Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Environmental Studies Solutions Chapter 6 Stone Age: Stone Tools Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 EVS Solutions Part 2 Chapter 6 Stone Age: Stone Tools
5th Std EVS 2 Digest Chapter 6 Stone Age: Stone Tools Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blank.
Question a.
That period, of which the tools that we find are mainly made from stone, is called the ………………….. .
(Copper Age, Iron Age, Stone Age)
Answer:
That period, of which the tools that we find are mainly made from stone, is called the Stone Age.
Question b.
………………. near Nashik is a well-known Old Stone Age site in Maharashtra.
(Gangapur, Sinnar, Chandwad)
Answer:
Gangapur near Nashik is a well-known Old Stone Age site in Maharashtra.
2. Find out the odd pair from the following.
Question 1.
Find out the odd pair from the following.
a. Rajasthan – Bagor
b. Madhya Pradesh – Bhimbetka
c. Gujarat – Langhnaj
d. Maharashtra – Bijapur
Answer:
d. Maharashtra – Bijapur
![]()
3. Answer the following question in brief.
Question a.
How did man use the percussion technique?
Answer:
1. The man in Old Stone Age used the percussion technique to make stone tools.
2. Percussion technique involves beating or striking one large pebble against another to obtain stone flakes.
Question b.
What revolution was brought about by Homo sapiens in the tool-making technique?
Answer:
- The Homo sapiens devised a technique of obtaining long and narrow blades of stone.
- He made knife, scraper, borer and chisel from these long blades.
- He used ivory and rare stones of the quartz variety for making tools and other articles.
4. Compare the tools from all the three periods of the Stone Age.
Question 1.
Compare the tools from all the three periods of the Stone Age.
Answer:
| Old Stone Age | Middle Stone Age | New Stone Age |
| 1. Tools were crude as these made by the percussion technique | 1. The quality of tools improved. Homo sapiens brought about a revolution in technique of making tools. | 1. The tools were polished and had smooth and shiny finish as new type of tool-making technique was developed. |
| 2. Chopper, hand-axe and clearer were made. | 2. Different tools were used for different kinds of work. | 2. Tools were mainly made for agricultural work as hunting had become a secondary activitiy. |
| 3. Large stones and their flakes were rather heavy and odd in size. | 3. Tools were light weight, durable proportionate and symmetrical. | 3. Tools were light weight, durable, proportionate, symmetrical and efficient. |
![]()
5. Which of the following modern machines has stone grinders?
Question 1.
Which of the following modern machines has stone grinders?
a. Mixer
b. Flour mill
c. Juicer
Answer:
b. Flour mill
6. Show the following places on the map of India.
Question 1.
Show the following places on the map of India.
a. A site of the Old Stone Age in Maharashtra.
b. A river basin with New Stone Age sites.
c. A site of the Middle Stone Age in Madhya Pradesh.
Answer:
a. A site of Old Stone Age in Maharashtra : Gangapur
b. A river basin with New Stone Age site : Basin of river Ganga.
c. A site of Middle Stone Age in Madhya Pradesh: Bhimbetka
Activity :
Question 1.
Visit various industries in your locality and collect information about the tools used there. Make a chart by classifying those tools.
![]()
Environmental Studies Part 2 Standard 5th Solutions Chapter 6 Stone Age: Stone Tools Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
- Apes like the chimpanzee also used ………………. to break seeds and nuts.
- Apes like the chimpanzee used ……………. to stir the ants out from ant hills to catch them.
- Early humans too, used bones, stones, twigs and sticks as
- Humans learnt that they could ………… rods, bones sticks and stones into tools to carry out their tasks more efficiently.
- They also learnt they could give their tools any …………. they desired.
- Humans made tools thousands of years ago, but only the …………. tools can be found today.
- The Stone Age is divided into ……… periods.
- Palaeolithic Age meAnswer:……….. Stone Age.
- Mesolithic Age meAnswer:…………… Stone Age.
- Neolithic Age meAnswer:……….. Stone Age
- Homo habilis and Homo erectus belonged to the ……………… Stone Age.
- Old Stone Age man used ………….. techniques to make tools.
- The first tools made in the Old Stone Age were ……………..
- ………. were tools with only one side having a sharp edge.
- Choppers were used for ………………… nuts or bones
- Tools like the hand-axe and cleaver were made by ………
- Homo erectus could……………… visualize his tools even before he actually shaped them.
- The Neanderthal Man made further ……….. in tool – making techniques.
- Homo sapiens brought about a ….. in the technique of making tools.
- He devised a technique of obtaining long and narrow ……….. of stone.
- Groups of Homo sapiens began to build ………… and live in them.
- They also started celebrating …………… festivals.
- Homo sapiens started using ornaments to ……….. themselves.
- ……………. were made from shells, bones and the teeth of animal.
- Fossils of a human skull and the …………….. bone of an Old Stone Age woman were found on the bank of the Narmada.
- A fossilized skull of a ……………… from the Stone Age was found at a village near Puducherry.
- Gangapur is on the banks of the ……………… river.
- Middle Stone Age man domesticated the …………….
- ……………………. started to harvest food grains that grew in the wild and to domesticate animals.
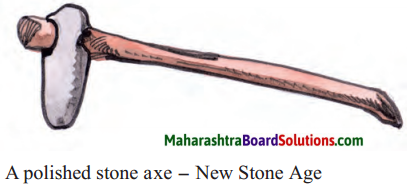
- In the New Stone Age, the stone tools were ………….. to give a smooth and shiny finish.
- In the New Stone Age, ……………….. was no more a major means of obtaining food.
- A……………….. is large/broad bladed axe.
- Tools like the hand-axe and cleaver were made by ……………..
- Groups of …….. had begun to build huts and live in them.
Answer:
- tones
- sticks
- tools
- sharpen
- shape
- stone
- three
- old
- middle
- new
- old
- percussion
- crude
- choppers
- breaking
- Homo erectus
- mentally
- progress
- revolution
- blades
- huts
- social
- adorn
- beads
- collar
- child
- Godavari
- dog
- Homo sapiens
- polished
- hunting
- clearer
- Homo erectus
- Homo sapiens
![]()
Match the columns :
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Fossil of a human skull | a. Along the Ganga river in South India |
| 2. Fossil of a child’s skull | b. Afghanistan and Sri Lanka |
| 3. New Stone Age site in India | c. Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh |
| 4. Remains of Old Stone Age | d. Patane in Jalgaon district in Maharashtra |
| 5. Site of Middle Stone Age | e. A village near Puducherry |
| 6. Knife and sickle | f. Homo erectus |
| 7. Antlers used as hammer | g. Homo sapiens |
| 8. Choppers and scrappers | h. Mesolithic Age |
| 9. Domesticated animals | i. Old Stone Age man |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Fossil of a human skull | c. Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh |
| 2. Fossil of a child’s skull | e. A village near Puducherry |
| 3. New Stone Age site in India | a. Along the Ganga river in South India |
| 4. Remains of Old Stone Age | b. Afghanistan and Sri Lanka |
| 5. Site of Middle Stone Age | d. Patane in Jalgaon district in Maharashtra |
| 6. Knife and sickle | g. Homo sapiens |
| 7. Antlers used as hammer | f. Homo erectus |
| 8. Choppers and scrappers | i. Old Stone Age man |
| 9. Domesticated animals | h. Mesolithic Age |
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
What did apes like the chimpanzees use to break seeds and nuts?
Answer:
Apes like the chimpanzees used stone to break seeds and nuts.
![]()
Question 2.
For what purpose did the apes like the chimpanzees use sticks?
Answer:
Apes like the chimpanzees used sticks to stir ants out from ant-hills to catch them.
Question 3.
What were the tools of the early man made of?
Answer:
The tools of the early man were made of bones, stones, dried twigs and sticks.
Question 4.
Why is the period of time called the ‘Stone Age’? ‘or’ What is meant by ‘Stone Age’?
Answer:
The period of time mainly stone tools found is called the Stone Age.
Question 5.
On what basis is the Stone Age divided?
Answer:
The Stone Age is divided on the basis of the shape and types of tools found.
Question 6.
Into how many periods is the Stone Age divided?
Answer:
The Stone Age is divided into three periods – Old Stone Age, Middle Stone Age and New Stone Age
Question 7.
What is the Old Stone Age also called?
Answer:
The Old Stone Age is also called the Palaeolithic Age.
Question 8.
What does Palaeolithic Age mean?
Answer:
Palaeo means ‘old’ and lithos means ‘stone’. Hence, Palaeolithic Age means the Old Stone Age’.
![]()
Question 9.
What is the Middle Stone Age called?
Answer:
The Middle Stone Age is called the Mesolithic Age.
Question 10.
What does Mesolithic mean?
Answer:
Mesolithic means ‘middle’. Hence, the Middle Stone Age.
Question 11.
What is the New Stone Age called?
Answer:
The New Stone Age is called the Neolithic Age.
Question 12.
What does Neolithic mean?
Answer:
Neo means ‘New’. Hence, Neolithic means the “New Stone Age
Question 13.
Which species of human evolution belong to Old Stone Age?
Answer:
The species Homo habilis and Homo erectus belong to Old Stone Age.
Question 14.
Who used the percussion technique of making tools?
Answer:
Homo habilis and Homo erectus used the percussion technique of making tools.
![]()
Question 15.
How were the frist tools of the Old Stone Age?
Answer:
The tools of the Old Stone Age were very crude
Question 16.
What were choppers?
Answer:
Choppers were crude tools, where only one side of which had a sharp edge.
Question 17.
For what purpose were the choppers used?
Answer:
Choppers were used to break nuts or bones.
Question 18.
Which tools made by Homo erectus were more proportionate and symmetrical than the tools made by Homo habilis?
Answer:
The hand-axe and cleaver were more proportionate and symmetrical” than the tools made by Homo habilis.
Question 19.
What could Homo erectus do before he actually shaped the tools?
Answer:
Homo erectus could mentally visualize his tools before he actually shaped them.
Question 20.
How did Homo erectus use antlers?
Answer:
He used things like antlers as hammers to obtain stone flakes.
![]()
Question 21.
How did Homo erectus make scrapers?
Answer:
He sharpened the edges of the flakes by scraping off smaller pieces to make scrapers with very sharp edges.
Question 22.
What benefits did Homo erectus acquire with his improved tools?
Answer:
With his improved tools, Homo erectus could have a greater variety of food as he could hunt a variety of big and small animals.
Question 23.
Who brought about a revolution in the technique of making tools?
Answer:
Homo sapiens brought about a revolution a in the technique of making tools.
Question 24.
What did the Homo sapiens build to live in?
Answer:
Homo sapiens built huts to live in.
Question 25.
What did the Homo sapiens start celebrating?
Answer:
Homo sapiens started celebrating social festivals.
Question 26.
What did the Homo sapiens create to enhance their festivals?
Answer:
The Homo sapiens created artistic objects and cave paintings to enhance their festivals.
![]()
Question 27.
How did they adorn themselves?
Answer:
They adorned themselves with ornaments and beads made from shells, bones and teeth of animals.
Question 28.
What fossils were found in Madhya Pradesh?
Answer:
Fossils of a human skull and the collar bone of an Old Stone Age woman was found on the bank of Narmada in Madhya Pradesh.
Question 29.
Which fossil was found at a village in Puducherry?
Answer:
A fossilized skull of a child from the Stone Age was found at a village in Puducherry.
Question 30.
Which are the well-known Old Stone Age sites in Maharashtra?
Answer:
Gangapur near Nasik and Chirki-Nevasa near Nevasa are among the few well-known Old Stone Age sites in Maharashtra.
Question 31.
Which animal did man of the Middle Stone Age domesticate?
Answer:
Man of the Middle Stone Age domesticated the dog.
![]()
Question 32.
Why did the life of humans begin to change?
Answer:
The life of humans began to change due to changes in the climate and environment.
Question 33.
What did the Homo sapiens begin to harvest?
Answer:
The Homo sapiens began to harvest food grains that grew in the wild.
Question 34.
How did the humans in the Middle Stone Age make their tools?
Answer:
He used to make implements like the knife and sickle by firmly fixing a row of blades as small as fingernails into a groove in a bone or a piece of wood.
Question 35.
What quality of tools were found in the Neolithic Age?
Answer:
In the Neolithic Age, the stone tools were polished to give a smooth, shiny finish.
Question 36.
What became the routine way of life for the humans in the New Stone Age?
Answer:
In the New Stone Age, agriculture and domestication of animals or animal husbandry had become a routine way of life.
![]()
Question 37.
Where are the sites of the New Stone Age culture in India?
Answer:
The sites of the New Stone Age culture in India are along the Ganga river and in South India.
Question 38.
What did Homo habilis use the flakes of stone for?
Answer:
Homo habilis used the flakes of stone for scraping meat from hide, for chopping meat and other foodstuffs, for sharpening wooden sticks, etc.
Give reasons for the following :
Question 1.
Only stone tools can be found today among those made by humans thousands of years ago.
Answer:
i. Rarely do we find tools made from bones.
ii. Since twigs and sticks decompose easily, we find only stone tools made by humans thousands of years ago.
Question 2.
The beginning of human culture goes back to the Old Stone Age.
Answer:
- The Homo sapiens made significant progress in knowing the environment, making tools for obtaining food.
- This enabled man to lead a stable life and live in one place.
- They started celebrating festivals and adorning themselves.
- Thus, we conclude that the beginning of human culture goes back to Old Stone Age.
![]()
Question 3.
Homo sapiens or the Middle Stone Age man now needed several different types of tools
that were light in weight and durable
Answer:
i. Besides hunting, the Homo sapiens began to undertake a variety of tasks like fishing, harvesting”, cutting of trees etc.
ii. Therefore, they now needed several different types of tools that were light in weight and durable.
Question 4.
Hunting was no more the major means of obtaining food.
Answer:
i. By the time of the New Stone Age, agriculture and animal husbandry became a routine way of life.
ii. Therefore, hunting was no more a major means of obtaining food.
Answer the following questions in brief :
Question 1.
List out the factors that determine the choice of tools.
Answer:
The four factors that determine the choice of tools is as follows:
- Availability of resources
- Minimal use of time and energy
- Maximum efficiency
- Skill of handling tools which is acquired through practice.
![]()
Question 2.
How did man learn to modify his tools?
Answer:
- Man began to observe the environment & nature around him, continuously and minutely
- With his inborn creativity, he learnt that he could sharpen rods, bones, sticks and stones into tools to carry out their task more efficiently.
- He also learnt that he could shape these objects and use it to his advantage.
Question 3.
How can we conclude that the early man used tools made of twigs, bones and stones?
Answer:
- The early man made tools using twigs, bones sticks and other materials available in nature.
- Since twigs and sticks decompose easily, we do not find any tools made from them.
- Only stone tools can be found today. Hence, we can conclude that the early man made tools not only out of stone but other materials also.
Question 4.
How is the Stone Age divided?
Answer:
The Stone Age is divided into 3 periods on the basis of the shape and the types of tools found.
- Old Stone Age or Palaeolithic Age.
- Middle Stone Age or Mesolithic Age
- New Stone Age or Neolithic Age.
Question 5.
What lead the Homo sapiens to lead a more stable life?
Answer:
- Homo sapiens made significant” progress in gaining knowledge of his environment and in the techniques of making tools and obtaining food.
- This enabled him to stay in one place so he build huts to live in
- They celebrated social festivals, made artistic objects and cave paintings.
- They started using ornaments to adorn themselves. All this meant that Homo sapiens lead a very stable life.
![]()
Question 6.
How did the life of humans change during the Mesolithic Age?
Answer:
- Due to the changes in the climate and the environment, the way of life in the Mesolithic Age began to change.
- Besides hunting, man started to harvest food grains that grew in the wild and also domesticated animals.
- Their diet also included various plant foods.
- They settled in one place, made different types of tools that were light in weight and durable, for hunting, fishing, harvesting and cutting of trees.
Question 7.
Compare the tools of all the three periods of the Stone Age.
Answer:
A comparative study of tools of all three periods of Stone Age is as follows:
Old Stone Age
- The tools made during the Palaeolithic Age were very crude.
- Tools were made from any material that was commonly available from nature eg. bones, sticks, twigs and stones.
- They used the percussion technique to make tools like choppers, hand – axe, cleavers and scrapers.
Middle Stone Age :
- The tool making devise had been revolutionized during this period.
- Man devised a technique of obtaining long and narrow blades of stone.
- He made various implements which were sharper, symmetrical and light-weighted than the earlier age.
- He made tools like knife, scraper, borer, chisel etc.
- He also recognized the quality of stones and began to use ivory and rare stones of quartz for making tools.
- He used ‘microliths’ to make arrows. He also made implements like knife and sickle.
New Stone Age :
- The tools made during this age were sharper and more polished.
- Man now made use of a tool-making technique where stone tools were polished to give a smooth and shiny finished look.
- Since hunting became a secondary occupation, man in this age concentrated on making implements for agricultural use.
![]()
Question 8.
Homo erectus could have a greater variety of food.
Answer:
- Homo erectus had improved tools.
- He could now hunt a variety of big and small animals.
- He could thus have a greater variety of food.
Question 9.
Middle Stone Age man began to settle in one place for a part of the year.
Answer:
- Due to changes in the climate and the environment in the Middle Stone Age, the way of life of humans had begun to change.
- The Middle Stone Age man had started to harvest food grains and domesticate animals.
- Thus, he began to settle in one place for a part of the year.
Question 10.
What is meant by a ‘Chopper’?
Answer:
- The first tools in the Old Stone Age were made with the percussion technique and were
crude. - Only one side of these tools had a sharp edge.
- These tools were called ‘Choppers’ and were used to break nuts or bones.
Question 10.
Where were the remains of Old Stone Age found in India?
Answer:
- Remains of the Old Stone Age were found in India at various places from Kashmir to Tamil Nadu.
- Fossils of a human skull and the collar bone of an Old Stone Age woman were found near Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh.
- The fossilized skull of a child was found at a village near Puducherry.
![]()
Glossary :
- domesticated : tame and keep as pet
- durable : not perishable
- Implements : piece le of equipments
- Antlers : branched horns on the head of an adult dear
- crude : in a natural or raw
- proportionate : corresponding in size or amount to something else
- symmetrical : exactly similar parts
- harvesting : gather crops
- acquired : buy or obtain
- minutely : with great attention to detail
- ivory : hard, creamy white elephant tusks
- quartz : a hard mineral, crystal
- significant : sufficiently great or important
- microliths : a small shaped flint
- grinder : machine used for grinding o something
- revolution: a forcible overthrow of a government
- enhance: intensify or o increase