Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Environmental Studies Solutions Chapter 8 Beginning of Settled Life Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 EVS Solutions Part 2 Chapter 8 Beginning of Settled Life
5th Std EVS 2 Digest Chapter 8 Beginning of Settled Life Tools Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blank.
Question a.
Archaeological evidence shows that agriculture first began about 11,000 years ago in Israel and …………. .
(Iran, Iraq, Dubai)
Answer:
Archaeological evidence shows that agriculture first began about 11,000 years ago in Israel and Iraq.
![]()
Question b.
The houses at the beginning of the New Stone Age were made of …………… .
(earth, bricks, wattle and daub)
Answer:
The houses at the beginning of the New Stone Age were made of wattle and daub.
2. Answer the following question in brief.
Question a.
What are the three main steps in the process of domesticating a wild animal?
Answer:
- Capture the wild animal.
- Taming the wild animal by giving them the training to live with humans.
- Obtaining useful materials like milk from these animals and training them to work as beasts of burden for the humans.
Question b.
How did some people in the community become skilled craftsmen?
Answer:
- As the food available was more than needed by the community, some men and women utilised their spare time in experimentation and for using their natural creativity to develop special skills.
- Persons with such special skills were given to work based on those skills.
- Thereby a class of skilled craftsmen emerged.
![]()
3. Complete the following concept chart.
Question 1.
Complete the following concept chart.
Answer:
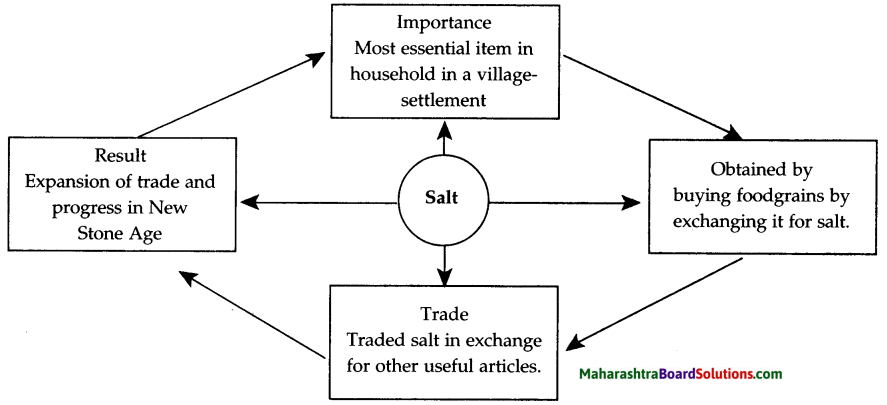
4. Write about the usefulness of any five domesticated animals.
Question 1.
Write about the usefulness of any five domesticated animals.
Answer:
- Cow : Cow is a very useful animal. It is domesticated for its milk. Cow-dung was used to smear mud walls and in courtyards. Cow-dung is used to make dung cakes for fuel and also is a very good natural manure for agriculture.
- Goats and Sheep : Sheep is useful for its wool and milk. They are also domesticated for their meat.
- Dog : A very useful and faithful animal. It guards household or village-settlements.
- Horse : A very useful, strong and a swift animal. Its strength is used to draw carriages or to transport heavy
- goods. It is also used in travelling.
- Bullocks : Bullocks are strong and obedient animals. Therefore, they are used to draw carts. They are also used to transport people and heavy objects from one place to another.
![]()
5. Which animal is used by the modern police? In what way?
Question 1.
Which animal is used by the modern police? In what way?
Answer:
- The dog is used by modern police.
- It is used in the investigation of crimes as a dog can sniff the body odour and blood-stains on the clothes.
- It leads police to the person who has committed heinous crimes like murder.
Activity :
Question 1.
Visit people in your locality practising five different occupations and collect information about their work.
Environmental Studies Part 2 Standard 5th Solutions Chapter 8 Beginning of Settled Life Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
- When the third step is achieved, the animal is supposed to be completely ……….
- Domesticating animals and keeping them for our own use is called ……….
- The …….. is the first animal to have been domesticated.
- ………..and………… were domesticated next.
- Dogs were used to help with ………….
- …….. are credited to have started cultivation.
- They used ………….. Sticks to sow seeds.
- People had to stay in one place because of the nature of ………… work.
- ………………….. production increased considerably after the plough drawn by animals came into use.
- …………. became the main source of livelihood.
- People began to worship ……. and various ………. for good crops.
- People in the village-settlements established some ………. and ……. to manage things.
- Before agriculture, all men and women were continuously engaged in getting ……….
- With agricultural production increasing, some men and women began to get ……….. time.
- They used their spare time for using their natural creativity to develop……… skills.
- Members with such special skills were given ………. based on those skills.
- It is believed that in the New Stone Age, ……… made earthen pots and other earthen objects by hand.
- The farmers in the village-settlements were now producing……….. food.
- They needed skilled ……………. for tasks like making agricultural implements and repairing them
- Craftsmen were paid in the form of …………..
- ………… is an essential item.
- Salt traders also traded articles they received in exchange of ………..
- The ………. trade helped in the expansion of trade in the New Stone Age.
- People responsible for the implementation of these rules became the ………… of village settlements.
- The chiefs were also entrusted with the …… of the village.
- The population of the village settlements ………. because food was available in plenty
- The ……… became permanent and expanded.
- People began to build ………. houses of sun dried bricks.
- It appears that the people of the village settlements belonged to a single …………..
- The entire village-settlement was an ………….. family.
- A dead person was buried either in the ……….. or in the ……..
- In the ………… system, it became possible to store food grains.
Answer:
- domesticated
- animal husbandry
- dog
- goat, sheep
- hunting
- uxomen
- pointed
- agricultural
- agricultural
- agriculture
- nature, deities
- rules, customs
- food
- spare
- special
- work
- women
- surplus
- craftsmen
- foodgrains
- salt
- salt
- salt
- chiefs
- protection
- grew
- village-settlements
- quadrangular
- clan
- extended
- house, courtyard
- agricultural
![]()
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Source of livelihood | a. Women |
| 2. Sowing of seeds | b. New Stone Age |
| 3. Earthen pots | c. Protection |
| 4. Moats | d. Agriculture |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Source of livelihood | d. Agriculture |
| 2. Sowing of seeds | a. Women |
| 3. Earthen pots | b. New Stone Age |
| 4. Moats | c. Protection |
Answer each of the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is animal husbandry?
Answer:
Domesticating animals and keeping them for one’s use is called animal husbandry.
Question 2.
Which is the first animal to have been domesticated?
Answer:
The dog is the first animal to have been domesticated.
Question 3.
Who domesticated the dog?
Answer:
Homo sapiens of the Middle Stone Age domesticated the dog.
Question 4.
How were the dogs used?
Answer:
Dogs were used to help in hunting.
![]()
Question 5.
Which animals were domesticated after the dog?
Answer:
The goat and sheep were domesticated after the dog
Question 6.
When and where did agriculture begin?
Answer:
Archaeological evidence is available to show that agriculture first began about 11,000 years ago in Israel and Iraq.
Question 7.
Who are given the credit to have started cultivation?
Answer:
Women are credited to have started cultivation
Question 8.
What did they use to sow seeds?
Answer:
They used pointed sticks to sow seeds.
Question 9.
How did the agricultural production increase considerably?
Answer:
Agricultural production increased considerably after the plough driven by animals came into use.
Question 10.
What was the main source of livelihood for people in the New Stone Age?
Answer:
Agriculture was the main source of livelihood for the people in the New Stone Age.
![]()
Question 11.
What did the people do in order to grow good crops?
Answer:
People began to worship nature and various deities to grow good crops.
Question 12.
What gained importance in the village settlement?
Answer:
Essential things like sharing of agricultural tasks and water resources and the security of the village-settlements gained importance.
Question 13.
How did the New Stone Age women make earthen pots?
Answer:
The New Stone Age women made earthen pots and other earthen objects by hand.
Question 14.
Why were the craftsmen needed?
Answer:
Craftsmen were needed for tasks like making agricultural implements and repairing them.
Question 15.
How were the craftsmen paid?
Answer:
The craftsmen were paid in the form of food grains or other articles.
![]()
Question 16.
What is the barter system?
Answer:
Buying and selling articles by exchanging goods for goods is called barter system.
Question 17.
What was an essential item in the village settlement?
Answer:
Salt was an essential item in the village settlement.
Question 18.
How did the salt traders trade?
Answer:
Salt traders traded articles they received in exchange of salt.
Question 19.
Why did the village community lay down rules?
Answer:
The village community laid rules for mutual co-operation in order to keep this system of trade and distribution of resources running smoothly.
![]()
Question 20.
Who became the chiefs of village settlements?
Answer:
People responsible for the implementation of these rules became the chiefs of villagesettlements.
Question 21.
Who was entrusted with the protection of the village?
Answer:
The chiefs were also entrusted with the task of protection of the village.
Question 22.
Why did they build protective walls and moats around the village-settlements?
Answer:
They built protective walls and moats around the village-settlements to protect them selues from floods, wild animals and outsiders who stole the village cattle.
Question 23.
What were the houses at the beginning of New Stone Age made of?
Answer:
Houses at the beginning of the New Stone Age were made of wattle and daub?
Question 24.
Why were there differences in the style of constructing houses?
Answer:
Regional differences are seen in the styles of constructing houses, depending on the local climate.
![]()
Question 25.
Why did the population of village settlements grow?
Answer:
The population of village-settlements grew because food was available in plenty.
Give reasons for the following:
Question 1.
The stick used for sowing was weighed in the centre using a perforated stone.
Answer:
In order to dig deeper into the soil to sow the seeds, the stick was weighted in the centre using a perforated stone.
Question 2.
Before agriculture, men and women in the community were continuously busy.
Answer:
- Before agriculture, people obtained food by hunting and gathering.
- But this food could not be stored for a long time.
- Therefore, all men and women in the community were continuously engaged in acquiring food.
Question 3.
Walls and moats were built around the village settlement.
Answer:
Protective walls and moats were built around the village-settlements to protect them from floods, wild animals and outsiders who stole village cattle.
Question 4.
The village-settlements grew.
Answer:
i. The population of the village-settlements grew because food was available in plenty after agriculture
ii. They also built bigger houses to accommodate their expanding population.
![]()
Question 5.
The entire village-settlement was an extended family.
Answer:
- It appears from the plans of the houses and the village-settlements that people staying there belonged to a single class.
- It means that they were all related to one another.
- Thus, the entire village-settlement was an extended family
Question 6.
Women and men began to get spare time to develop special skills.
Answer:
- In the agricultural system, it became possible to store foodgrains for a long period.
- There was sufficient food for the community.
- Therefore, women and men began to get spare time to use their natural creativity to develop special skills.
Question 7.
People began to worship nature and various deities.
Answer:
i. Agriculture became the main source of livelihood in the New Stone Age period.
ii. Thus, people began to worship nature and various deities for good crops.
![]()
Question 8.
The farmers needed skilled craftsmen.
Answer:
i. Farmers in the village-settlements were producing surplus food.
ii. Therefore, they needed skilled craftsmen for making agricultural implements and repairing them.
Question 9.
A dead person was buried either in the house or in the courtyard.
Answer:
The people thought that the dead person’s bond with family should not get cut off after death.
Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
How was cultivation carried out by women?
Answer:
- Women are credited to have started cultivation.
- They used pointed sticks to sow seeds.
- In order to help dig deeper into the soil, the stick was weighted in the centre using a perforated stone.
![]()
Question 2.
How did a social system based on agriculture came into existence?
Answer:
- Essential things like sharing of agricultural tasks and water resources and the security of the village-settlement gained importance.
- People in the village-settlements established some rules and customs to manage these things.
- Thus, a social system based on agriculture came into existence.
Question 3.
How was barter system established?
Answer:
- When the farmers in the village-settlements
- produced surplus food, they felt the need for skilled craftsmen who would provide them with agricultural implements and also repair them.
- Such craftsmen were paid in the form of food grains or other articles. The craftsmen also purchased the required raw material in the form of foodgrains and other useful articles.
- Thus, buying and selling by exchanging goods for goods called barter system was established.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the structure of houses in the New Stone Age.
Answer:
- The houses at the beginning of the New Stone Age were made of wattle and daub i.e. the walls were screens woven from sticks or bamboo and plastered with mud or cow dog.
- Later when the population in the village ettlement grew, people began to build quadrangular” houses of sun-dried bricks. These houses were also bigger and had more than one room.
- Regional differences are seen in the styles of constructing houses, depending on the local climate.
Question 5.
Describe the ritual of burying the dead in the village settlements.
Answer:
i. A dead person was buried either in the house or in the courtyard with the idea that the person’s bond with the family should not get cut off even after death.
ii. Families would also bury various articles with the dead person for them to use even after death.
Question 7.
How did the village administrative system came into being?
Answer:
- The village community made rules for mutual co-operation in order to keep trade running smoothly.
- People responsible for the implementation of these rules became the chiefs of village settlements
- These chiefs were also entrusted with the protection of the village.
- This is how the village administrative system came into being.
![]()
Glossary :
- entrusted : assigned the responsibility to doing something to (someone)
- archaeological : of history
- implementation : put into effect
- deities : gods and goddesses
- moats : a deep, wide ditch surrounding a house.
- wattle : and
- daub : material used in building walls.
- perforated : pierced with a hote.
- accommodate : provide sufficient space for.
- surplus : extra.
- abundance : a large quantity fo something
- experimentation: procedure.
- complied : meet specified standards.
- quadrangular : having four sides