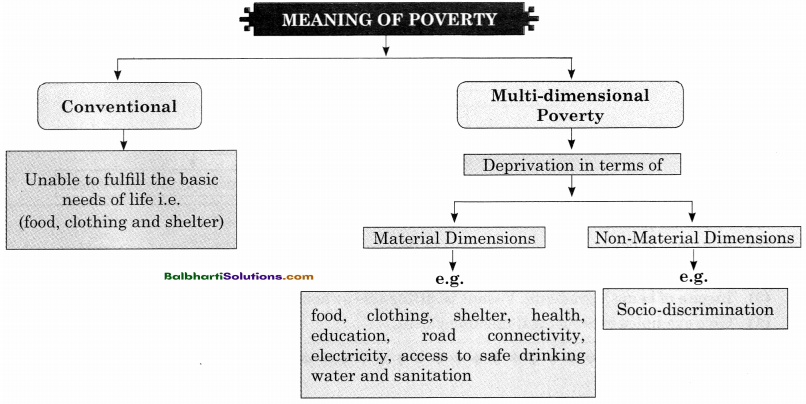
→ Meaning Of Poverty:
- Conventional
- Material Dimensions Poverty
1. Conventional:
Unable to fulfill the basic needs of life i.e. (food, clothing and shelter)
2. Material Dimensions Poverty:
Deprivation in terms of Material Dimensions
e.g.:
food, clothing, shelter, health,
education, road connectivity,
electricity, access to safe drinking
water and sanitation
Deprivation in terms of Non-Material Dimensions
e.g.:
Socio-discrimination
![]()
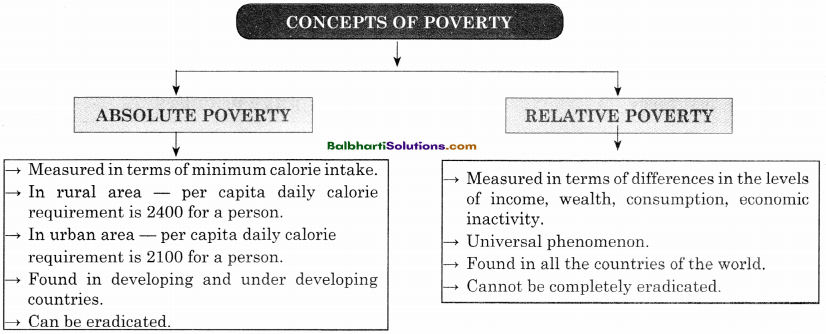
→ Concept Of Poverty:
Absolute Poverty:
- Measured in terms of minimum calorie intake.
- In rural area — per capita daily calorie requirement is 2400 for a person.
- In urban area — per capita daily calorie requirement is 2100 for a person.
- Found in developing and under developing count ries.
- Can be eradicated.
Relative Poverty:
- Measured in terms of differences in the levels of income, wealth, consumption economic inactivity.
- Universal phenomenon.
- Found in all the countries of the world.
- Cannot be completely eradicated.
→ Poverty line
- It is as imaginary line that divides the poor and non-poor.
- Determined in terms of per capita household expenditure.
- As per task Force on Eliminating Poverty constituted by NUT Aayog it is defined as “the threshold expenditure”
OR
the amount necessary to purchase a basket of goods and services that are considered necessary to satisfy human needs at socially acceptable levels.
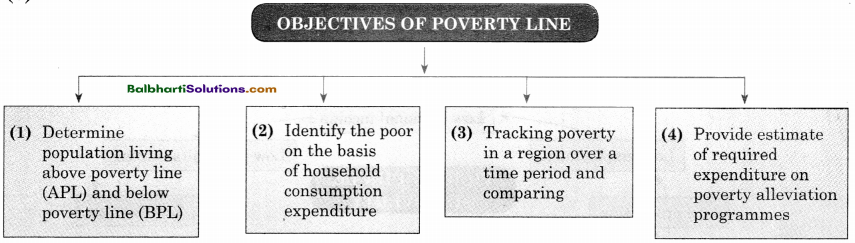
→ Objectives Of Poverty Line:
- Determine population living above poverty line (APL) and below poverty line (BPL)
- Identify the poor on the basis of household consumption expenditure
- Tracking poverty in a region over a time period and comparing
- Provide estimate of required expenditure on poverty alleviation programmes
![]()
→ Income Pyramid:

→ Types Of Poverty:
1. Rural Poverty
Deprivation of basic needs among section of people living in the villages
Found Among:
- small and marginal farmers.
- agricultural labourers
- contractual labourers
- landless labourers
Reasons:
- low agricultural productivity
- drought
- poor rural infrastructure
- illiteracy
- lack of alternative jobs
- rural indebtedness
Urban Poverty:
Absence of basic needs among section of people living in town and cities
Reasons:
- spillover effects of migration
- lack of affordable housing
- illiteracy
- slow industrial growth
Effects
- growth of slums
- informal sector
- creates law and order problems
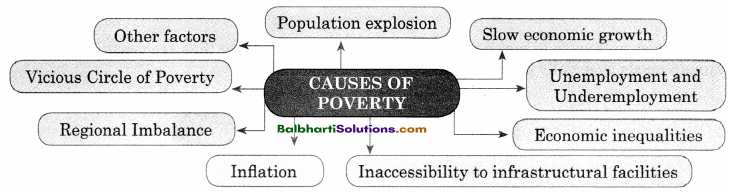
→ Causes Of Poverty :
- Other factors
- Population explosion
- Slow economic growth
- Vicious Circle of Poverty
- Unemployment and Underemployment
- Regional Imbalance
- Economic inequalities
- Inflation
- Inaccessibility to infrastructural facilities
![]()
→ Vicious Circle Of Poverty:
- Low investments
- Low production
- Less employment
- Low National income
- Low per capita income
- Low savings
- Low capital formation

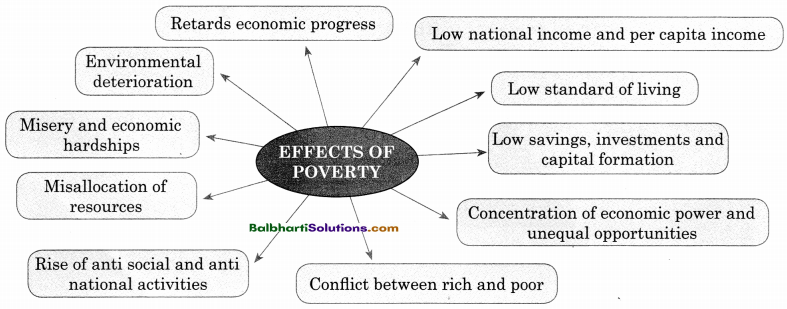
→ Effects Of Poverty:
- Retards economic progress
- Low national income and per capita income
- Environmental deterioration
- Low standard of living
- Misery and economic hardships
- Low savings, investments and capital formation
- Misallocation of resources
- Concentration of economic power and unequal opportunities
- Rise of anti social and anti national activities.
- Conflict between rich and poor
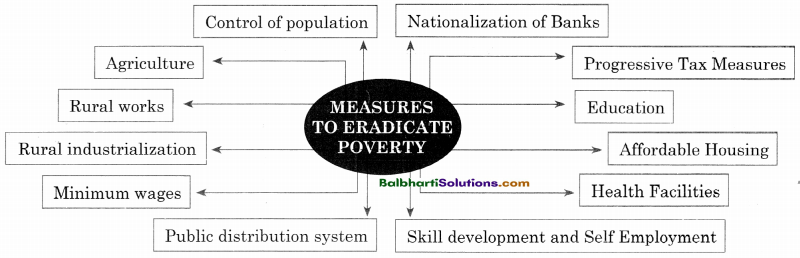
→ Measures To Eradicate Poverty:
- Control of population
- Nationalization of Banks
- Agriculture
- Progressive Tax Measures
- Rural works
- Education
- Rural industrialization
- Affordable Housing
- Minimum wages
- Health Facilities
- Public distribution system
- Skill development and Self Employment
![]()
→ 17th October is observed as International Day for Eradication of poverty.
Word Meaning:
phenomenon – a situation that happens, imaginary – unreal, perceived – to consider, threshold – beginning, exclusion – excluding, trapped – shut in, deprivation – to lack something, miseries – hardships/sufferings, denial – not having something, drain – getting exhausted, racial – relating to race of individual, recurrence
– occurring of event again and again, conventional – ordinary, emerged – appear, civil liberties – individual freedom for betterment of society, starvation – lack of food, misallocation – wrong distribution, multifaceted
– many features, vulnerable – risk, calories – energy value of foods, nationalization – transfer of branch of industry from private to state ownership, spillover – over flow, beverages – liquid refreshment to drink, – conveyance – transport, bottlenecks – obstruction, vicious – dangerous, rehabilitation – restoring/ resettlement, correlate – to connect, enrolment – to seek admission.