Functions Class 11 Commerce Maths 1 Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce Maths Solution Book Pdf Chapter 2 Functions Ex 2.1 Questions and Answers.
Std 11 Maths 1 Exercise 2.1 Solutions Commerce Maths
Question 1.
Check if the following relations are functions.
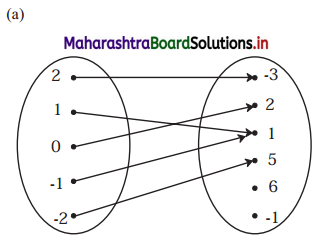
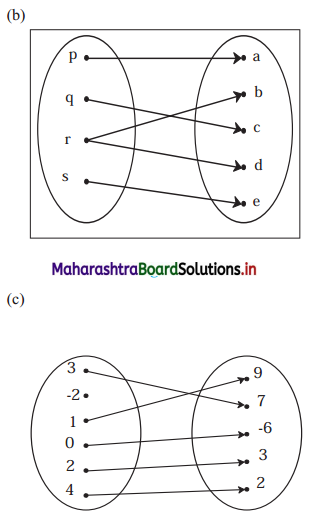
Solution:
(a) Yes
Reason: Every element of set A has been assigned a unique element in set B.
(b) No
Reason: An element of set A has been assigned more than one element from set B.
(c) No
Reason: Not every element of set A has been assigned an image from set B.
![]()
Question 2.
Which sets of ordered pairs represent functions from A = {1, 2, 3, 4} to B = {-1, 0, 1, 2, 3}? Justify.
(i) {(1, 0), (3, 3), (2, -1), (4, 1), (2, 2)}
(ii) {(1, 2), (2, -1), (3, 1), (4, 3)}
(iii) {(1, 3), (4, 1), (2, 2)}
(iv) {(1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1)}
Solution:
(i) {(1, 0), (3, 3), (2, -1), (4, 1), (2, 2)} does not represent a function.
Reason: (2, -1) and (2, 2) show that element 2 ∈ A has been assigned two images -1 and 2 from set B.
(ii) {(1, 2), (2, -1), (3, 1), (4, 3)} represents a function.
Reason: Every element of set A has a unique image in set B.
(iii) {(1, 3), (4, 1), (2, 2)} does not represent a function.
Reason: 3 ∈ A does not have an image in set B.
(iv) {(1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1)} represents a function
Reason: Every element of set A has been assigned a unique image in set B.
Question 3.
If f(m) = m2 – 3m + 1, find
(i) f(0)
(ii) f(-3)
(iii) f(\(\frac{1}{2}\))
(iv) f(x + 1)
(v) f(-x)
Solution:
f(m) = m2 – 3m + 1
(i) f(0) = 02 – 3(0) + 1 = 1
(ii) f(-3) = (-3)2 – 3(-3) + 1
= 9 + 9 + 1
= 19
(iii) \(f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}-3\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)+1\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}-\frac{3}{2}+1\)
= \(\frac{1-6+4}{4}\)
= \(-\frac{1}{4}\)
(iv) f(x + 1) = (x + 1)2 – 3(x + 1) + 1
= x2 + 2x + 1 – 3x – 3 + 1
= x2 – x – 1
(v) f(-x) = (-x)2 – 3(-x) + 1 = x2 + 3x + 1
![]()
Question 4.
Find x, if g(x) = 0 where
(i) g(x) = \(\frac{5 x-6}{7}\)
(ii) g(x) = \(\frac{18-2 x^{2}}{7}\)
(iii) g(x) = 6x2 + x – 2
Solution:
(i) g(x) = \(\frac{5 x-6}{7}\)
g(x) = 0
∴ \(\frac{5 x-6}{7}\) = 0
∴ 5x – 6 = 0
∴ x = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
(ii) g(x) = \(\frac{18-2 x^{2}}{7}\)
g(x) = 0
∴ \(\frac{18-2 x^{2}}{7}\) = 0
∴ 18 – 2x2 = 0
∴ x2 = 9
∴ x = ±3
(iii) g(x) = 6x2 + x – 2
g(x) = 0
∴ 6x2 + x – 2 = 0
∴ 6x2 + 4x – 3x – 2 = 0
∴ 2x(3x + 2) – 1(3x + 2) = 0
∴ (2x – 1)(3x + 2) = 0
∴ 2x – 1 = 0 or 3x + 2 = 0
∴ x = \(\frac{1}{2}\) or x = \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
Question 5.
Find x, if f(x) = g(x) where f(x) = x4 + 2x2, g(x) = 11x2.
Solution:
f(x) = x4 + 2x2, g(x) = 11x2
f(x) = g(x)
∴ x4 + 2x2 = 11x2
∴ x4 – 9x2 = 0
∴ x2(x2 – 9) = 0
∴ x2 = 0 or x2 – 9 = 0
∴ x = 0 or x2 = 9
∴ x = 0 or x = ±3
![]()
Question 6.
If f(x) = \(\begin{cases}x^{2}+3, & x \leq 2 \\ 5 x+7, & x>2\end{cases}\), then find
(i) f(3)
(ii) f(2)
(iii) f(0)
Solution:
f(x) = x2 + 3, x ≤ 2
= 5x + 7, x > 2
(i) f(3) = 5(3) + 7 = 15 + 7 = 22
(ii) f(2) = 22 + 3 = 4 + 3 = 7
(iii) f(0) = 02 + 3 = 3
Question 7.
If f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{cl}
4 x-2, & x \leq-3 \\
5, & -3<x<3 \\
x^{2}, & x \geq 3
\end{array}\right.\), then fmd
(i) f(-4)
(ii) f(-3)
(iii) f(1)
(iv) f(5)
Solution:
f(x) = 4x – 2, x ≤ -3
= 5, -3 < x < 3
= x2, x ≥ 3
(i) f(-4) = 4(-4) – 2 = -16 – 2 = -18
(ii) f(-3) = 4(-3) – 2 = -12 – 2 = -14
(iii) f(1) = 5
(iv) f(5) = 52 = 25
![]()
Question 8.
If f(x) = 3x + 5, g(x) = 6x – 1, then find
(i) (f + g)(x)
(ii) (f – g)(2)
(iii) (fg)(3)
(iv) \(\left(\frac{\mathbf{f}}{\mathbf{g}}\right)(x)\) and its domain
Solution:
f(x) = 3x + 5, g(x) = 6x – 1
(i) (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x)
= 3x + 5 + 6x – 1
= 9x + 4
(ii) (f – g) (2) = f(2) – g(2)
= [3(2) + 5] – [6(2) – 1]
= 6 + 5 – 12 + 1
= 0
(iii) (fg)(3) = f(3) g(3)
= [3(3) + 5] [6(3) – 1]
= (14) (17)
= 238
(iv) \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{f}}{\mathrm{g}}\right) x=\frac{\mathrm{f}(x)}{\mathrm{g}(x)}=\frac{3 x+5}{6 x-1}, x \neq \frac{1}{6}\)
Domain = R – {\(\frac{1}{6}\)}
Question 9.
If f(x) = 2x2 + 3, g(x) = 5x – 2, then find
(i) fog
(ii) gof
(iii) fof
(iv) gog
Solution:
f(x) = 2x2 + 3, g(x) = 5x – 2
(i) (fog)(x) = f(g(x))
= f(5x – 2)
= 2(5x – 2)2 + 3
= 2(25x2 – 20x + 4) + 3
= 50x2 – 40x + 8 + 3
= 50x2 – 40x + 11
(ii) (gof)(x) = g(f(x))
= g(2x2 + 3)
= 5(2x2 + 3) – 2
= 10x2 + 15 – 2
= 10x2 + 13
![]()
(iii) (fof)(x) = f(f(x))
= f(2x2 + 3)
= 2(2x2 + 3)2 + 3
= 2(4x4 + 12x2 + 9) + 3
= 8x4 + 24x2 + 18 + 3
= 8x4 + 24x2 + 21
(iv) (gog)(x) = g(g(x))
= g(5x – 2)
= 5(5x – 2) – 2
= 25x – 10 – 2
= 25x – 12
Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce Maths
- Sets and Relations Ex 1.1 11th Commerce Maths
- Sets and Relations Ex 1.2 11th Commerce Maths
- Sets and Relations Miscellaneous Exercise 1 11th Commerce Maths
- Functions Ex 2.1 11th Commerce Maths
- Functions Miscellaneous Exercise 2 11th Commerce Maths
- Complex Numbers Ex 3.1 11th Commerce Maths
- Complex Numbers Ex 3.2 11th Commerce Maths
- Complex Numbers Ex 3.3 11th Commerce Maths
- Complex Numbers Miscellaneous Exercise 3 11th Commerce Maths