Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Marathi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 2 हत्तीचे चातुर्य Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Marathi Sulabhbharati Solutions Chapter 2 हत्तीचे चातुर्य
5th Standard Marathi Digest Chapter 2 हत्तीचे चातुर्य Textbook Questions and Answers
1. पाहा. ऐका. वाचा.
प्रश्न 1.
पाहा. ऐका. वाचा.
 उत्तर:
उत्तर:
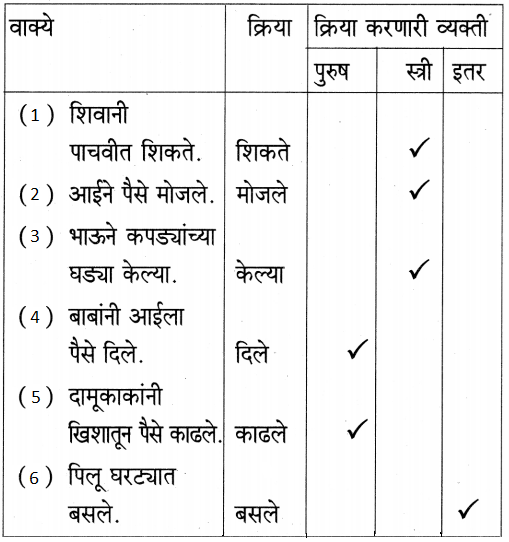
- जसे : मुले मैदानात फुटबॉल खेळत आहेत.
- मला फुटबॉल खेळायला खूप आवडते.
- ससे बसले आहेत.
- पावसात रस्त्यावरील खड्ड्यात पाणी भरले.
- आईने फळीवर डबा ठेवला.
- हत्ती नदीवर आंघोळ करत होता.
![]()
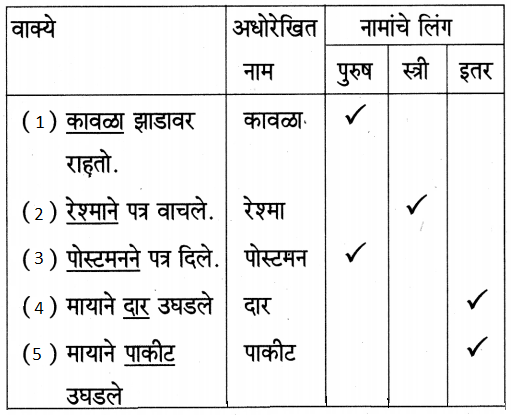
2. पाहा. सांगा.
प्रश्न 1.
पाहा. सांगा.
उत्तर:
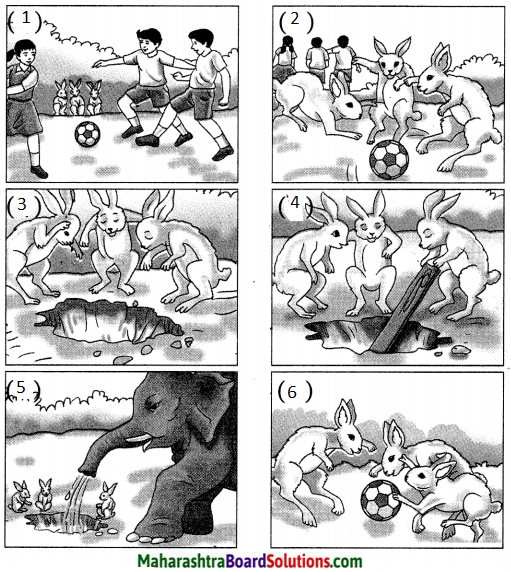

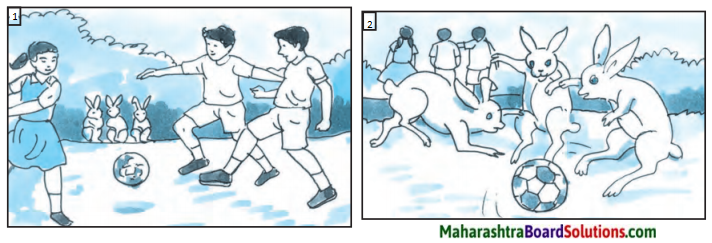
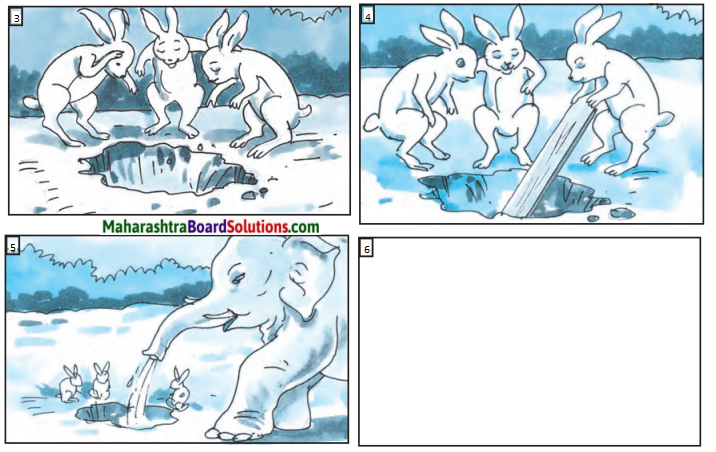
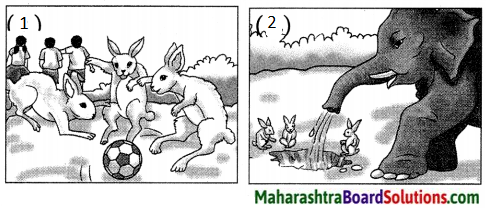
एकदा एका मैदानात काही मुले फुटबॉल खेळत होती. या मुलांचा हा खेळ तीन ससे पाहत होते. या मुलांचे खेळून झाल्यावर त्या तीन सशांनी फुटबॉल खेळण्यास प्रारंभ केला. खेळता खेळता अचानक त्यांचा फुटबॉल एका मोठ्या खड्ड्यात गेला. ससे विचारात पडले. आता हा फुटबॉल कसा काढावा बरं? त्यांनी एक युक्ती लढवली व एक फळी आणली ती फळी खड्ड्यात घातली, पण तो बॉल काही वर आला नाही. एक हत्ती हे सगळं पाहत होता. सशांच्या धडपडीची त्याला गंमत वाटली व दया आली. त्याने सोंडेत पाणी भरून ते पाणी खड्ड्यात सोडले. त्याबरोबर फुटबॉल वर आला. हत्तीने आपल्या सोंडेने फुटबॉल काढला. ससे पुन्हा आनंदाने खेळू लागले. हत्तीच्या चातुर्यामुळे त्यांना फुटबॉल परत मिळाला. तात्पर्य – सयमसुचकता (Sense of presence) दाखवली तर अडचणीतून मार्ग निघतो.
प्रश्न 1.
सुरुवातीला दिलेल्या चित्रांवालील नावे सांगा.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
प्रत्येक चित्रात काय काय दिसते ते सांगा.
प्रश्न 3.
चित्र पाहा. कोण ते सांगा.
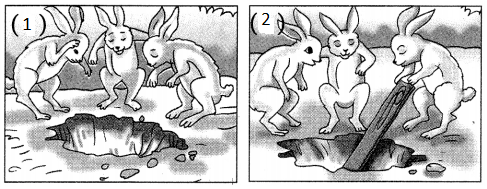
(अ) खड्ड्यातील फुटबॉल काढण्यासाठी प्रयत्न करणारे –
(आ) सशांना मदत करणारा –
उत्तर:
(अ) ससे
(आ) हत्ती
प्रश्न 4.
गोष्टीत शेवटी काय झाले असेल ते कल्पना करून सांगा व रिकाम्या चौकटीत चित्र काटा.
प्रश्न 5.
सर्व चित्रे पाहा व गोष्ट सांगा.
प्रश्न 6.
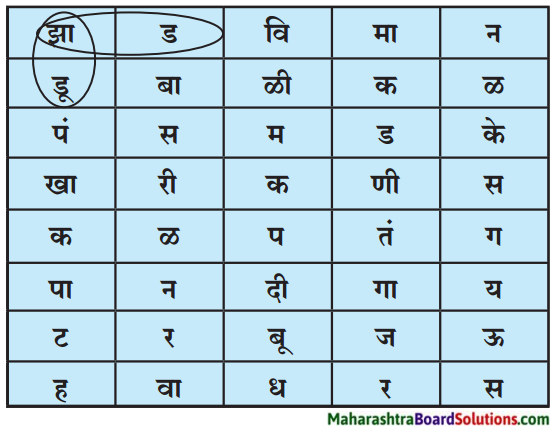
घ,ठ, थाप या अक्षरांपासून चित्रे तयार केली आहेत. त्यांचे निरीक्षण करा. यांसारख्या इतर अक्षरांपासून तुम्हालाही वेगळी चित्रे काढता येतील. कल्पना करा आणि चित्रे काढा.

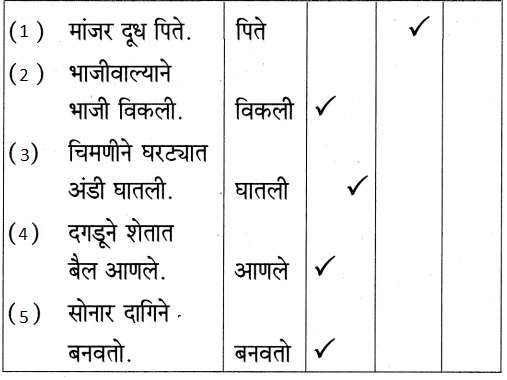
1. शब्द ओळखा व कार्यावर लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.

उत्तर:
(अ) वेगळा
(ब) बगळा
प्रश्न 2.
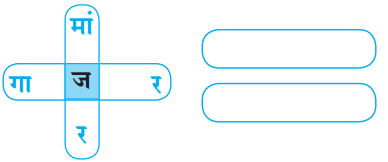
उत्तर:
(अ) गाजर
(ब) मांजर
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
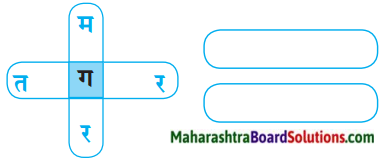
उत्तर:
(अ) मगर
(ब) नगर
प्रश्न 4.
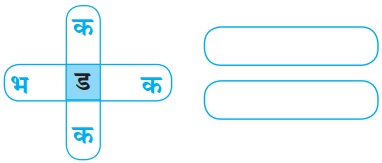
उत्तर:
(अ) कडक
(ब) भडक
प्रश्न 5.
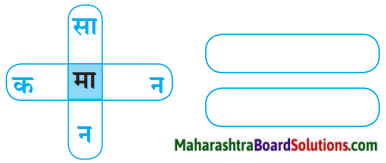
उत्तर:
(अ) सामान
(ब) कमान
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
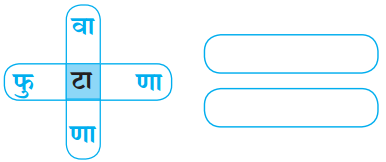
उत्तर:
(अ) वाटाणा
(ब) फुटाणा
प्रश्न 7.

उत्तर:
(अ) आकाश
(ब) प्रकाश
प्रश्न 8.
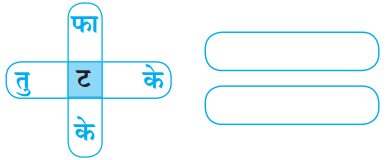
उत्तर:
(अ) फाटके
(ब) तुटके
Marathi Sulabhbharati Class 5 Solutions Chapter 2 हत्तीचे चातुर्य Additional Important Questions and Answers
1. खालील प्रश्नांची एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
चित्रात किती ससे आहे?
उत्तर:
चित्रात तीन ससे आहेत.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
चित्रात मुले कोणता खेळ खेळत आहेत?
उत्तर:
चित्रात मुले फुटबॉल खेळत आहेत.
प्रश्न 3.
मुले फुटबॉल खेळताना त्यांच्याकडे कोण पाहत आहे?
उत्तरः
मुले फुटबॉल खेळताना त्यांच्याकडे ससे पाहत आहेत.
प्रश्न 4.
खेळत असतांना फुटबॉल कुठे गेला?
उत्तर:
खेळ खेळता खेळता फुटबॉल खड्ड्यात गेला.
प्रश्न 5.
ससे फुटबॉल कशाप्रकारे बाहेर काढत आहेत?
उत्तर:
ससे फळीने फुटबॉल बाहेर काढण्याचा प्रयत्न करत आहेत.
प्रश्न 6.
फुटबॉल बाहेर काढण्यासाठी शेवटी कोणी प्रयत्न केला?
उत्तर:
फुटबॉल बाहेर काढण्यासाठी शेवटी हत्तीने प्रयत्न केला.
प्रश्न 7.
हत्तीने खड्ड्यात पाणी कशातून टाकले?
उत्तर:
हत्तीने खड्ड्यात पाणी सोंडेतून टाकले.
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
खड्ड्यात पाणी टाकल्याने काय झाले?
उत्तर:
खड्ड्यात पाणी टाकल्याने फुटबॉल वर आला.
प्रश्न 9.
सशांना केव्हा आनंद झाला?
उत्तर:
फुटबॉल खड्ड्यातून वर आल्याने सशांना आनंद झाला.
प्रश्न 10.
शक्तिपेक्षा काय श्रेष्ठ असते?
उत्तर:
शक्तिपेक्षा युक्ति श्रेष्ठ असते.
2. पुढील दिलेली चित्रे पाहून कोण ते लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील दिलेली चित्रे पाहून कोण ते लिहा.
1. मुलांचा खेळ पाहून फुटबॉल खेळणारे –
2. सोंडेने खड्ड्यात पाणी सोडणारा –
उत्तर:
1. ससे
2. हत्ती
प्रश्न 2.
पुढील मुद्द्यांच्या व चित्रांच्या मदतीने गोष्ट तयार करून लिहा.
उत्तर:
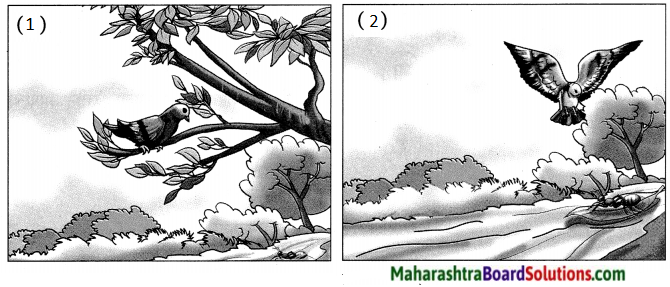
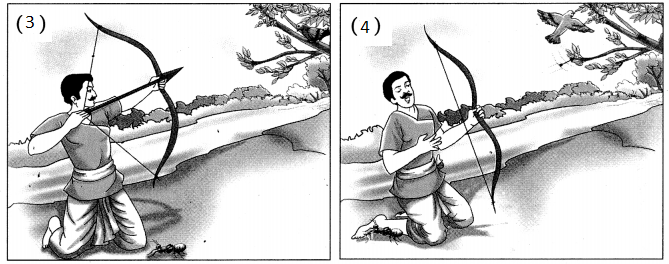
मुंगी ……….. कबुतर मैत्री …………. एक दिवस मुंगी पाण्यात ………………. कबुतराने पान टाकणे . मुंगीचे पानावर चढणे ………….. प्राण वाचणे ………. जाणीव एके दिवशी जंगलात शिकारी …………….. कबुतराच्या शिकारीचा नेम …………… मुंगीचा शिकाऱ्याच्या पायाला चावा ……त्याचा नेम चुकणे ………….. कबुतराचे प्राण वाचणे.
![]()
कथा (खरे मित्र):
एकदा एका जंगलात मुंगी-कबुतराची मैत्री झाली. मुंगी पाणी पीत असताना पाय घसरून पडली. कबुतराने लगेच झाडाचे पान टाकून तिला वाचवले. मुंगीला या गोष्टीची जाणीव होती की कबुतरामुळेच आपले प्राण वाचले, नाहीतर आपण बुडून मरून गेलो असतो. एके दिवशी त्याच जंगलात एक शिकारी आला. शिकाऱ्याने इकडे-तिकडे पाहिले. त्याला एका झाडावर कबुतर दिसले. त्याच्या मनात कबुतराची शिकार करावी असे आले. शिकाऱ्याने लगेचच नेम धरला व बंदूकीने गोळी कबुतराला मारणार इतक्यात मुंगीचे लक्ष शिकाऱ्याकडे गेले. मुंगीला काय करावे सुचेना. अखेरीस मुंगीने शिकाऱ्याच्या पायाचा कडकडून चावा घेतला. त्याचा नेम चुकला व अशात-हेने कबुतराचे प्राण वाचले. कबुतर व मुंगी आता खूपच चांगले मित्र झाले.
तात्पर्य:
1. आपल्यावर उपकार करणाऱ्याला कधी विसरू नये.
2. खरे मित्र संकटकाळात एकमेकांची मदत करतात.
हत्तीचे चातुर्य Summary in Marathi
पाठ्यपरिचय:
प्रस्तुत पाठात चित्ररूपाने आलेल्या कथेत हत्तीने दाखवलेल्या समयसुचकतेचे व चातुर्याचे वर्णन केले आहे.
शब्दार्थ/Meanings:
- हत्ती – गज (an elephant)
- चातुर्य – हुशारी (cleverness)
- मुले – बालके (children)
- फुटबॉल – (name of outdoor game)
- ससा – (rabbit)
- खड्डा – जमिनीचा खचलेला भाग (a hole, pit)
- फळी – लाकडाचा तुकडा (a bat, board, plank)
- सोंड – (Trunk)
- विचारात पडणे – (think deeply)
- युक्ति – (idea)
- निराश – उदास (nervous)
- आनंद – खुशी (happiness)