By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 5 Secondary Economic Activities students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 5 Secondary Economic Activities
→ Some products obtained from primary activities are consumed directly by man.
→ However, some products need to be processed to make them more useful and durable.
→ Thus, products obtained from primary activities are used as raw materials in secondary activities.
→ Processing of products from primary activities takes place in manufacturing industries where they are changed into finished product to be sold in markets.
→ Thus, secondary activities increases the value of primary products by transforming raw material into finished products.
![]()
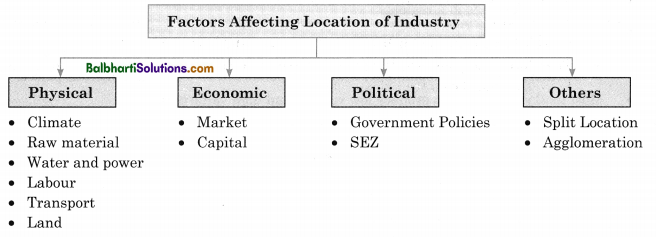
Physical Factors
→ Extreme climate is not suitable for the development of industries. Hence, most of the industries develop in the areas of moderate climate.
→ Industries using perishable, heavy, bulky and weight-losing raw materials are located near the raw material producing areas.
→ Water is one of the most important factor for the industries. Power or energy like coal, electricity, etc., are indispensable resources for running the machinery of industries.
→ Different types of industries require different labour. Some industries need semi-skilled whereas some need skilled labour.
→ The cost of transportation and time required to transport raw material and finished product is known as economic distance.
→ Low cost of transportation is deciding factor of location of industry.
→ Large area is necessary for the construction of industry and therefore, flat and well-served areas with transportation facilities are important for the development of industries.
Economic Factors
→ The entire process of manufacturing is futile until the finished goods reach the market. Therefore, nearness to market is an added advantage for quick disposal of finished products.
→ Capital is a very important factor in the development of industries as huge investments is necessary for establishing industries.
Political Factors
→ The government can encourage or discourage the development of industries in certain areas by providing facilities and vice-versa.
→ Governments support establishing zones or regions which are specially developed for industrial production. In India, they are called Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
![]()
Other Factors
→ Some productions are decentralized and are arranged at different places to reduce transport cost which is referred to as split location.
→ A proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production is called economy of scale or agglomeration.
→ By using available opportunities according to ‘economies of scale’, the region attracts more and more industries in a region.
Footloose Industries
→ Footloose industries are industries which does not depend much on available resources, production skills and consumers on which it depends can be found in numerous places.
→ Most footloose industries produce low volume and high-value outputs.
Characteristic Features of Industrial Regions
- Agglomeration of industries.
- Dense population growth, large labour force.
- Employment to large working populations.
- Large banking and credit facilities.
- A large network of transportation.
- Excellent communication facilities
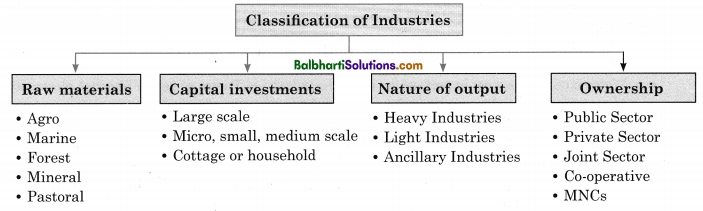
Classification based on raw material
→ Agro-based Industries:
Industries using agricultural produce as a raw material are known as agro-based industries.
→ Marine-based Industries :
All those units involved in processing and canning of fish, fish products and other marine products known as marine-based industries.
→ Forest-based Industries :
Industries using products from forests which are processed are known as forest-based industries.
→ Mineral-based Industries :
Industries in which manufacturing is based on minerals are mineral-based industries.
→ Pastoral-based Industries:
Industries which depend upon animals as their raw material are pastoral-based industries.
![]()
Classification based on the basis of capital investment
→ Large scale Industries
In India, industries requiring an investment of more than X 10 crore are large-scale industries.
→ Micro, Small and Medium Industries
Micro industries: Here, investment in plant and machinery is not more than X 25 lakh and investment in equipments not more than X 10 lakh.
→ Small scale industries:
Here, investment in plant and machinery more than X 25 lakh but does not exceed X 5 crore and investment in equipment is more than X 10 lakh but not more than X 2 crores.
→ Medium-scale industries:
Here, investment in plant and machinery is more than X 5 crores but does exceed X 10 crores and investment in equipment more than X 2 crores but does not exceed X 5 crores.
→ Cottage or Household Industry
Cottage industry is a basic industry. It needs little capital and involves less transportation cost.
Classification based on nature of output
→ Heavy Industries:
Industries producing materials, which are used as raw material in other industries, are known as heavy industries or basic industries.
→ Light Industries
Industries producing goods for direct consumption for consumers are called light industries or consumer goods industries.
→ Ancillary Industries
Industries which manufacture spare parts to be used in other industries are called ancillary industries.
![]()
Classification based on ownerships
→ Public sector industries
Industries owned by the State are called public sector industries.
→ Private-sector industries
Industries owned by private individual or partnerships of private individuals are known as private sector industries.
→ Joint sector industries
Industries which are managed by an individual and government or between two or more governments are called joint sector industries.
→ Co-operative sector industries
A group of people pool their resources to set up and manage industry on cooperative basis are called cooperative sector industries.
→ MNCs
Privately or public owned industries in the process of manufacturing involve more than one country are called multinational corporation.