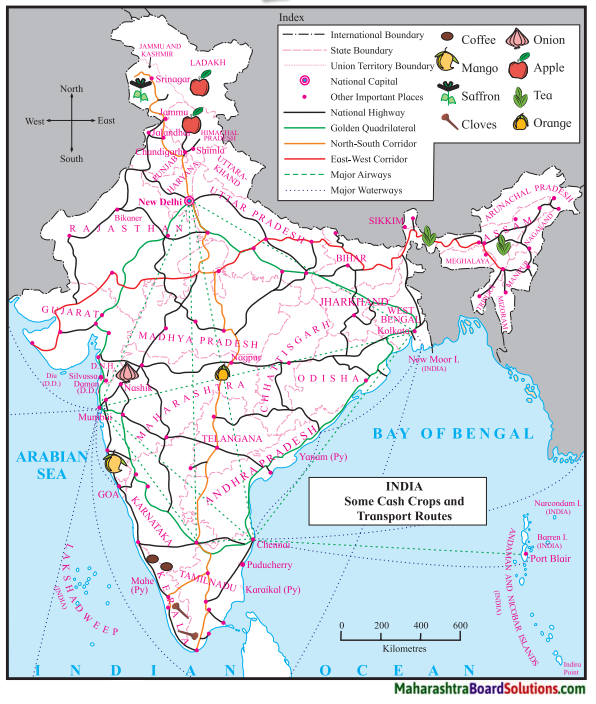
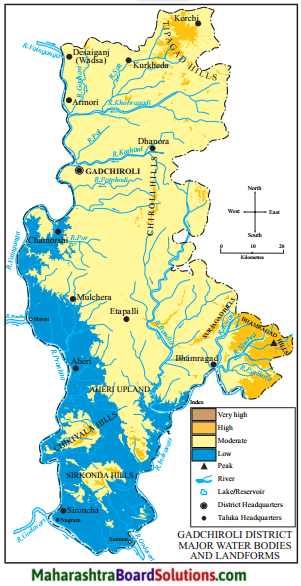
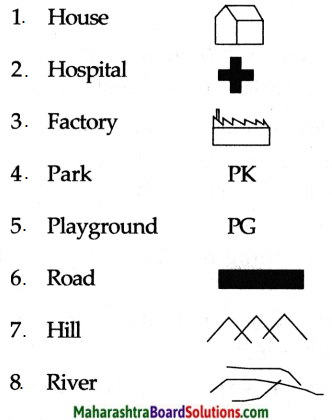
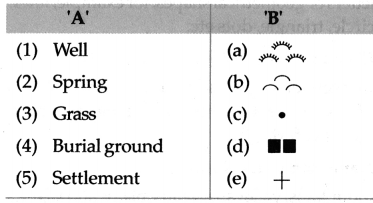
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Environmental Studies Solutions Chapter 14 Transport Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 EVS Solutions Part 1 Chapter 14 Transport
5th Std EVS 1 Digest Chapter 14 Transport Textbook Questions and Answers
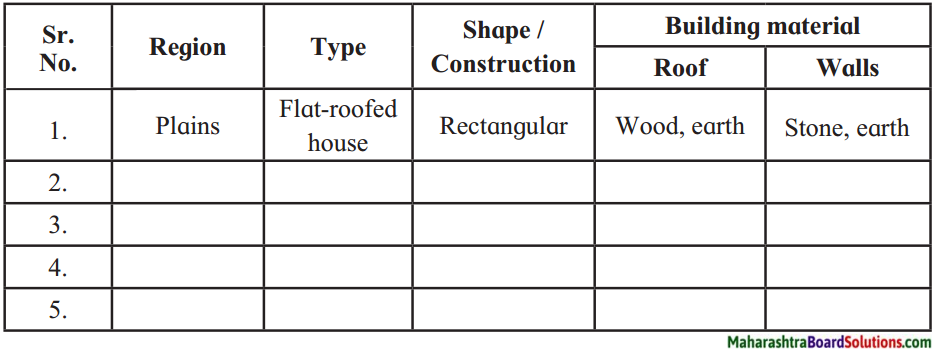
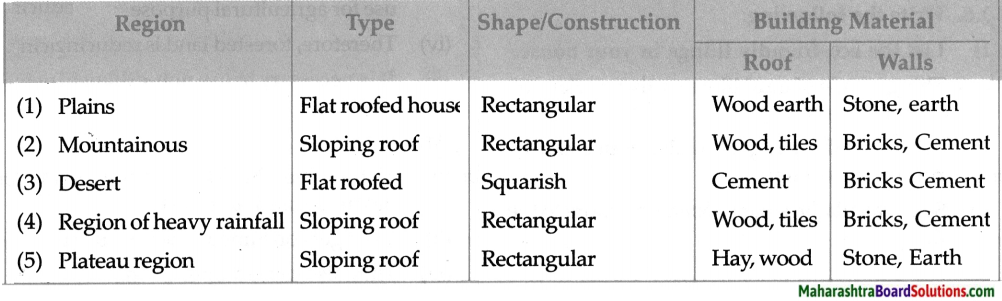
1. Write five sentences on how you have benefited from transport facilities.
Question 1.
Write five sentences on how you have benefited from transport facilities.
Answer:
Due to transport facilities:
- Work gets done soon.
- Time and effort are saved.
- Trade is facilitated easily.
- Connection to different parts of the world easily.
- It has improved lifestyle by education and health services.
![]()
2. List four other facilities that have become available in the local area due to transport facilities.
Question 1.
List four other facilities that have become available in the local area due to transport facilities.
Answer:
Due to transport, we are able to get vegetables and fruits. Milk is supplied on time. We are able to go to the market and malls. We are able to visit relatives and friends.
3. Suggest four solutions to reduce the burden on the local transport.
Question 1.
Suggest four solutions to reduce the burden on the local transport.
Answer:
To reduce the burden on local transport build flyovers, walk short distance, avoid unnecessary travel and go to school and work place close to our house.
4. Find the area in your locality with the least pollution. why is this the least polluted area?
5. What is the full form of CNG and LPG.
Question 1.
What is the full form of:
Answer:
1. CNG: Compressed National Gas
2. LPG: Liquidified Petroleum Gas
![]()
6.

Question (a)
In the above picture, which vehicle is causing pollution?
Answer:
The Bus
Question (b)
What remedy will you suggest to reduce the pollution caused by this vehicle?
Answer:
The bus should do PUC to control the smoke given out.
Can you tell?
Question 1.
(a) Walking
(b) Riding a bicycle
(c) Using a private vehicle
(d) Using a public vehicle
Which of the above options will you choose on the following occasions?
Answer:
- Going to study at a friend’s house who lives near by [a]
- Going to your school which is about one kilometre away. [b]
- Taking materials to a science exhibition in another town. [c]
- Going to a wedding in the next town. [d]
Environmental Studies Part 1 Standard 5th Solutions Chapter 14 Transport Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks with the correct answers from the options given below:
Question 1.
Using a vehicle saves ……………….. and ……………… .
(a) time
(b) money
(c) effort
(d) energy
Answer:
(a) time , (c) effort
![]()
Question 2.
The burning of fuel in vehicles emits ……………… and ………………… .
(a) water
(b) ash
(c) gases
(d) smoke
Answer:
(c) gas , (d) smoke
Question 3.
If there are traffic jams, ……………….. and …………………. pollution in that area increases.
(a) air
(b) water
(c) noise
(d) land
Answer:
(a) air , (c) noise
Question 4.
Indigenous trees adopt easily to the local environment and help in enhancing ……………….. .
(a) nature
(b) climate
(c) biodiversity
Answer:
(c) biodiversity
Question 5.
We use ………………… in automobiles.
(a) fuels
(b) water
(c) turbines
(d) air
Answer:
(a) fuels
Question 6.
Automobiles cause ………………… and ………………. pollution.
(a) air
(b) land
(c) noise
(d) water
Answer:
(a) air , (c) noise
Question 7.
Different parts of the world are now ………………… due to transport facilities.
(a) known
(b) connected
(c) enemies
(d) friends
Answer:
(b) connected
![]()
Question 8.
The transport of goods even on a ………………… level has become simple and easy.
(a) national
(b) state
(c) global
(d) equal
Answer:
(c) global
Question 9.
There is constant ………………. on a busy road.
(a) smoke
(b) water
(c) breeze
(d) traffic
Answer:
(d) traffic
Question 10.
When fuel is burnt in vehicles, minute particles of carbon and lead are released into the ……………………. .
(a) water
(b) air
(c) land
(d) fire
Answer:
(b) air
Question 11.
Growth and development of plants is affected adversely, due to …………………. pollution.
(a) water
(b) air
(c) land
(d) fire
Answer:
(b) air
Question 12.
Constant traffic through forest areas can ……………….. the habitat of plants and animals living there.
(a) harm
(b) protect
(c) befriend
(d) develop
Answer:
(a) harm
![]()
Question 13.
The constant sounds of vehicles create …………………… on a large scale.
(a) headache
(b) noise
(c) accidents
(d) music
Answer:
(b) noise
Question 14.
Traffic ………………. causes injuries, deaths and damage to the vehicles.
(a) accidents
(b) jam
(c) noise
(d) smoke
Answer:
(a) accidents
Question 15.
We should cultivate habits such as ………………… short distances.
(a) jogging
(b) riding
(c) flying
(d) walking
Answer:
(d) walking
Question 16.
Our environment is sensitive, that is why, ………………. has destructive effects on it.
(a) pollution
(b) solution
(c) resolution
(d) transportation
Answer:
(a) pollution
2. Match the following:
Question 1.
Match the following:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. Karanj | (a) Traffic accidents |
| 2. LPG | (b) Noise |
| 3. Headaches | (c) Local variety |
| 4. Deaths | (d) Fuel |
Answer:
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| 1. Karanj | (c) Local variety |
| 2. LPG | (d) Fuel |
| 3. Headaches | (b) Noise |
| 4. Deaths | (a) Traffic accidents |
![]()
Name the following:
Question 1.
Pollution caused by automobiles.
Answer:
Air and noise.
Question 2.
Gases emitted through burning of fuels.
Answer:
Carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, suphur dioxide.
Question 3.
Indigenous variety of trees.
Answer:
Banyan, Peepul, Neem, Karanj.
Question 4.
Fuels that do not cause pollution.
Answer:
LPG and CNG.
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
What facilities grow due to speedier modem means of transport?
Answer:
Modem means of transport speeds up facilities of tourism, health and education.
Question 2.
What is air pollution?
Answer:
An excess of carbon and lead substances lowers the quality of air in the environment which is called air pollution.
Question 3.
What harm do traffic accidents cause?
Answer:
Traffic accidents cause injuries, deaths and damage to the vehicles.
![]()
Question 4.
What habit should we cultivate if we have to travel a short distance?
Answer:
If we have to travel a short distance, we should cultivate the habit of working.
Question 5.
What mode of transport saves time and effort?
Answer:
Using a vehicle saves time and effort.
Question 6.
What causes air and noise pollution?
Answer:
Automobiles causes air and noise pollution.
Question 7.
What do vehicles constantly emit?
Answer:
Due to burning of fuel in vehicles, they constantly emit smoke and some poisonous gases.
Question 8.
Name some poisonous gases emitted by burning of fuels.
Answer:
Some of the poisonous gases emitted by burning of fuels include carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide.
Question 9.
What happens when there is constant traffic through forest areas?
Answer:
Constant traffic through forest areas can harm the habitat of plants and animals living there so, the wild animals in these forests migrate elsewhere.
Question 10.
What are the ill-effects of noise pollution to man?
Answer:
Noise pollution causes restlessness, irritability, headaches, lack of concentration, psychological disorders etc.
![]()
What are the effects of following on humans, plants and animals?
Question 1.
Air pollution on humans
Answer:
It increases trachea, lung and eye disorders, e.g. burning of the eyes
Question 2.
Air pollution on plants.
Answer:
The leaves of plants shrivel up and fall, sprouts, get scorched. The growth and development of plants is affected.
Question 3.
Air pollution on animals.
Answer:
The habitat of the animals is harmed and wild animals migrate elsewhere.
Question 4.
Sound pollution on humans.
Answer:
Sound pollution causes restlessness, irritability, headaches, lack of concentration, and psychological disorders.
Answer in brief:
Question 1.
What are sailing ships?
Answer:
In olden times, ships did not use fuel engines. They had sails which helped to use the force of wind. They were called sailing ships.
Question 2.
What options should we consider to help reduce pollution?
Answer:
We can help reduce pollution in the following ways:
1. By cultivating a habit to walk short distances.
2. By riding a bicycle for slightly longer distances.
3. By using public transport as far as possible.
![]()
Write short notes:
Question 1.
Remedies for reducing pollution.
Answer:
The following are the remedies for reducing pollution:
- Use fuels that cause less pollution.
- Maintain and repair vehicles from time to time.
- Use public transport mostly.
- Use private vehicles only when necessary.
- Plant indigenous trees to enhance biodiversity.
- Use LPG and CNG fuels which do not cause pollution.
Question 2.
Advantages of using a bicycle.
Answer:
The advantages of using a bicycle are as follows:
- Physical exercise
- Small loads can be carried
- Pollution free
- Self-reliance
- Saves time
- Can be stored in a small space
- Saves money
- Less crowding of vehicles on the streets
What’s the solution?
Question 1.
Rohan and Sania walk to school. Their school is thirty minutes away from their house. There is a cultural function at their school today. Their grandmother will accompany them to the function. But she gets tired easily because of her age. Which of the options listed below would you suggest for taking her to school?
(a) Walking
(b) Autorickshaw
(c) Bus
(d) Scooter
(e) Car
Answer:
Bus
![]()
Can you tell?
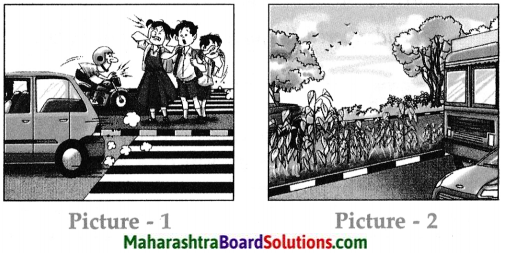
1. Observe the pictures and answer the following questions:
Picture: 1
Question 1.
Where have the children stopped?
Answer:
The children have stopped on the road divide.
Question 2.
Why have they stopped there?
Answer:
They have stopped there to cross the road due to heavy traffic.
Question 3.
What are the children doing?
Answer:
The children are rubbing their eyes, coughing and closing their ears.
Question 4.
What is troubling them?
Answer:
The noise and air pollution due to transport routes is troubling them.
![]()
Picture – 2:
1. State the difference between the plants close to the road and those for away from the road based on the following points:
Question (a)
Freshness of leaves.
Answer:
The leaves close to the road appear dull compared to the one’s that are far away from the road.
Question (b)
Colour of the leaves.
Answer:
The leaves near the road are brown as they are covered with a thick layer of dust and mud whereas those far away are green in colour.
Question (c)
Appearance of plants.
Answer:
The growth of plants is affected due to the pollution. The plants near the road have few leaves.
![]()
Glossary:
- restlessness – lacking quiet and rest
- irritability -the state of being irritable
- pyschological – problem related to the mind
- indigenous – occuring naturally in a particular place.
- shrivel – wrinkle and contract
- scorched – burnt
- migrate – move from one region to another
- facilitated – made easier
- remedies – medicine or treatment.