Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 History Solutions Chapter 8 Civil Disobedience Movement Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 8 History Solutions Chapter 8 Civil Disobedience Movement
Class 8 History Chapter 8 Civil Disobedience Movement Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options :
(Mahatma Gandhi, Khuda-i-Khidmatgar, [ Ramsay Mac Donald, Sarojini Naidu)
Question 1.
……………. organised the Round Table Conference in London.
Answer:
Ramsay Mac Donald
![]()
Question 2.
Khan Abdul Gafar Khan established the organisation named …………….
Answer:
Khuda-i-Khidmatgar
Question 3.
……………. led the Dharasana Satyagraha.
Answer:
Sarojini Naidu
Question 4.
In the Second Round Table Conference ……………. participated as a representative of Indian National Congress.
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi.
2. Explain the following statements with reasons :
Question 1.
Chandrasing Thakur was court martialled and severely punished.
Answer:
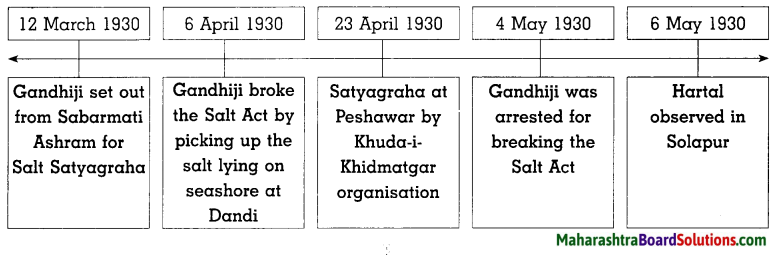
- Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan began Satyagraha at Peshawar on 23rd April, 1930. His organisation Khuda-i Khidmatgar led the satyagraha.
- They kept Peshawar town in their control for a week.
- The British government ordered Garhwal regiment to fire on the satyagrahis.
- Chandrasing Thakur an officer of the Garhwal Regiment refused to fire on the satyagrahis.
Therefore, he was court-martialled and severely punished.
Question 2.
The Government declared Martial Law at Solapur.
Answer:
- After the Salt Satyagraha many movements which were integral of Civil Disobedience Movement started.
- The mill workers in Solapur observed hartal and organised a huge procession on 6th May 1930.
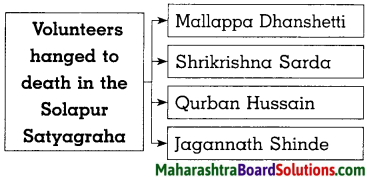
- The District Collector ordered firing on procession. Many volunteers including Shankar Shivdare died in the firing.
- People got enraged and attacked railway stations, police stations, courts, municipal buildings, etc.
Therefore, Martial law was imposed in Solapur by the government.
![]()
Question 3.
The deliberation in the First Round Table Conference proved to be meaningless.
Answer:
- The Civil Disobedience Movement intensified in India in 1930.
- The British Prime Minister, Ramsay Mac Donald organised Round Table Conference at London to discuss constitutional issues related to India.
- The representatives of many political parties and princely states participated in the conference. Indian National Congress did not participate in it.
- Without the participation of the Congress which was a body that represented the country deliberations were meaningless.
Thus, the deliberation in the First Round Table Conference proved to be meaningless.
Question 4.
Gandhiji began fast unto death in the Yerwada jail.
Answer:
- The Communal Award declared by the British Prime Minister Ramsay Mac Donald provided separate electorates for the Dalits.
- This division of the society on the basis of caste was not acceptable to Gandhiji.
- Therefore, to protest against the Award, Gandhiji began fast unto death in the Yerawada jail.
3. Answer the following questions in 25 to 30 words :
Question 1.
Why did Gandhiji decide to break the Salt Act to begin the Satyagraha?
Answer:
1. Before launching the Civil Disobedience Movement Gandhiji demanded cancellation of salt tax and end the monopoly of the British government to manufacture it.
2. Being an important ingredient in the food of the common people, it was unjust to impose a tax on salt.
3. Gandhiji decided to launch the Salt Satyagraha by a violation of the Salt Act, which was symbolic in breaking all unjust and oppressive laws of the British.
![]()
Question 2.
Why did the Indian National Congress withdraw the Civil Disobedience Movement?
Answer:
1. After the failure of the First Round Table Conference, Prime Minister Ramsay Mac Donald hoped that Indian National Congress would participate in the Second Round Table Conference.
2. In order to create a conducive atmosphere Gandhiji and other political leaders were released from jail.
3. A pact was signed after discussion between Gandhiji and Viceroy Irwin.
4. According to the pact, the British Government gave an assurance of providing Responsible Government in the proposed constitution of India.
5. So, the congress agreed to suspend the Civil Disobedience Movement and participate in the Second Round Table Conference.
4. Complete the following timeline of Civil Disobedience Movement:
Question 1.
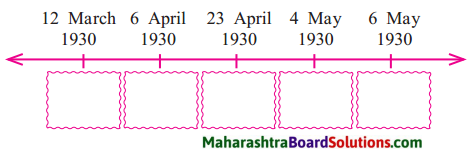
Answer:
![]()
Do you Know?
Features of the Civil Disobedience Movement :
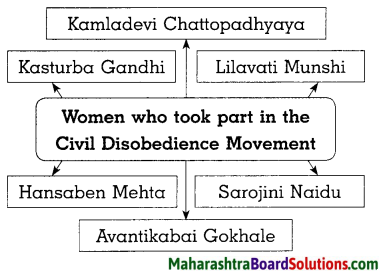
1. All the movements, till now, were limited only to urban areas. But this movement became a nationwide movement. People from rural areas registered their participation. Women also took part in large numbers. Kasturba Gandhi, Kamladevi Chattopadhyay, Ayantikaba I Gokha le, Lilavati Munshi, Hansaben Mehta led the satyagraha.
2. This movement was based on complete nonviolence. The British Government was trying to greatly suppress the movement, but the people protested unarmed. Due to this, the Indian people became fearless.
project:
Question 1.
Gather additional information along with photographs about the work of the following personalities in the Civil Disobedience Movement and exhibit it in the class. (a) Sarojini Naidu (b) Khan Abdul Gafar Khan (c) Babu Genu Said.
![]()
Question 2.
The plot on an outline map of India, the places mentioned in the chapter where the Civil Disobedience Movement took place.
Class 8 History Chapter 8 Civil Disobedience Movement Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options :
Question 1.
After the resolution of Complete Independence was passed in Lahore session, Gandhiji decided to launch ……………. Movement.
(a) Home Rule
(b) Non-co-operation
(c) Quit India
(d) Civil Disobedience
Answer:
(d) Civil Disobedience
Question 2.
During Civil Disobedience Movement, government imposed Martial law in ……………. .
(a) Peshawar
(b) Solapur
(c) Pune
(d) Mumbai
Answer:
(b) Solapur
Question 3.
Gandhiji withdrew the Civil Disobedience Movement in ……………. .
(a) April 1934
(b) March 1930
(c) November 1932
(d) May 1933
Answer:
(a) April 1934
![]()
Question 4.
Gandhiji broke the Salt Act at ……………. .
(a) Dandi
(b) Peshawar
(c) Dharasana
(d) Yerwada
Answer:
(a) Dandi
Question 5.
The British government gave orders to regiment in Peshawar to ……………. open fire on the satyagrahis.
(a) Garhwal
(b) Sikh
(c) Maratha
(d) Rajput
Answer:
(a) Garhwal
Name the following :
Question 1.
Follower of Gandhiji known as Frontier Gandhi.
Answer:
Khan Abdul Gafar Khan
Question 2.
Volunteer who died in firing at Solapur satyagraha.
Answer:
Shankar Shivdare
Question 3.
Laid down his life in front of the truck boycotting foreign goods in Mumbai.
Answer:
Babu Genu Said
Question 4.
Attended the Second Round Table Conference as representative of Dalits.
Answer:
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar.
Answer the following questions in one sentence :
Question 1.
What was the objective of Gandhiji in starting the Civil Disobedience?
Answer:
The objective of Gandhiji was to break the oppressive and unjust laws of the British Government through peace and Satyagraha.
![]()
Question 2.
From which place and when did the Dandi March start?
Answer:
The Dandi March started from Sabarmati Ashram in Ahmedabad on 12 March, 1930.
Question 3.
Name the leaders present at the First Round Table Conference.
Answer:
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar, Sir Tej Bahadur Sapru, Barrister Jinnah were the leaders present at the First Round Table Conference.
Question 4.
Which issues were discussed in the First Round Table Conference?
Answer:
The issues like Responsible Government at centre and establishment of Federal State in India were discussed.
Question 5.
What decision was made in the Poona Pact?
Answer:
According to the Poona Pact, separate electorates for the Dalits was cancelled and a provision for reserved seats was made.
Do as Directed :
Complete the graphical presentation :
Question 1.
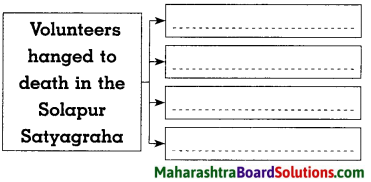
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
Answer:
Question 3.
Answer:
Write short notes :
Question 1.
Gandhi-Irwin Pact :
Answer:
1. On the appeal of the Prime Minister, the Viceroy released Gandhiji and other political leaders from prison.
2. In this conducive atmosphere, a pact was signed between Gandhiji and Viceroy Irwin. It is known as Gandhi-Irwin Pact.
- According to the pact, the British Government gave an assurance of providing Responsible Government in the proposed constitution of India.
- Congress decided to withdraw the Civil Disobedience Movement.
- Agreed to participate in the Second Round Table Conference.
![]()
Question 2.
Second Round Table Conference :
Answer:
- The Second Round Table Conference was held in 1931.
- Gandhiji participated as the sole representative of the Indian National Congress.
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar represented the Dalits. The representatives of the various castes and communities, political parties and the princely states also participated.
- The issues of minority representation and nature of proposed federal constitution were discussed.
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar demanded separate electorates for the Dalits.
- Gandhiji tried to bring unanimity but he was unsuccessful. ‘
- So, he was disappointed and returned to India.
Question 3.
Poona Pact :
Answer:
- After the Second Round Table Conference, the British Prime Minister Ramsay Mac Donald declared Communal Awards.
- Communal Awards granted separate electorates to the Dalits as demanded by Dr. Ambedkar.
- Gandhiji was against the division on the basis of caste. He started fast unto death in Yerwada jail.
- The leaders of Indian National Congress requested Dr. Ambedkar to reconsider his demand in the interest of the nation.
- So, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar signed the. Poona Pact with Gandhiji in 1932.
- It provided reserved seats instead of separate electorates for the Dalits.
Question 4.
The Round Table Conference :
Answer:
- The British Prime Minister, Ramsay Mac Donald wanted to discuss constitutional issues related to India.
- For this purpose, he organised Three Round Table Conferences at London between 1930 and 1932.
- Representatives of various communities, castes, political parties and princely states attended the conferences.
- Gandhiji attended the Second Round Table Conference as the representative of Indian National Congress.
- As no important decision was taken in them, all these conferences proved to be futile.
Answer the following questions in 25 to 30 words :
Question 1.
Write about the sacrifice of Babu Genu.
Answer:
- There was agitation against foreign goods in Mumbai.
- Babu Genu Said, a mill worker, was at the forefront in this Satyagraha.
- He threw himself in front of a truck carrying foreign goods in order to stop it.
- He did not budge even after the police threatened him.
- In the end, he was crushed under the truck.
- His martyrdom was a source of inspiration for the national movement.
![]()
Question 2.
Write features of Civil Disobedience Movement.
Answer:
The Civil Disobedience Movement launched in 1930 had the following features :
- All the movements launched till then were limited to urban areas.
- But this movement became nationwide as the people from rural areas also participated.
- Women participated in large numbers in the movement and even led it at many places.
- The movement was based on non-violence. People faced the suppressive measures of the government unarmed and fearlessly.
Question 3.
What suppressive measures were adopted by the British government after the Second Round Table Conference?
Answer:
- Gandhiji resumed the Civil Disobedience Movement after he failed and returned from the Second Round Table Conference.
- The government responded by resorting to inhuman oppressive measures.
- Civic rights were strangled.
- The Indian National Congress and associated institutions were declared illegal.
- Restrictions were imposed on national newspapers and literature.
Explain the following statements with reasons :
Question 1.
Gandhiji was arrested on 4th May 1930.
Answer:
- Gandhiji started Salt Satyagraha on 6th April 1930 at Dandi by breaking the Salt act.
- With this the Civil Disobedience Movement started all over India.
- In spite of suppressive measures undertaken by the British Government, they could not suppress the movement.
The British government found itself in a difficult situation. So, Gandhiji was arrested on 4th May 1930.
![]()
Question 2.
Gandhiji returned disappointed from the Second Round Table Conference.
Answer:
- The British Government raised the issue of representation of the minorities and the nature of the federal constitution.
- There were differences of opinion among the representatives.
- Moreover, the efforts of Gandhiji to arrive at a consensus did not succeed.
- This disappointed Gandhiji and he returned from the Second Round Table Conference.
Read the passage and answer the questions given below:
Passage:
The satyagraha at …………….
………………… Malavan and Shiroda.
Question 1.
Who led the Dharasana Satyagraha?
Answer:
Sarojini Naidu led the Dharasana Satyagraha in Gujarat.
Question 2.
At which places in Maharashtra did Salt Satyagraha take place?
Answer:
The Salt Satyagraha in Maharashtra took place at Wadala, Malvan and Shiroda.
Question 3.
Give a brief account of the Dharasana Satyagraha.
Answer:
- The leadership of salt satyagraha was taken over by Sarojini Naidu at Dharasana in Gujarat after the arrest of Gandhiji.
- The police lathi-charged the batches of the satyagrahis who came forward to break the Salt Act.
- They silently tolerated the blows of the lathis.
- The injured were provided medical aid and another batch of satyagrahis would replace them.
- This chain of satyagrahis continued endlessly at Dharasana.
Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Explain the extensive nature of Civil Disobedience Movement.
Answer:
- After the resolution of complete independence was passed, Mahatma Gandhi decided to launch the Civil Disobedience Movement.
- he Salt Satyagraha was launched on 6th April 1930 at Dandi. It was a symbolic act by Gandhiji.
- The main objective was to break all unjust and oppressive laws of the British through peace and Satyagraha.
- Salt Satyagraha took place at Dharasana in Gujarat and at Wadala, Malvan and Shiroda in Maharashtra.
- The mill workers were on the forefront in the Solapur Satyagraha.
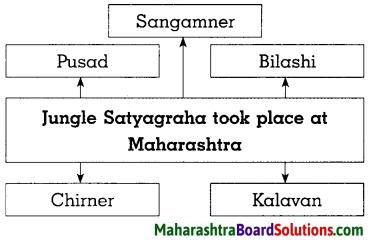
- The forest Satyagraha was undertaken at Bilashi, Sangamner, Kalavan, Chirner and Pusad by tribals in Maharashtra.
- In the Northwest Frontier Province, the Satyagraha was organised under the leadership of Khan Abdul Gafar Khan.
- The satyagrahis in Mumbai obstructed the trucks loaded with foreign goods.
- Women also participated in large numbers.
- This movement reached urban as well as the rural areas, thus making it a national movement.
![]()
Question 2.
Write information of Dandi March.
Answer:
- Gandhiji decided to launch Civil Disobedience Movement to cancel unjust tax on salt and to end the monopoly of the British Government to manufacture of salt.
- Salt, an important ingredient in the food of common people, was chosen by Gandhiji.
- On 12th March 1930 he set out from Sabarmati ashram with his 7 followers.
- Gandhiji delivered speeches in the villages on his way to Dandi.
- Due to Gandhiji’s speech the message of Civil Disobedience spread everywhere and a favorable atmosphere was created.
- He appealed to the people to join the movement fearlessly.
- Covering a distance of 35 km, Gandhiji reached Dandi, a seashore, on 5th April 1930.
- On 6th April, he broke the salt act by picking up the salt lying on the seashore.
- With this, the Civil Disobedience Movement started all over the country.
Question 3.
Do you feel Gandhiji’s Civil Disobedience technique can be used in present times?
Answer:
- Gandhiji opposed the unjust and oppressive laws of the British and broke them through peace and Satyagraha.
- I strongly feel India needs such ways in present times. Political parties and organisations call for strike or start a movement against decisions of government.
- They resort to unconstitutional acts such as stopping the vehicles, vandalising public property, setting objects on fire and starting riots.
- They destroy property of the nation by involving in all this anti-social activities. Innocent people get killed.
- It brings development to a halt, creates a divide in society.
- The feeling of unity, co-operation and tolerance remains no more. Society becomes unsafe.
- Therefore, I feel that even today the nation requires technique of Civil Disobedience.