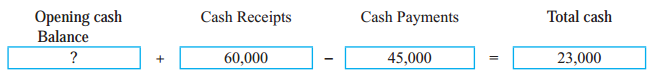
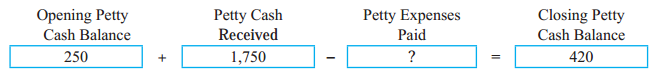
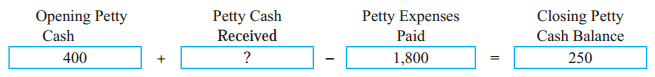
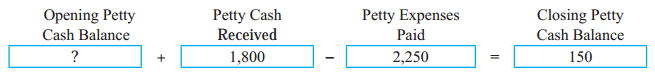
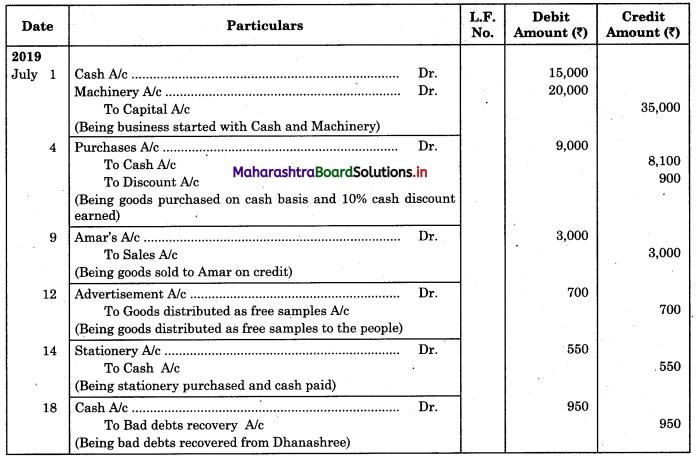
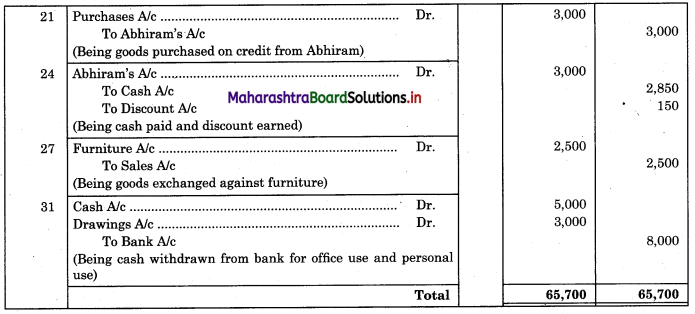
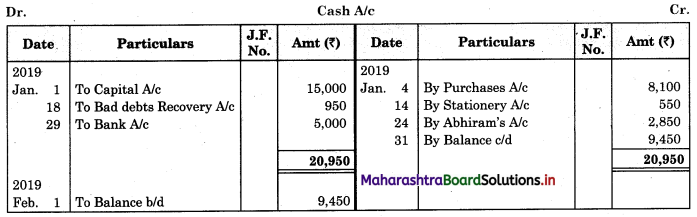
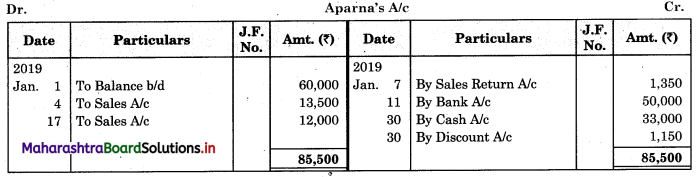
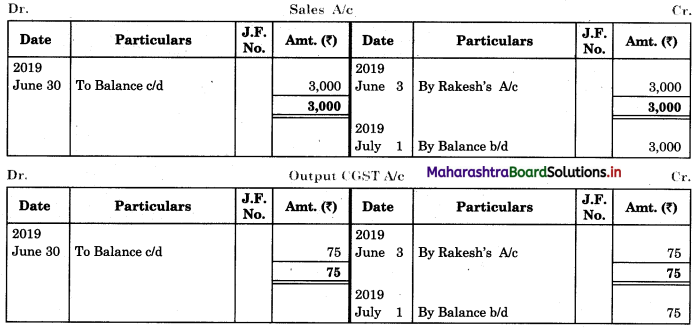
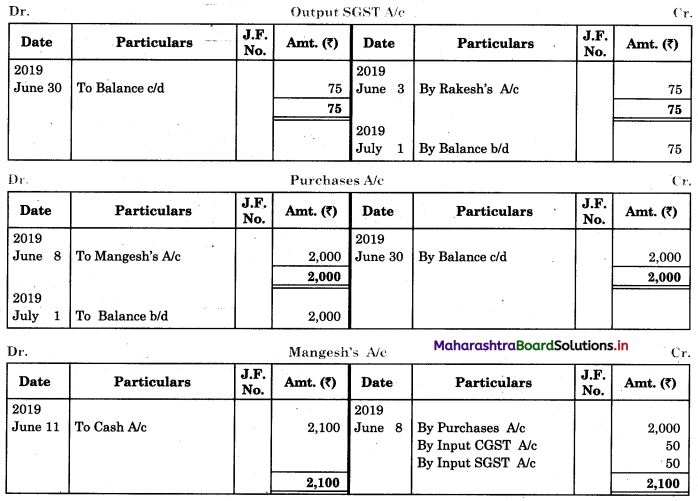
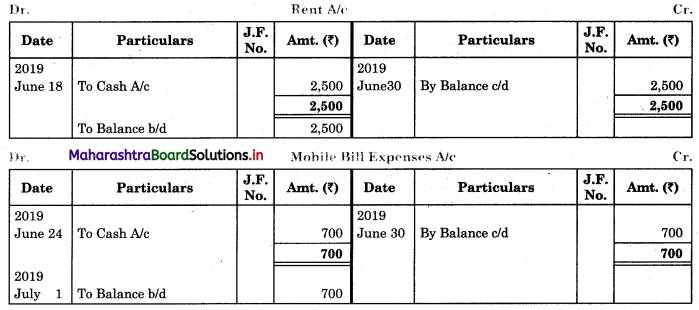
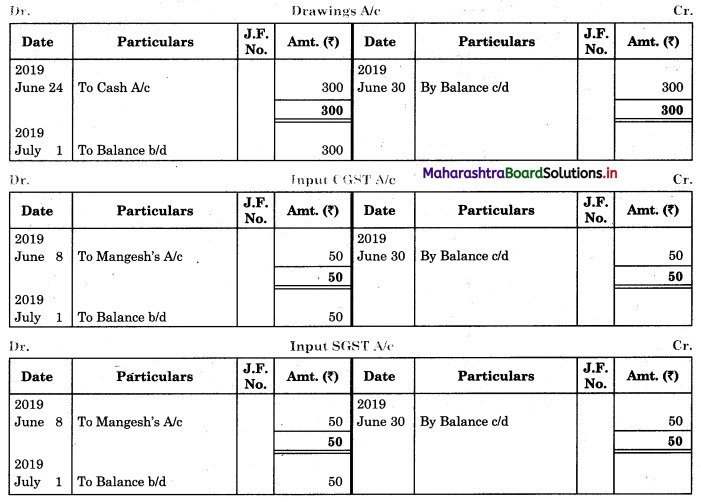
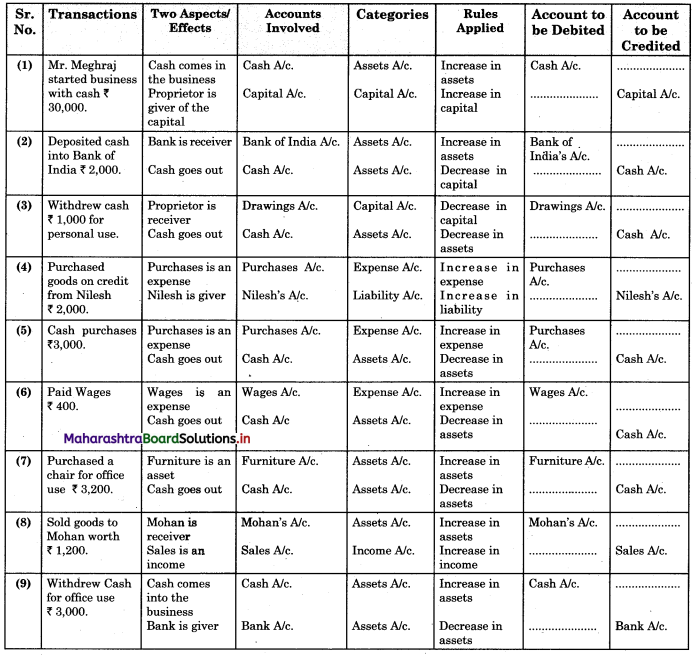
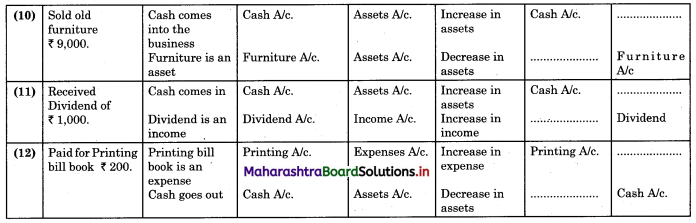
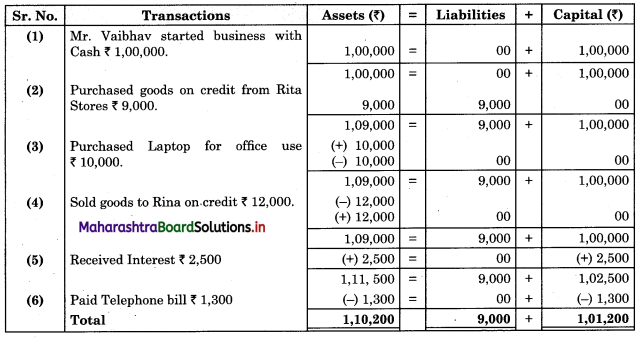
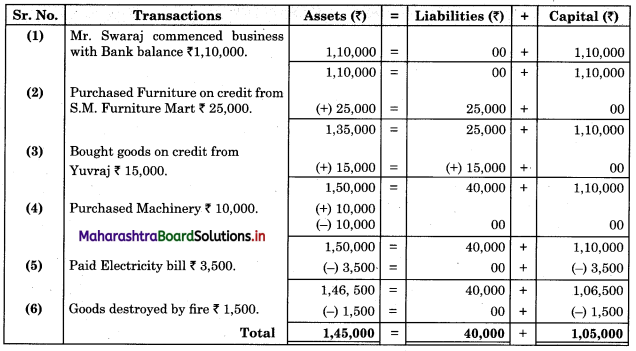
Bank Reconciliation Statement 11th BK Commerce Chapter 6 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Bookkeeping and Accountancy 11th Solutions Chapter 6 Bank Reconciliation Statement Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 11 Commerce BK Chapter 6 Exercise Solutions
1. Answer in one sentence.
Question 1.
Who prepares a bank Pass Book?
Answer:
The Bank passbook is prepared by the bank.
Question 2.
What is a pay-in-slip?
Answer:
Pay-in-slip is the slip that is filled when the bank account holder deposits a cheque or cash into his bank account.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a bank overdraft?
Answer:
The amount withdrawn by the account holder from his current account in excess of the balance standing in that account up to, specified limit is known as bank overdraft.
Question 4.
What is a withdrawal slip?
Answer:
It is a document/form, which is used by the savings account holder for withdrawing cash from his bank account.
Question 5.
Who sends the bank statement?
Answer:
A bank statement is sent by the Bank manager to the account holder informing about debit or credit given by the bank.
Question 6.
What does a debit balance in Cash Book represent?
Answer:
The debit balance of the cash Book indicates a positive Bank balance as per Cash Book.
Question 7.
Who prepares the Bank Reconciliation Statement?
Answer:
A Businessman, trader, or accountant prepares Bank Reconciliation Statement at the end of every month.
![]()
Question 8.
What does the debit balance in Pass Book represent?
Answer:
The debit balance of Passbook represents Overdraft as per passbook.
Question 9.
On which side is interest on bank deposit recorded in Pass Book?
Answer:
Interest on bank deposits is recorded on the credit side of the passbook.
Question 10.
Why is Bank Reconciliation Statement prepared?
Answer:
A bank reconciliation statement is prepared to disclose the causes of the difference between the balances shown by the cash book and passbook.
2. Give one word/term/phrase which can substitute each of the following statements:
Question 1.
The account on which overdraft facility is allowed by the bank.
Answer:
Current Account
Question 2.
Extract of ledger account of the account holder in the books of the bank.
Answer:
Pass Book
![]()
Question 3.
Alphanumeric code that facilitates electronic funds transfer in India.
Answer:
IFSC (Indian Financial System Code)
Question 4.
Statement showing the causes of disagreement between the balance of Cash Book and Pass Book.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement
Question 5.
Debit balance in Pass Book.
Answer:
Overdraft as per Pass Book
Question 6.
A form which is filled for depositing cash or cheque into bank.
Answer:
Pay-in-slip
Question 7.
The left-hand side of Pay-in-slip.
Answer:
Counterfoil
Question 8.
Credit balance in Cash Book.
Answer:
Overdraft as per Cash Book
![]()
Question 9.
A book maintained by traders to record banking transactions.
Answer:
Cash Book
Question 10.
Excess of bank deposits over withdrawals by a businessman in bank current account.
Answer:
Bank Balance (favourable balance)
3. Do you agree or disagree with the following statements:
Question 1.
The bank column of Cash Book represents the bank account.
Answer:
Agree
Question 2.
A bank statement enables the account holder to prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement.
Answer:
Agree
Question 3.
Cheques issued for payment but not presented to bank appear in Cash Book only.
Answer:
Agree
![]()
Question 4.
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared only during the year-end.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 5.
Bank Reconciliation Statement is similar to the bank statement.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 6.
Bank balance as per Cash Book is always equal to bank balance as per Pass Book.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 7.
Bank advice is sent by the businessman to the bank.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 8.
Pay-in-slip is used for depositing cheques into banks.
Answer:
Agree
Question 9.
The difference in Cash Book Balance and Pass Book balance may arise due to errors committed while recording.
Answer:
Agree
![]()
Question 10.
Payment and receipt of cash through internet banking generate an automatic proof.
Answer:
Agree
4. Select the most appropriate alternative from those given and rewrite the following statements:
Question 1.
Overdraft means ____________ balance of Cash Book.
(a) closing
(b) debit
(c) opening
(d) credit
Answer:
(d) credit
Question 2.
When a cheque is deposited and collected by bank Pass Book is ____________
(a) dishonoured
(b) debited
(c) credited
(d) written
Answer:
(c) credited
Question 3.
A ____________ is a summary of financial transactions that take place over a period of time on a bank account.
(a) withdrawal slip
(b) bank advice
(c) bank statement
(d) Pay-in-slip
Answer:
(c) bank statement
Question 4.
Debiting an entry in Cash Book ____________ cash balance.
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) nullifies
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) increases
Question 5.
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared by ____________
(a) student
(b) businessman
(c) bank
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) businessman
![]()
Question 6.
Bank balance as per Pass Book means ____________ balance of Pass Book.
(a) credit
(b) opening
(c) debit
(d) closing
Answer:
(a) credit
Question 7.
Bank gives overdraft facility to ____________ account holder.
(a) savings
(b) recurring
(c) current
(d) fixed
Answer:
(c) current
Question 8.
Debit balance as per Cash Book is also known as ____________ balance.
(a) favourable
(b) overdraft
(c) abnormal
(d) unfavourable
Answer:
(a) favourable
Question 9.
When extracts of Cash Book and Pass Book are given for uncommon periods, only ____________ items are considered for preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement.
(a) uncommon
(b) normal
(c) favourable
(d) common
Answer:
(d) common
![]()
Question 10.
When extract of Cash Book and Pass Book is given for common period, only ____________ items are considered
for preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement.
(a) uncommon
(b) common
(c) favourable
(d) unfavourable
Answer:
(a) uncommon
5. Complete the following statements:
Question 1.
Payments credited in Cash Book are ____________ in Pass Book.
Answer:
Debited
Question 2.
While preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement only ____________ column of Cash Book is considered.
Answer:
Bank
Question 3.
Cheques issued to creditors appear first in ____________ book.
Answer:
Cash
Question 4.
A statement showing the reasons for the difference in Cash Book Balance and Pass Book balance is known as ____________
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement
Question 5.
Overcast on receipt side of Pass Book means ____________ in Pass Book balance.
Answer:
Increase
Question 6.
Online transfer made to our creditors appear on the ____________ side of Cash Book.
Answer:
Payment/Credit
![]()
Question 7.
Interest on overdraft charged by bank is ____________ in Pass Book.
Answer:
Debited
Question 8.
Normally the Cash Book shows debit balance and Pass Book shows ____________ balance.
Answer:
Credit
Question 9.
The form filled for withdrawing cash from bank is known as ____________
Answer:
Withdrawal Slip
Question 10.
A businessman can update his records on receiving ____________
Answer:
Bank Advice
6. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons:
Question 1.
Cheques deposited into the bank but not yet cleared appears in the Pass Book only.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Cheques deposited into the bank but not yet cleared appears in the cash book only. Bank records entry in the passbook only after the cheque is cleared. So there is no entry for this transaction in the Pass Book.
Question 2.
Direct deposit made by debtors into a businessman’s bank account is recorded on the credit side of Pass Book.
Answer:
This statement is True.
The credit side of the passbook means deposits made in the bank account. When direct deposits are made by debtors into a businessman’s bank account. It increases the bank balance and it is recorded on the credit side of Pass Book.
Question 3.
A businessman can prepare a Bank Reconciliation statement only with Cash Book Balance.
Answer:
This statement is False.
The businessman can prepare a Bank Reconciliation statement with the help of a cash book, bank column, and passbook. It is a comparison between the two to correct the differences. Both i.e. cash book and pass book/Bank statement are required to prepare a Bank Reconciliation statement.
![]()
Question 4.
When overdraft as per Cash Book is given, bank charges debited in Pass Book only are to be added.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Bank overdraft as per cash book means negative bank balance. The businessman has to pay the Bank. Bank charges are expenses for the business and this increases the amount payable to the bank so bank charges debited in the passbook only are to be added in the cash book.
Question 5.
Bank Statement is sent by Bank to the businessman.
Answer:
This statement is True.
A bank statement is a statement issued by the bank to the current account holder informing about the bank transactions during a particular period of time. Generally, it is issued every i.e. month. It gives details information about bank deposits and withdrawals etc.
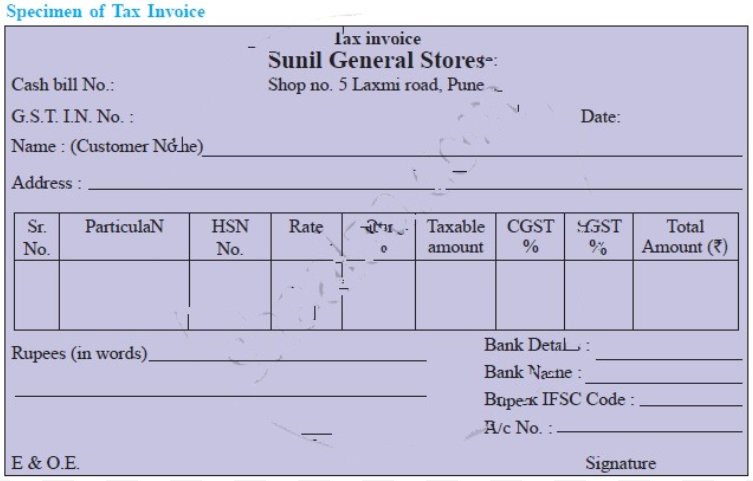
7. Draft the following specimen with imaginary Name, Account Number, Amount.
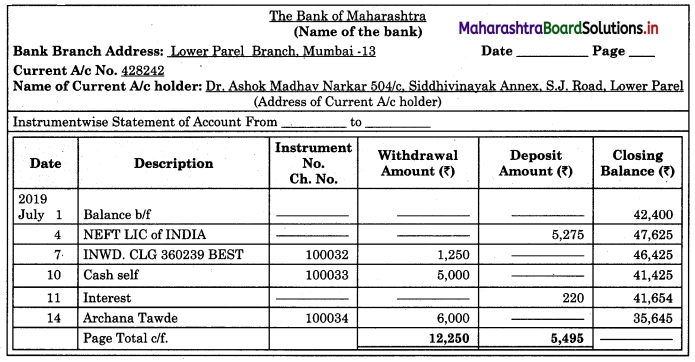
Question 1.
Bank Statement
Answer:
Specimen of Bank Statement is given below:
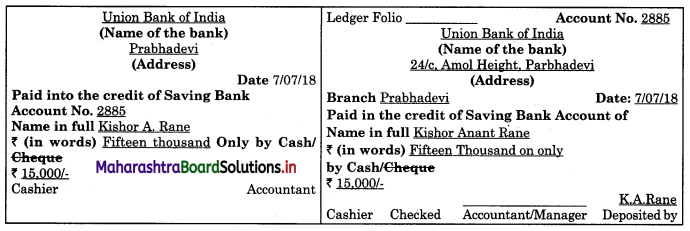
Question 2.
Pay-in-slip
Answer:
(a) Specimen of pay-in-slip is given below: Front side
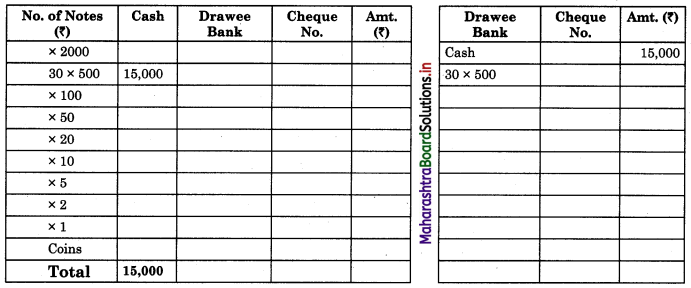
(b) Reverse (Back-side) of Pay-in-slip:
Question 3.
Withdrawal slip
Answer:
Specimen form of a withdrawal slip is given below:

![]()
Question 4.
Bank Advice
Answer:
Specimen of bank advice is given below:
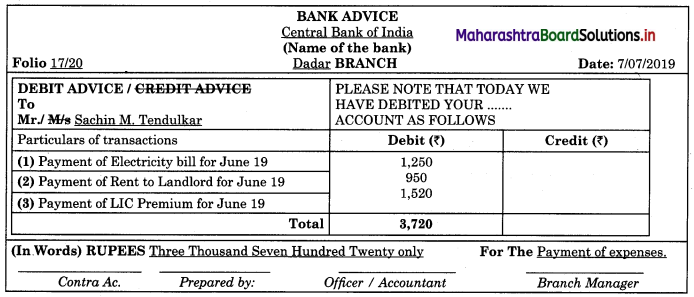
Question 5.
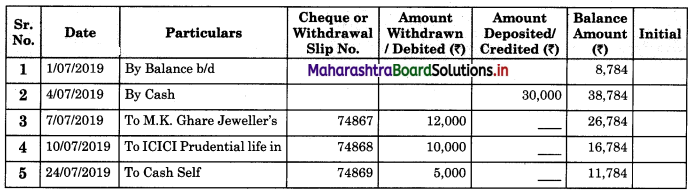
Pass Book
Answer:
Specimen form of the Bank passbook is given below:
Bank Pass Book
8. Correct and rewrite the following statements.
Question 1.
The form filled for depositing cash or cheque into the bank is known as Pass Book.
Answer:
The form filled for depositing cash or cheque into the bank is known as Pay in slip.
Question 2.
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared by Bank.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared by Businessman.
Question 3.
Debit balance as per Pass Book is known as favourable balance.
Answer:
Debit balance as per Pass Book is known as unfavorable balance.
Question 4.
When a cheque is deposited into Bank it is credited to Cashbook.
Answer:
When a cheque is deposited into Bank it is debited in Cash Book.
![]()
Question 5.
When extracts are given for the common period only common items are to be considered.
Answer:
When extracts are given for the common period only uncommon items are to be considered.
9. Complete the following table.
Question 1.
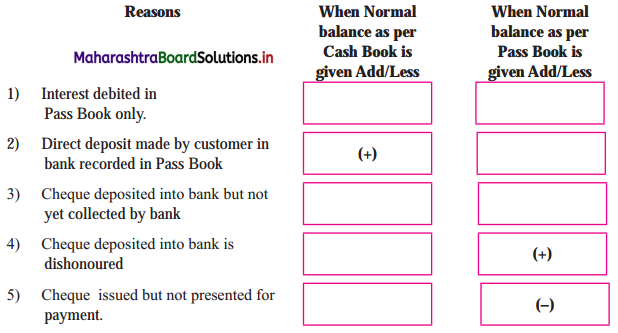
Answer:
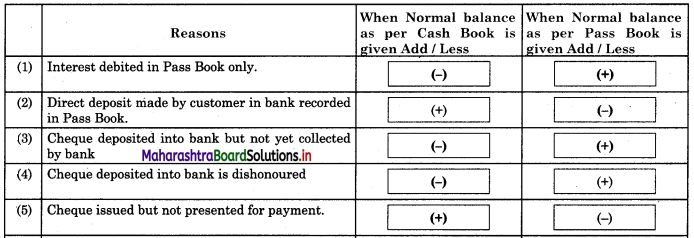
Practical Problems
Question 1.
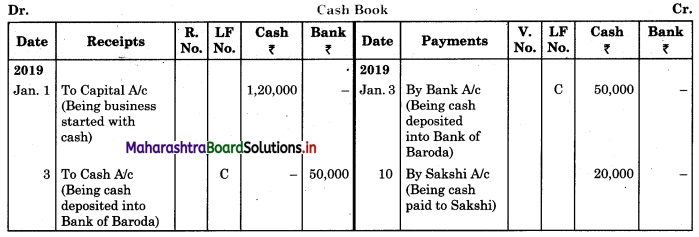
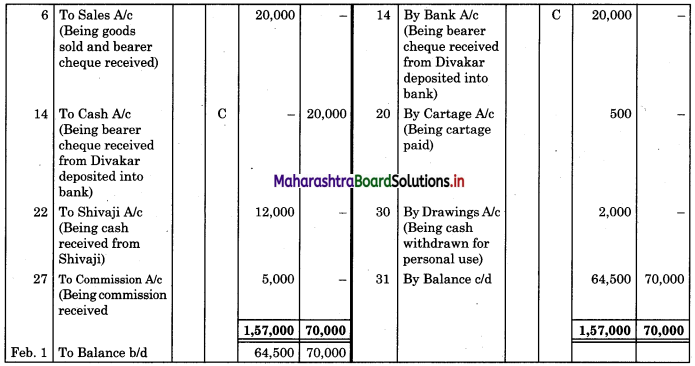
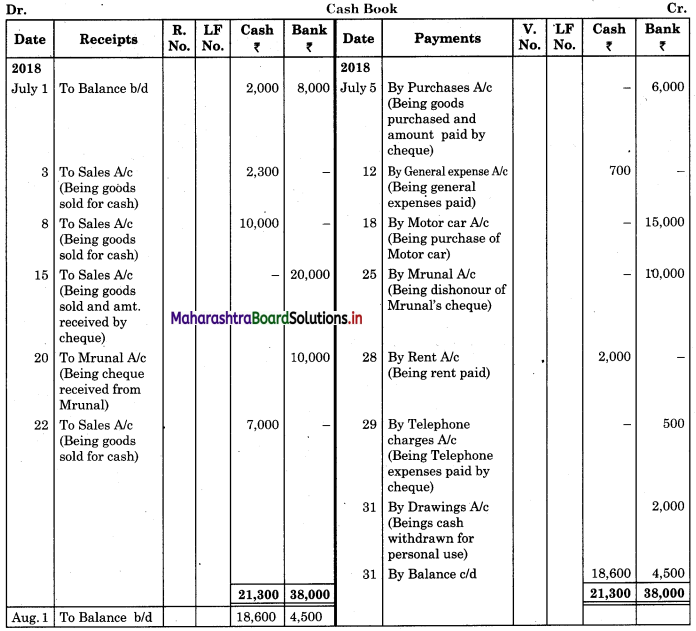
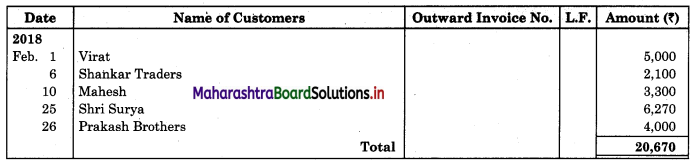
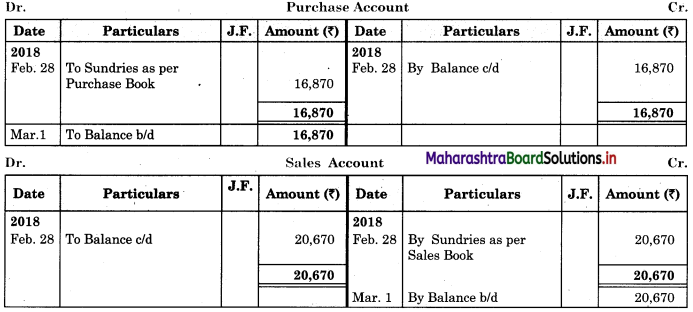
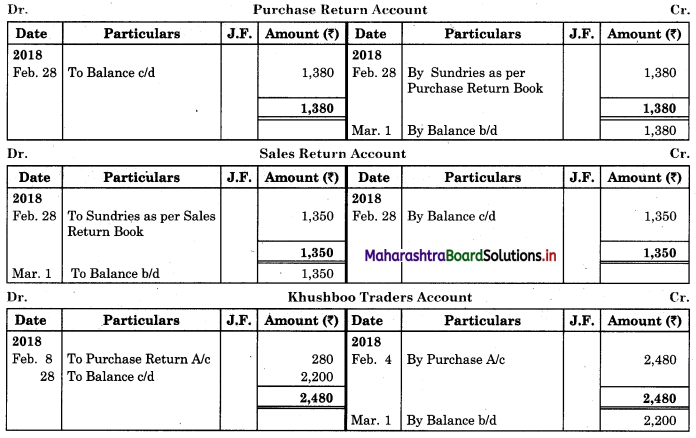
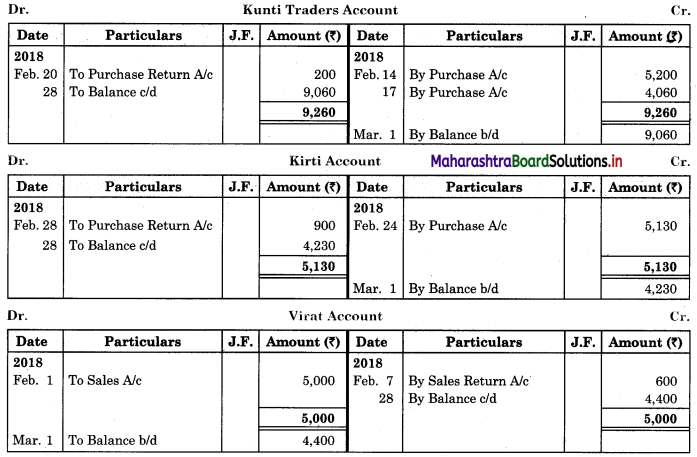
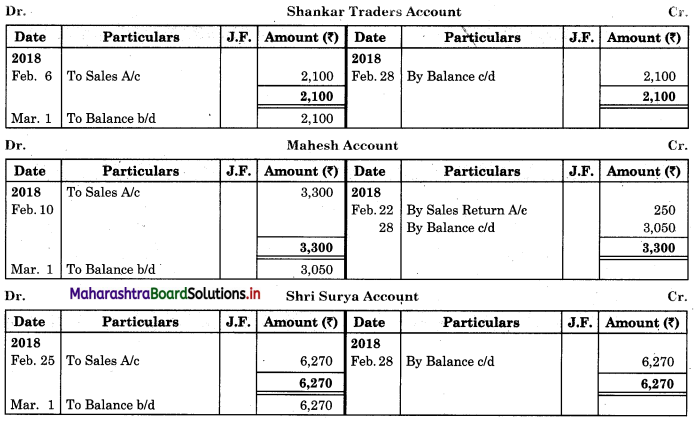
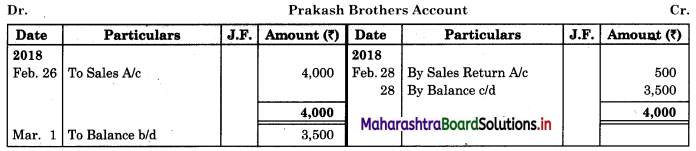
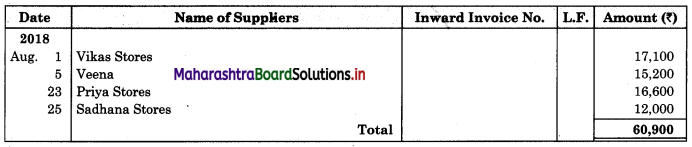
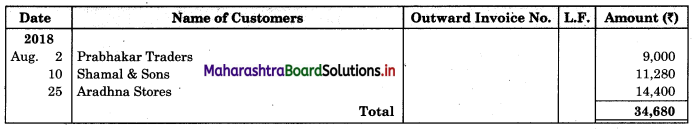
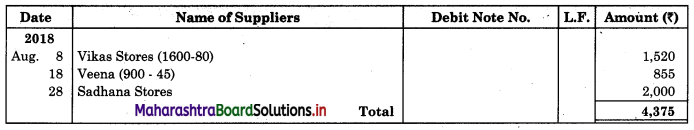
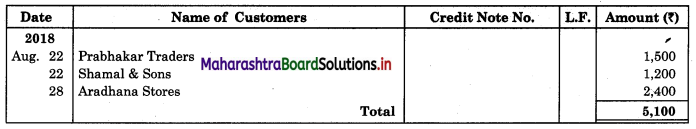
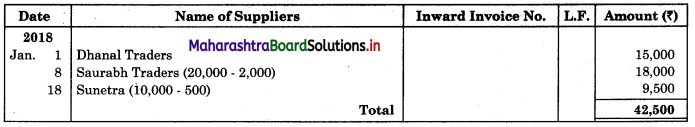
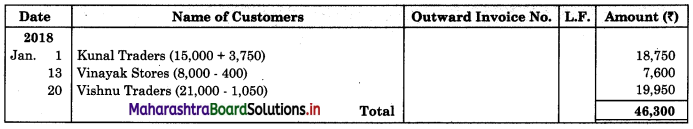
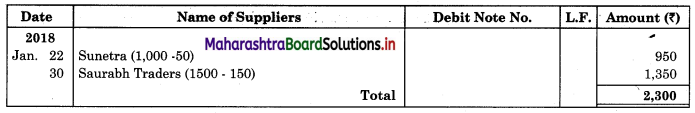
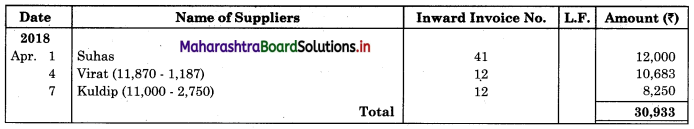
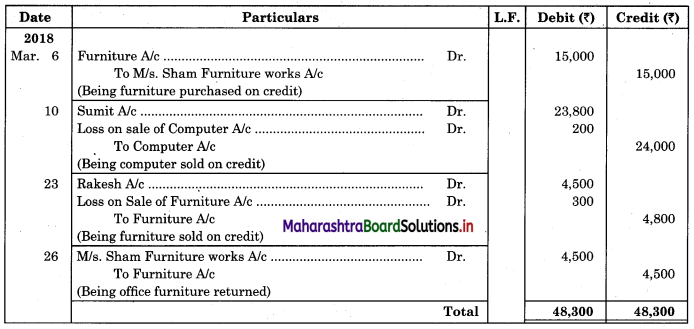
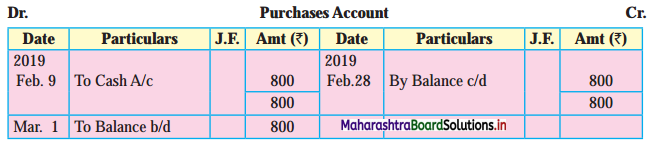
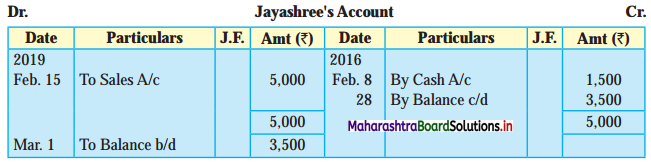
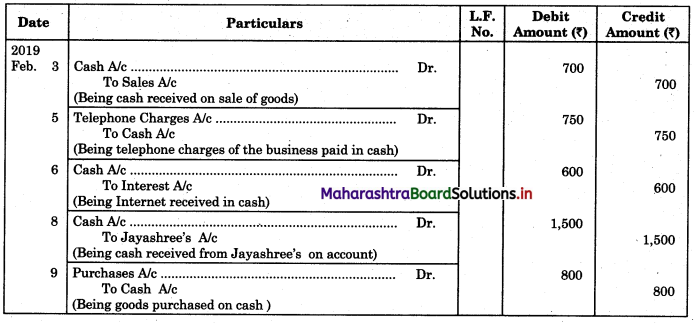
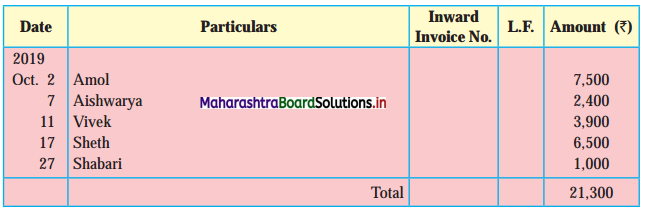
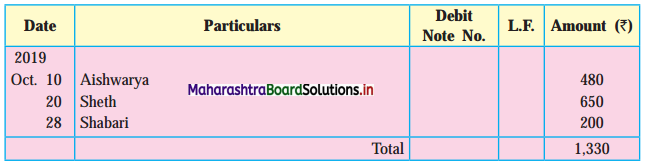
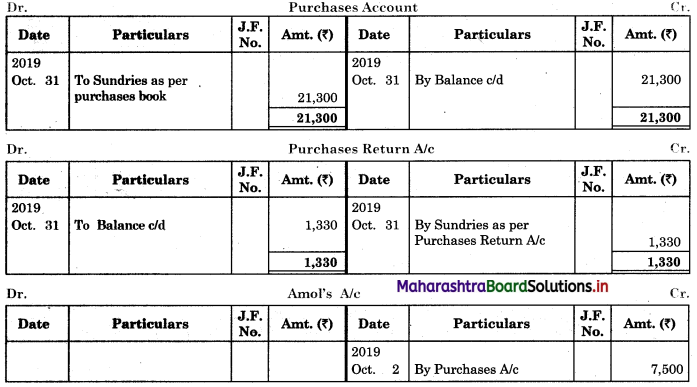
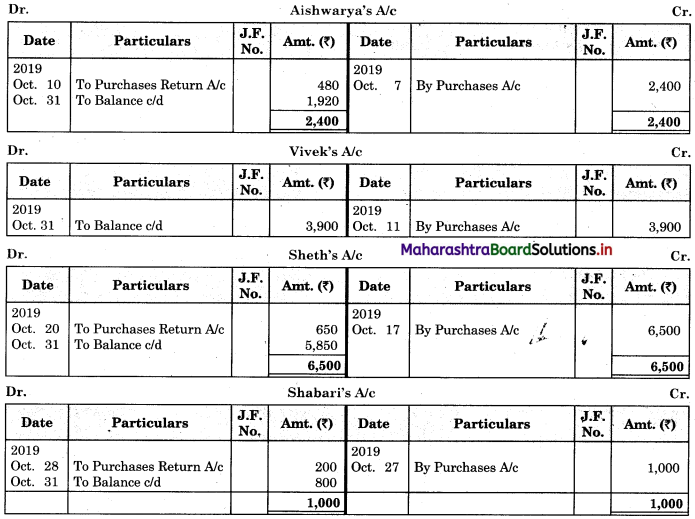
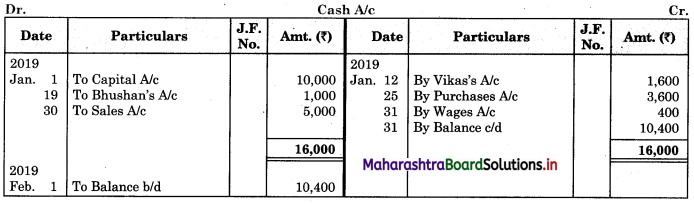
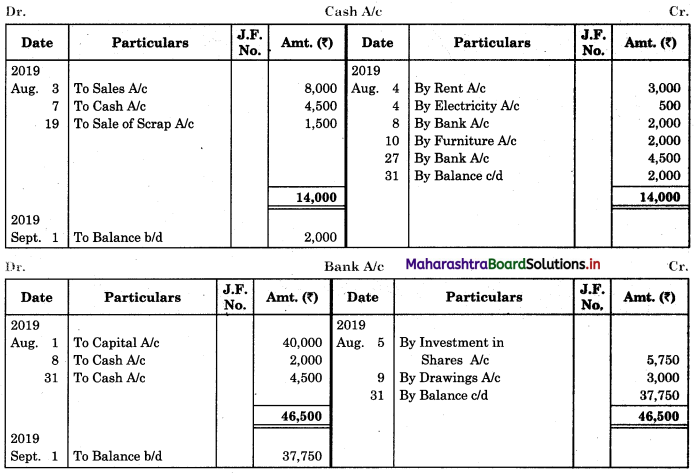
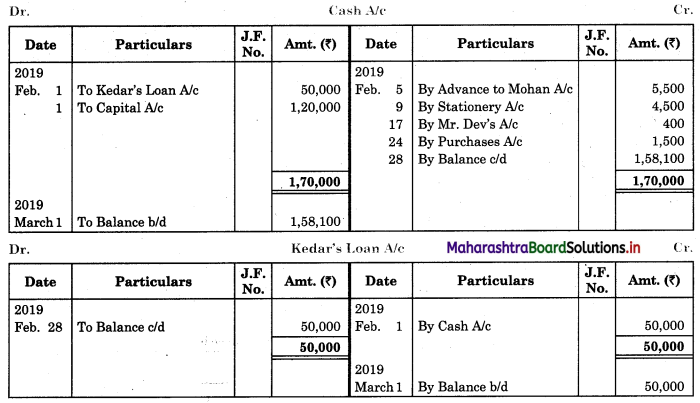
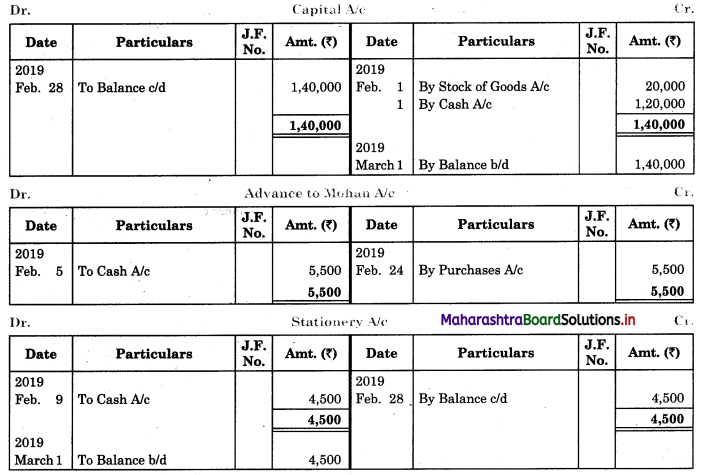
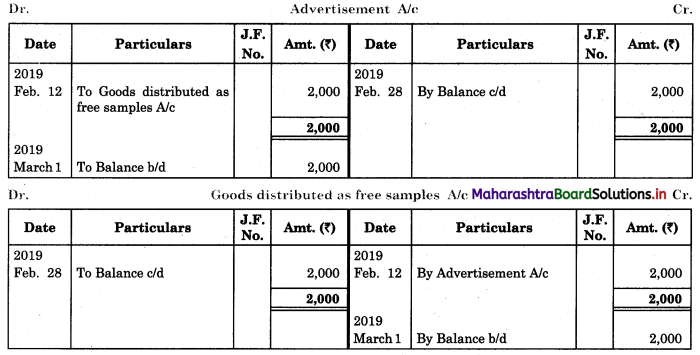
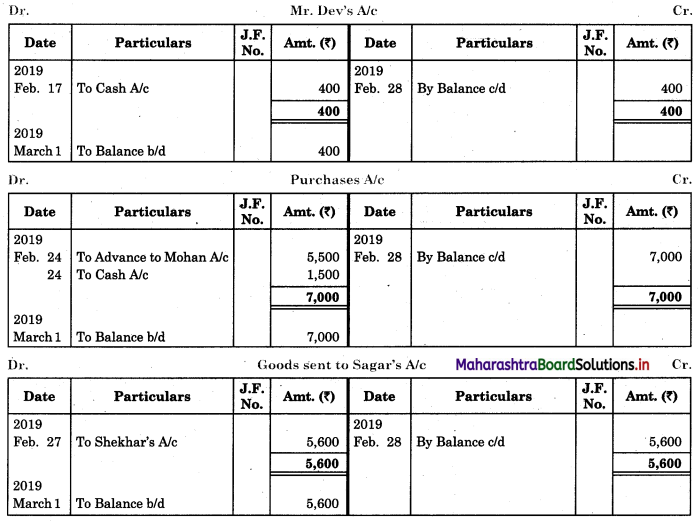
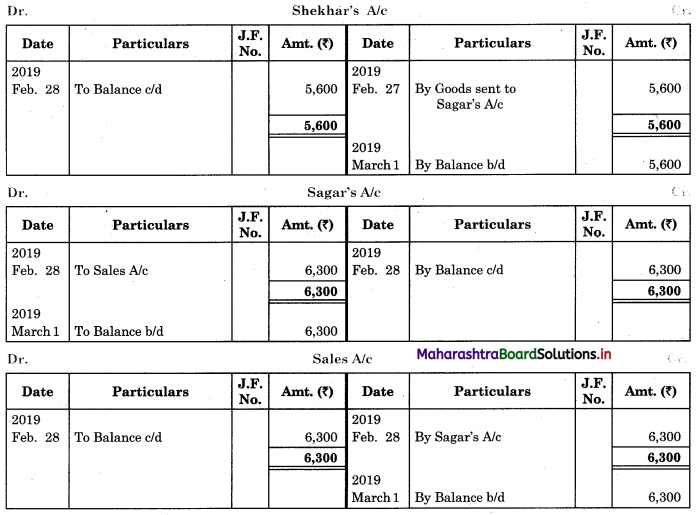
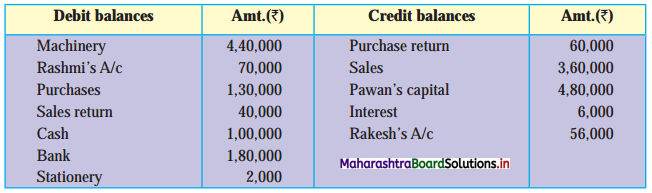
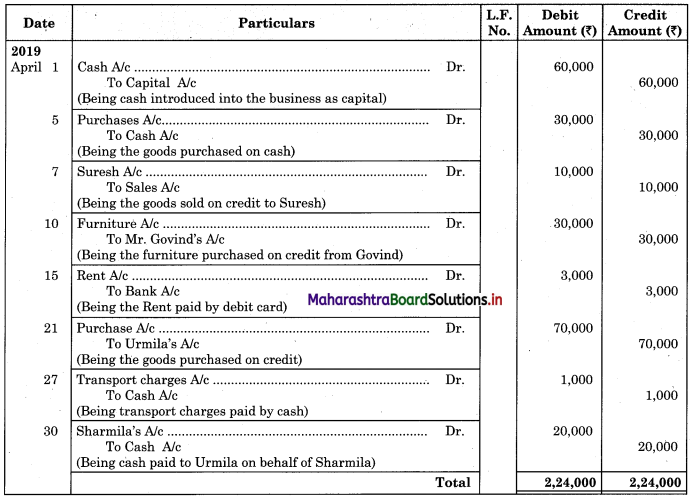
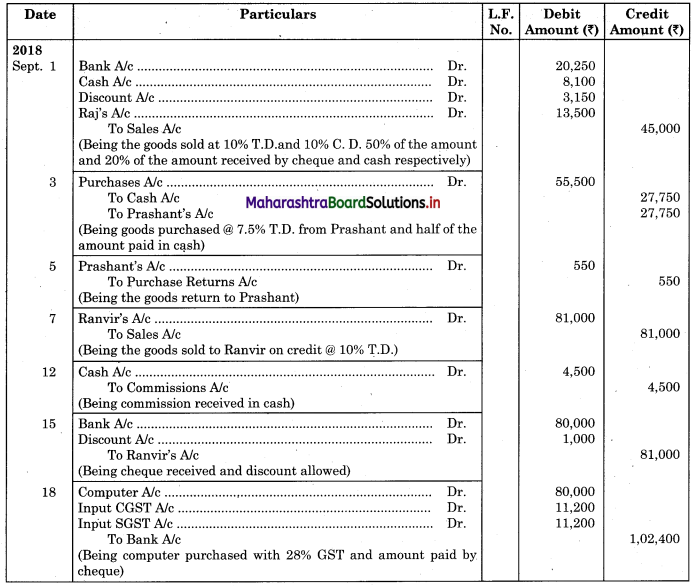
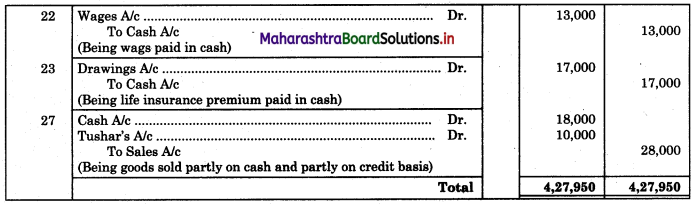
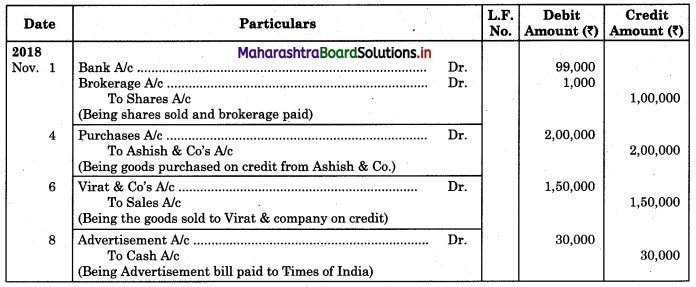
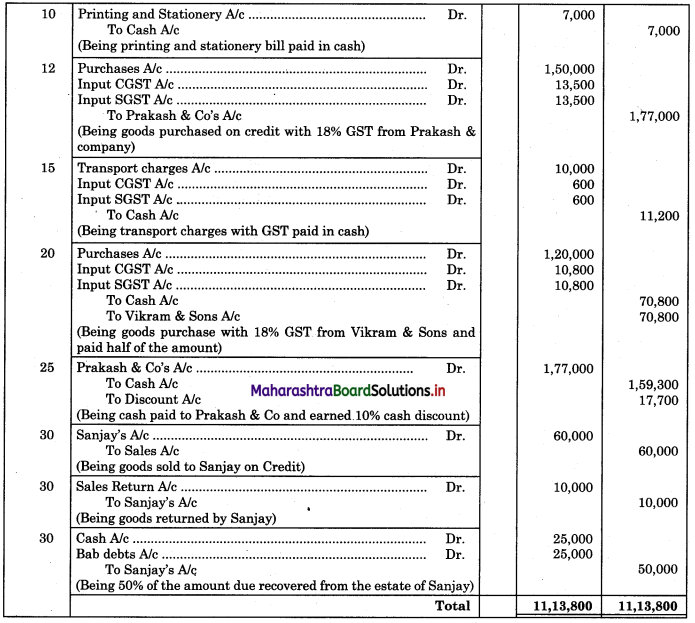
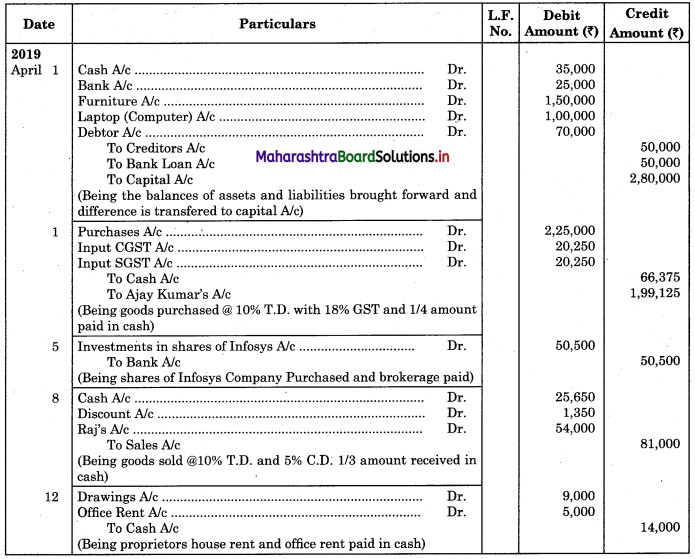
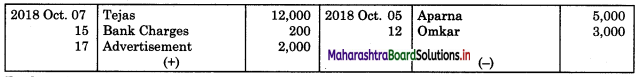
Following is the extract of the Cash Book (Bank Column only) and passbook. Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st Oct. 2018.
In the books of ____________
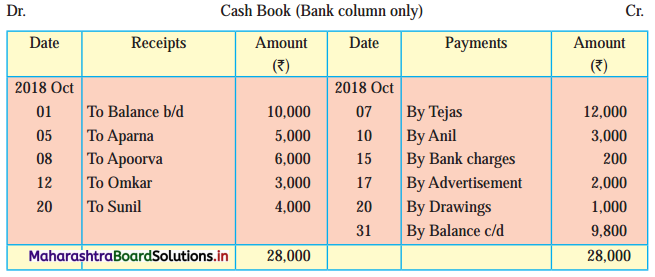
In the books of Bank
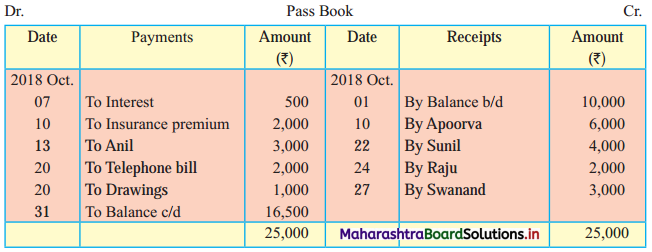
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st October 2018.
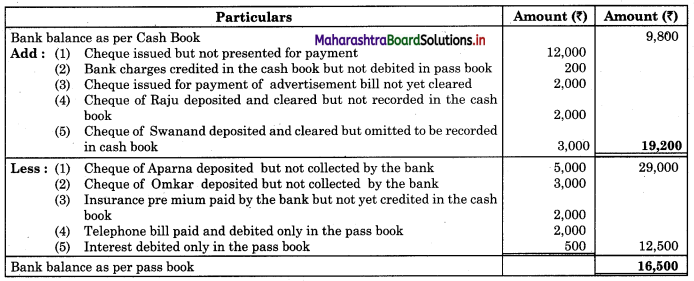
Working Notes:
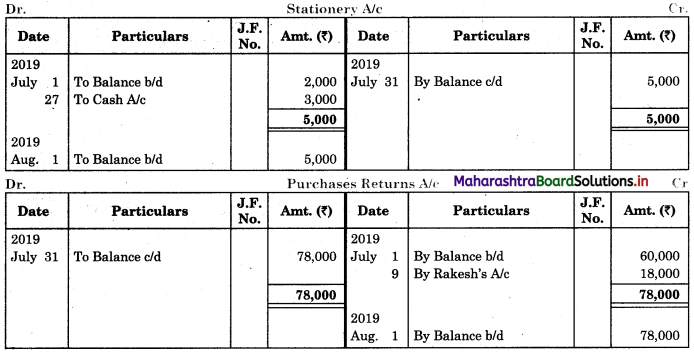
When extract of Cashbook and passbook are given for the same period i.e. for the month of April 2018, we have to consider only uncommon entries for adding and deducting from Bank Reconciliation Statement. This is shown in the following working notes.
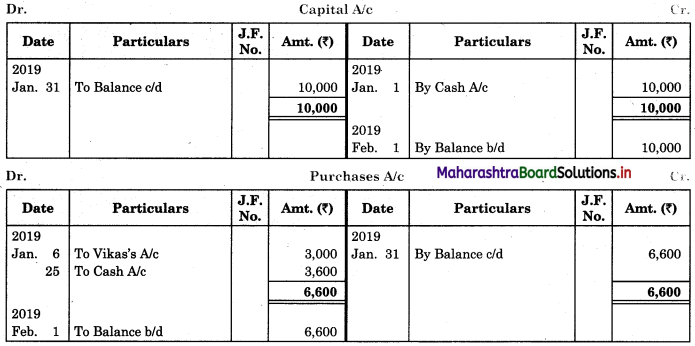
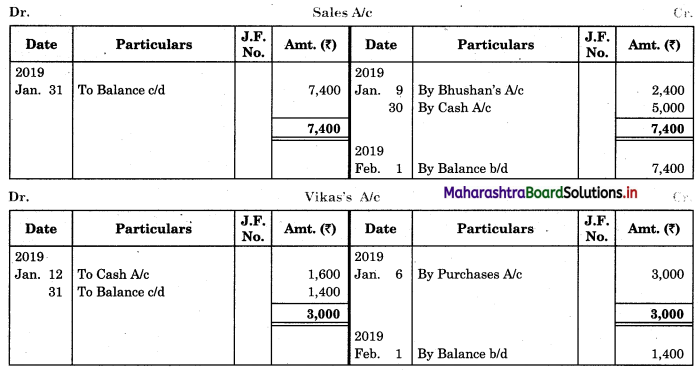
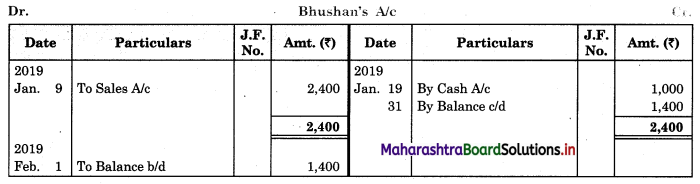
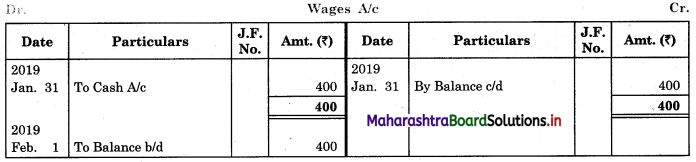
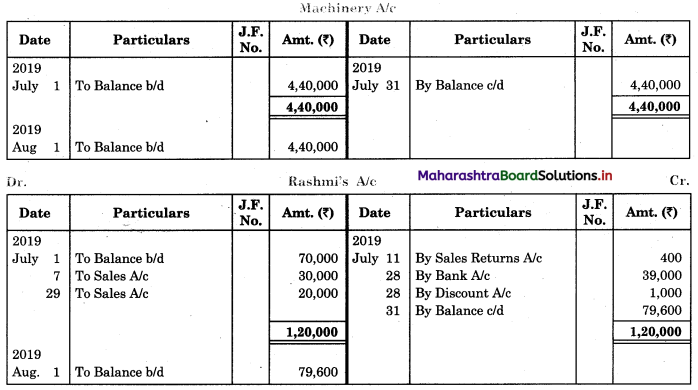
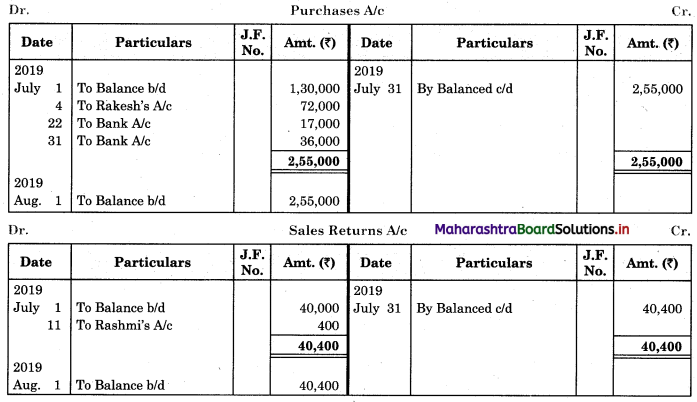
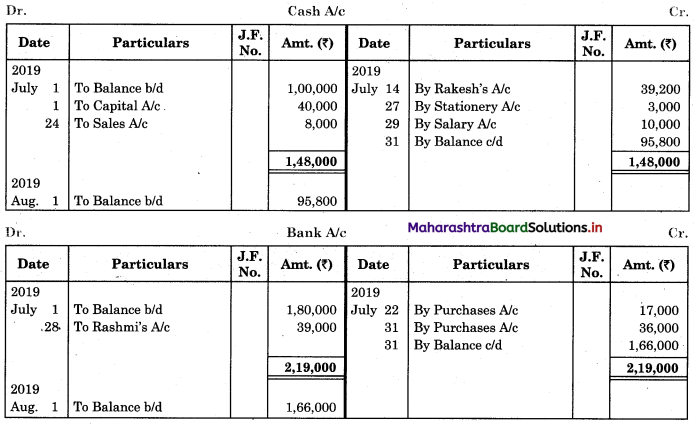
In order to find out items to be added and items to be deducted in the Bank Reconciliation Statement, we have to prepare Cash Book and passbook on the basis of accounting information given in the problem:
Cash Book
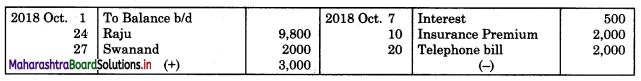
Bank Pass Book
![]()
Explanation:
1. First record the opening balance in the appropriate book i.e. either in Cashbook or passbook.
2. Bank balance of ₹ 9,800 as per Cashbook is recorded on the debit side of Cashbook in a box.
3. In this problem, the entries which are passed on the debit side of the Cashbook and passbook are to be added in the Bank Reconciliation Statement and the entries passed on the credit side of the Cashbook and passbook are to be deducted in the Bank Reconciliation Statement. This is because the opening balance appears on the debit side of the Cash Book.
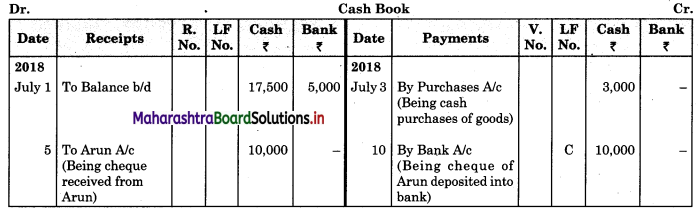
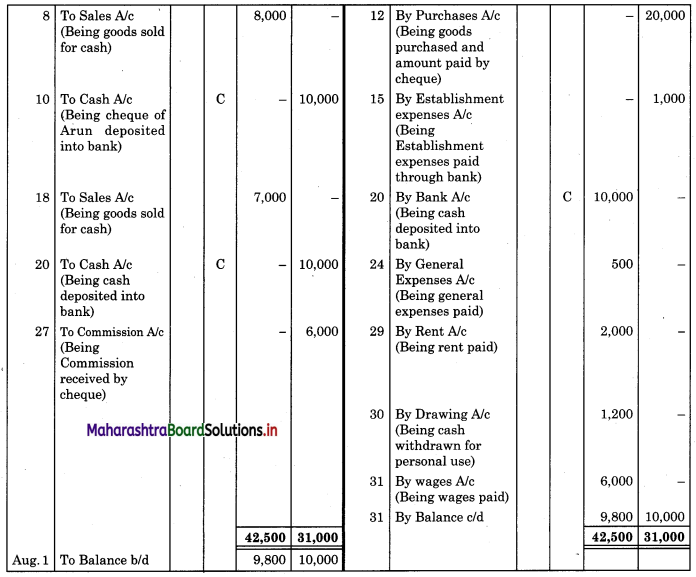
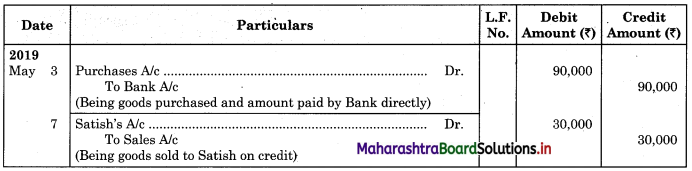
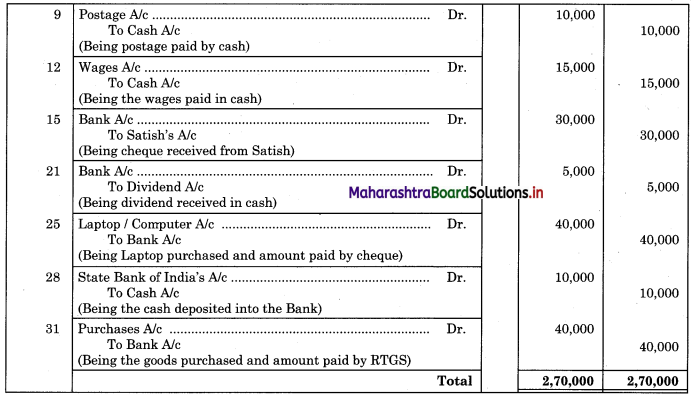
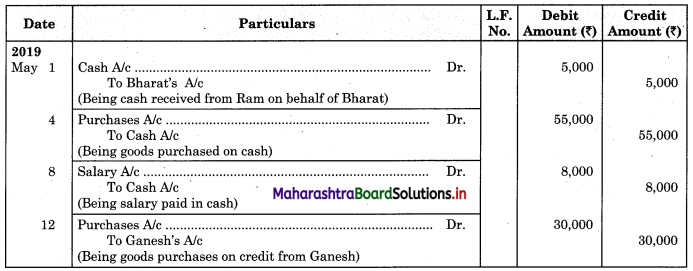
Question 2.
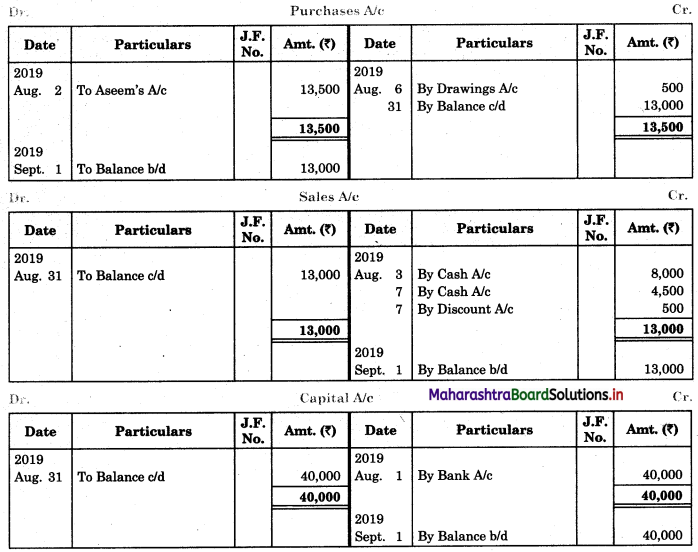
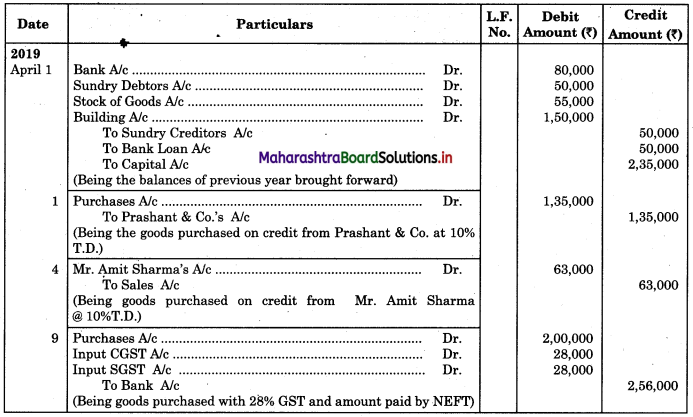
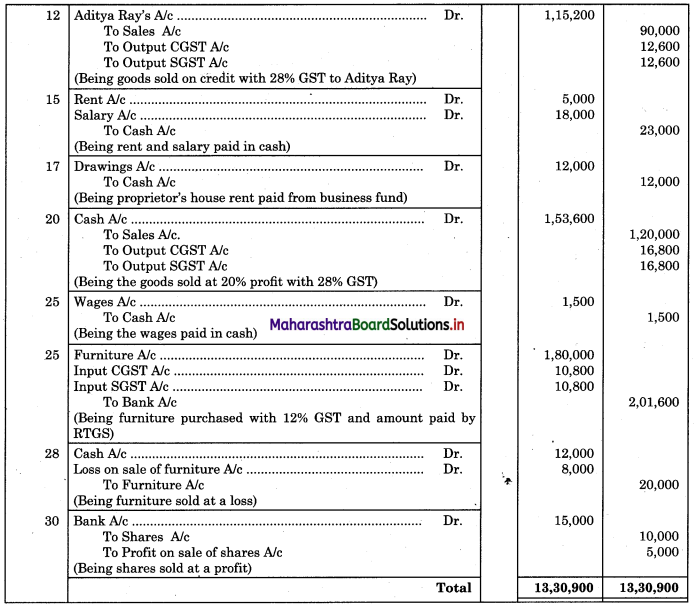
From the following extract of Cash Book and Pass Book prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st March 2019.
In the books of ____________
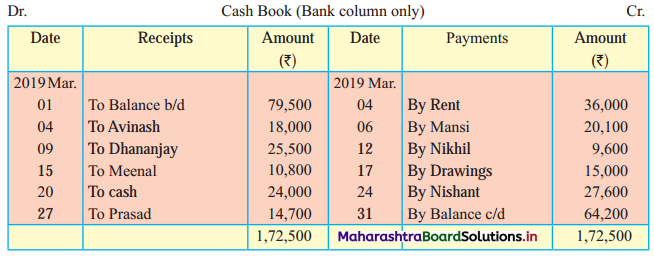
In the books of Bank
Bank Pass Book
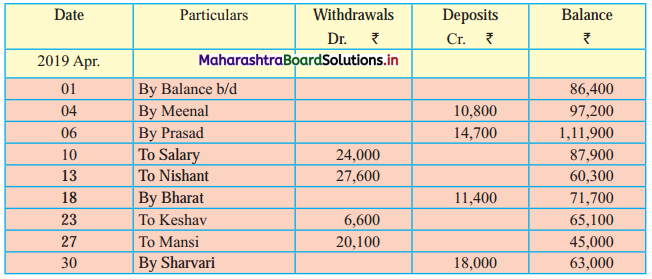
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st March 2019

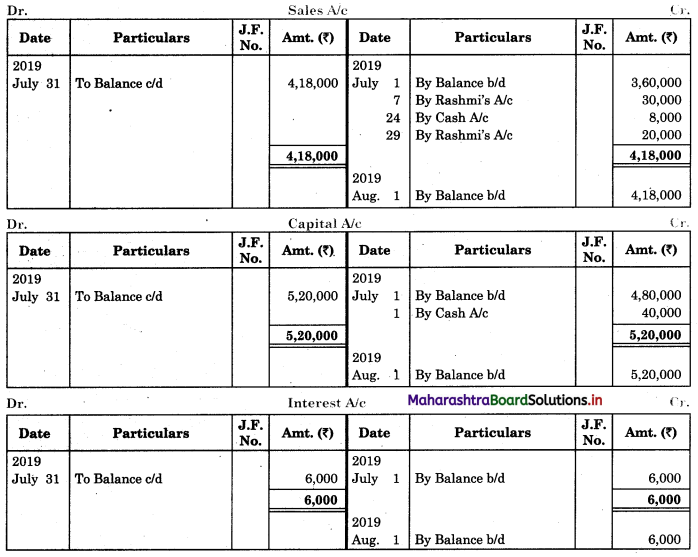
Working Notes:
When extract of Cashbook and passbook are given for the same period i.e. for the month of April 2011, we have to consider only uncommon entries for adding and deducting from Bank Reconciliation Statement. This is shown in the following working notes.
In order to find out items to be added and items to be deducted in the Bank Reconciliation Statement, we have to prepare Cash Book and passbook on the basis of accounting information given in the problem:
Cash Book
![]()
Bank Pass Book

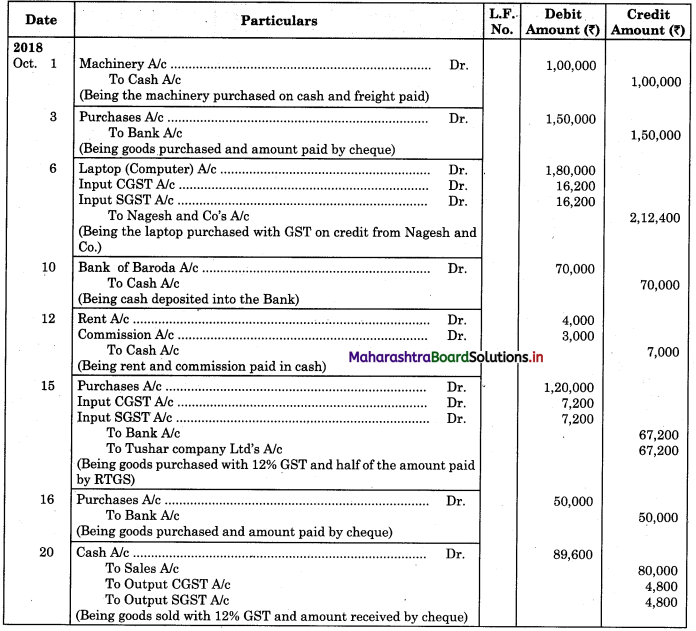
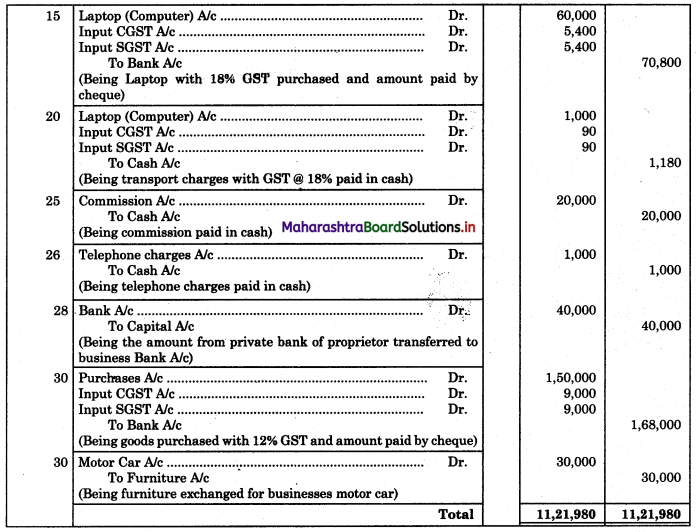
Question 3.
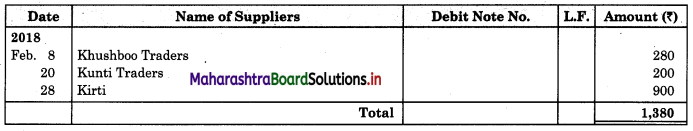
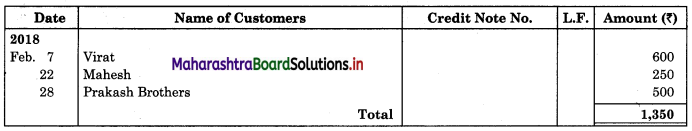
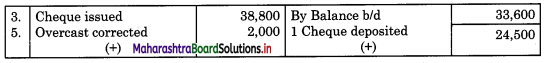
On 31st August 2018 bank passbook of Mr. Ravi showed a credit balance of ₹ 33,600, but Cash Book showed a different balance. On comparing the two books following differences were noticed:
1. Cheques paid into the bank but not credited before 31st Aug 2018 amounted to ₹ 24,500.
2. Direct deposit by the customer through NEFT ₹ 33,000 recorded in the passbook only.
3. Cheques issued on 28th Aug 2018 were presented for payment on 5th Sep. 2018 amounted to ₹ 38,800.
4. A bill receivable for ₹ 15,000 discounted with the bank was dishonored on 30th Aug 2018. Intimation of the same was received only on 3rd Sep 2018.
5. Passbook credit side was overcast ₹ 2,000.
6. Bank debited ₹ 400 for bank charges in the passbook, which was not recorded in Cash Book.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st August 2018.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st August 2018.

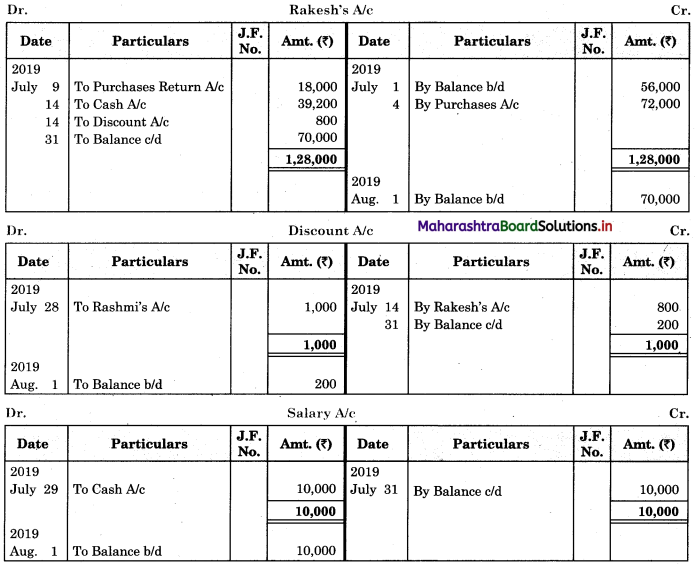
Working Notes:
In order to find out items to be added and items to be deducted in the Bank Reconciliation Statement, we have to prepare Cash Book and passbook on the basic information given in the problem:
Cash Book (With Bank Column)
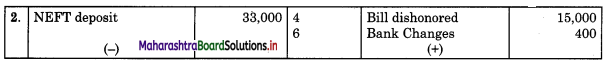
Bank Pass Book
Explanation:
1. First record the opening balance in the appropriate book and at the appropriate side i.e. either in Cashbook or passbook.
2. In the above problem Bank balance of ₹ 33,600 as per the passbook is recorded on the credit side of the passbook in a box.
3. In this problem, the entries which are passed on the credit side of the Cashbook and passbook are to be added in the Bank Reconciliation Statement and the entries passed on the debit side of the Cash Book and passbook are to be deducted in the Bank Reconciliation Statement. This is because the opening balance appears on the credit side of the passbook.
4. Pass the entry of the given transactions in the book in which entry is not passed due to one or another reason, e.g. cheque of ₹ 24,300 is deposited but not collected. In this case, entry is not passed in the passbook, as the cheque is not collected by the bank. Now draft the entry for the given transaction on the credit side of the passbook. This is because, after the collection of cheques, the bank balance is increased. In the same way for remaining transactions pass the entry in that book where entry is not passed corresponding.
![]()
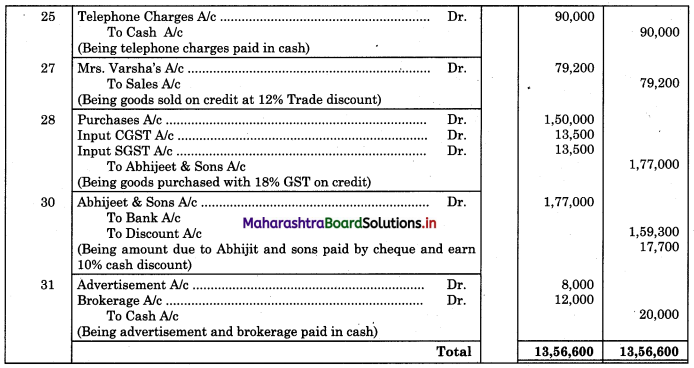
Question 4.
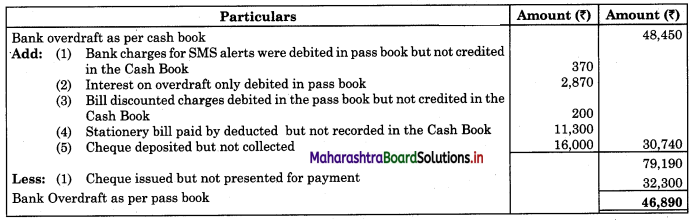
From the following details prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st Dec. 2018.
1. Bank overdraft as per Cash Book on 31st Dec. 2018 was ₹ 48,450.
2. Bank charges for SMS alerts ₹ 370 were debited in passbook but not recorded in Cash Book.
3. Interest in overdraft ₹ 2,870 did not appear in Cash Book.
4. A bill for ₹ 12,000 discounted with bank appears in Cash Book at the full amount but the bank has deducted ₹ 200 discounting charges.
5. Cheques issued but not presented for payment before 31st Dec. 2018 amounted to ₹ 32,300.
6. Cheques amounting to ₹ 24,000 were deposited into the bank but only a cheque of ₹ 8,000 was collected by the bank before 31st Dec. 2018.
7. Paid stationary bill ₹ 11,300 by debit card. It was not recorded in Cash Book.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st December 2018.
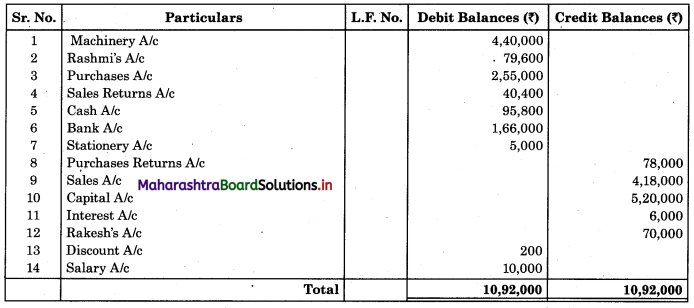
Working Notes:
Cash Book (With Bank Column)
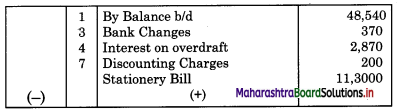
Bank Pass Book

Question 5.
From the following particulars prepare Rank Reconciliation Statement as of 30th June 2019.
1. Credit balance as per pass book ₹ 20,000.
2. A cheque for ₹ 3,500 was issued and paid by the bank, recorded in Pass Book as ₹ 5,300.
3. Cheque deposited ₹ 9,700 collected by the bank was not recorded in Cash Book.
4. Payment side of the Cash Book was undercast by ₹ 100.
5. Electricity bill paid by bank ₹ 6,200 was recorded twice in Pass Book.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 30th June 2019.

Working Notes:
Cash Rook (With Rank Column)
![]()
Bank Pass Book

Question 6.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement from the following information as of 31st March 2019.
1. Balance as per Cash Book ₹ 10,000.
2. Cheque of ₹ 2,000 issued but not presented to Bank for payment.
3. Our debtor directly deposited ₹ 3,500 to our Bank account by NEFT, not recorded in the Cash Book.
4. Bank paid electricity bill on our behalf ₹ 450 and charged Bank charges ₹ 100.
5. Paid ₹ 1,500 to ABC & company, our supplier by business debit card but recorded in Cash Book as ₹ 150.
6. Bank credited interest on Investment ₹ 500.
7. Cheque of ₹ 885 issued and presented to Bank but wrongly entered in the Pass Book as ₹ 865.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31st March 2019

Working Notes:
Cash Book (With Bank Column)
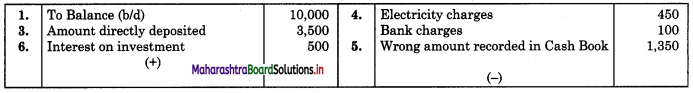
Bank Pass Book

![]()
Question 7.
On 31st January 2018 Bank balance as per Cash Book was ₹ 40,000 but Pass Book was showing some other balances following were the causes of the difference.
1. Cheques were issued for ₹ 1,00,000 in January 2018 but cheques of ₹ 50,000 were only presented to the Bank for payment before January 31st, 2018
2. Cheques were sent to the Bank for collection of ₹ 2,00,000 out of which cheques of ₹ 80,000 were only credited by the Bank in January 2018.
3. Following entries were shown in the passbook in January 2018, but no corresponding entries were made in the Cash Book.
(i) Payment of ₹ 6,400 by Bank for Electricity Bill by ECS.
(ii) Interest credited by Bank ₹ 12,000
(iii) Bank debited commission ₹ 1,000 and Bank charges for ₹ 600.
(iv) Direct deposit made by customer ₹ 1,000 by NEFT to our account.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st January 2018.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st January 2018
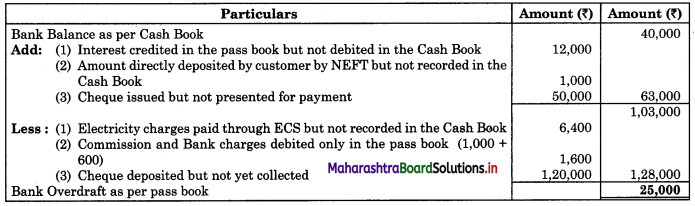
Working Notes:
Cash Book (With Bank Column)
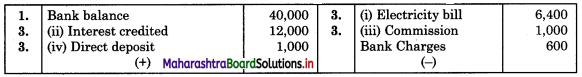
Bank Pass Book
![]()
Question 8.
In January 2018, the Pass Book of Mr. Girish Kumbhar showed a bank balance of ₹ 14,000. A comparison of the Cash Book with the Pass Book revealed the following.
1. Cheque deposited but not credited by Bank ₹ 10,000
2. Dividend on shares collected by Bank but not recorded in the Cash Book ₹ 1,000
3. Bank paid Insurance premium as per standing instruction by ECS ₹ 500, no corresponding entry was passed in the Cash Book.
4. Bank debited Commission ₹ 75.
5. A debit of ₹ 900 in respect of cheque dishonored appears in Pass Book only.
6. Cheque of ₹ 1,500 deposited into Bank wrongly recorded twice in the Cash Book.
7. Total cheques of ₹ 20,000 were issued during the month of January 2018, but cheques of ₹ 8,000 only were presented for payment in January 2018.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st January 2018.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st March 2019

Working Notes:
Cash Book (With Bank Column)
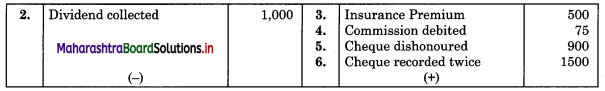
Pass Book

Question 9.
Form the following details provided by Prasharit enterprises, prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st March 2018.
1. Overdraft as per Cash Book ₹ 28,000
2. Cheque issued of ₹ 2,000 and presented to Bank returned dishonored but the effect of dishonored is not recorded in the Cash Book.
3. Bank debited Bank charges ₹ 150.
4. Bank transferred ₹ 2,500 to the savings account of the proprietor but not recorded in the Cash Book.
5. Cheque issued to the supplier but not presented to Bank before 21st March 2018, ₹ 1,600
6. Cheques of ₹ 3,000 and ₹ 2,000 were deposited into Bank but cheques of ₹ 3,000 were only credited by Bank before 31st March 2018.
7. Out customer directly deposited ₹ 1,500 in our Bank account but wrongly recorded it in the cash column of the Cash Book.
8. Bank debited interest on overdraft ₹ 750.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st March 2018.


Working Notes:
Cash Book (Bank column)
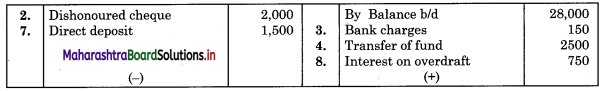
Pass Book
![]()
![]()
Question 10.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st Dec. 2018
1. Debit balance as per pass book ₹ 16,000
2. Customer directly deposited in our Bank account by NEFT ₹ 8,000.
3. Cheques deposited into Bank but not credited by Bank ₹ 10,500.
4. Pass Book shows a debit entry for Bank commission ₹ 300, not recorded in Cash Book.
5. A Bill of Exchange of ₹ 3,500 was discounted with the Bank in December 2018, returned dishonored in January 2019.
6. As per standing instructions Bank paid the Telephone bill of ₹ 650, not recorded in the Cash Book.
7. Cheque of ₹ 975 deposited into the Bank but wrongly recorded on ₹ 795 in Cash Book.
Solution:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as of 31st December 2018.

Working Notes:
Cash Book (with Bank column)
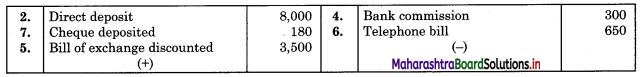
Bank Pass Book
![]()
Class 11 Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Textbook Solutions
- Introduction to Book Keeping and Accountancy Class 11 Commerce BK
- Meaning and Fundamentals of Double Entry Book-Keeping Class 11 Commerce BK
- Journal Class 11 Commerce BK
- Ledger Class 11 Commerce BK
- Subsidiary Books Class 11 Commerce BK
- Bank Reconciliation Statement Class 11 Commerce BK
- Depreciation Class 11 Commerce BK
- Rectification of Errors Class 11 Commerce BK
- Final Accounts of a Proprietary Concern Class 11 Commerce BK
- Single Entry System Class 11 Commerce BK