By going through these Maharashtra State Board Secretarial Practice 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 9 Business Communication Skills of Secretary students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Secretarial Practice Notes Chapter 9 Business Communication Skills of Secretary
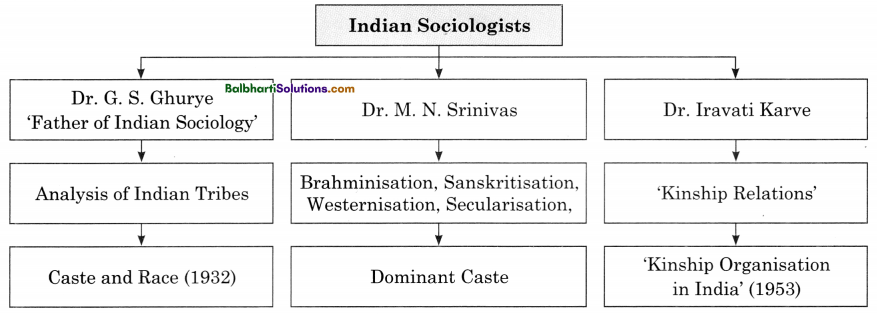
Communication-
- Latin word — ‘Communis’ meaning “Common”- “Shared by all”
- Definition : “It is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons” — George R, Terry
Business Communication : Definition-
“It is the expression channeling, receiving and interchanging of ideas in commerce and industry.” — Brennar
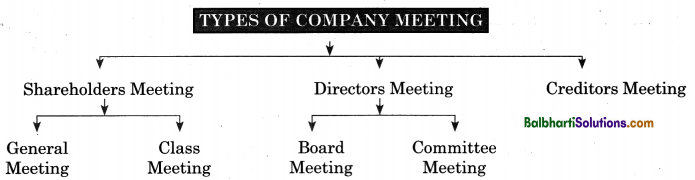
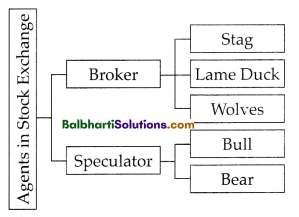
Types of Communication-
- Internal Communication
- External Communication
Internal Communication:
- within various
- departments of an
- organization
External Communication
- between business
- organizations and outsiders.
- (banks, suppliers, creditors, Government, etc.)

![]()
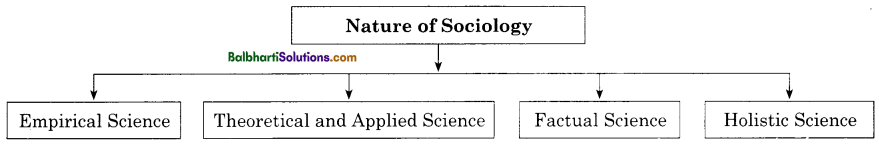
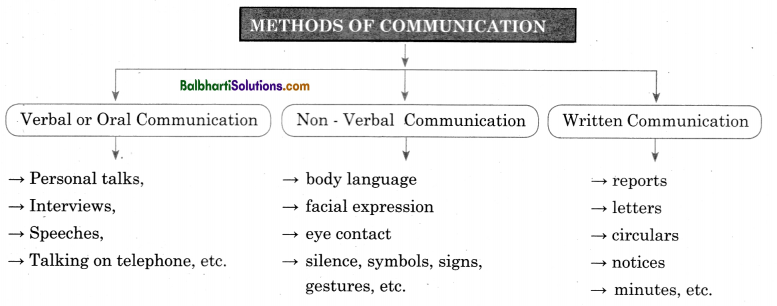
Method of Communication-
- Verbal or Oral Communication
- Non – Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
1. Verbal or Oral Communication
- Personal talks,
- Interviews,
- Speeches,
- Talking on telephone, etc.
2. Non – Verbal Communication
- body language
- facial expression
- eye contact
- silence, symbols, signs, gestures, etc.
3. Written Communicatin:
- reports
- letters
- circulars
- notices
- minutes, etc.
![]()
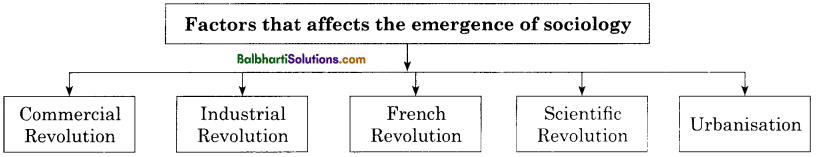
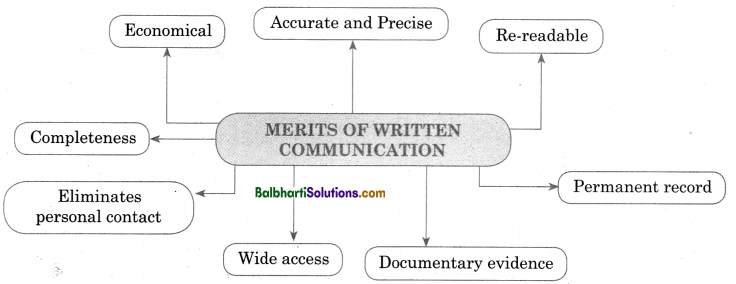
Merits of Written Communication-
- Accurate and Precise
- Economical
- Re-readab1e
- Completeness
- Eliminates personal contact
- personal contact
- Wide acces
- Documentary evidence
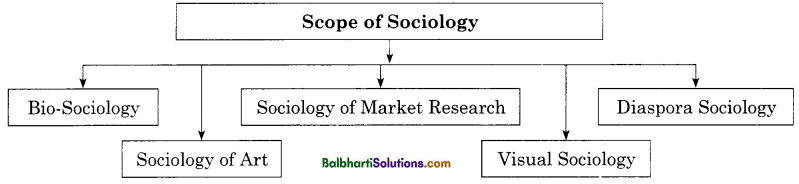
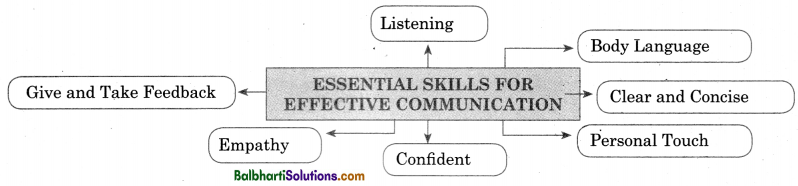
Essential Skills for Effective Communication-
- Listening
- body Language
- Give and Take Feedback
- Clear and Concise
- Empathy
- Confident
- Personal Touch
![]()
Business Letter: “It is a message that attempts to influence its recipients to take some action or attitude
desired by the sender.” – Robert
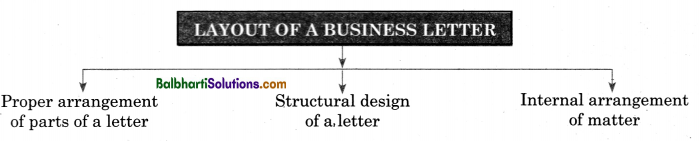
Layout of A Business Letter-
- Proper arrangement of parts of a letter
- Structural design of a. letter
- Internal arrangement of matter
Layout of Business Letter-
- Heading – name, address, telephone number, fax number, email Id, CIN, website, etc.
- Date – British style or American Style
- Reference number – left hand side below heading
- Inside Address – name and address of receiver
- Subject – shows purpose of the letter
- Salutation – left hand margin below inside address
- Body of the letter – introduction, main message and conclusion
- Complimentary close – should match salutation
- Signature – signature and name of person with designation
- Enclosure – written on left hand side as ‘Enel’
- Carbon Copy notation (C.C.) – left hand side below enclosure
- Postscript – additional information after completion of letter
- Identification Initials – initials of dictator and typist
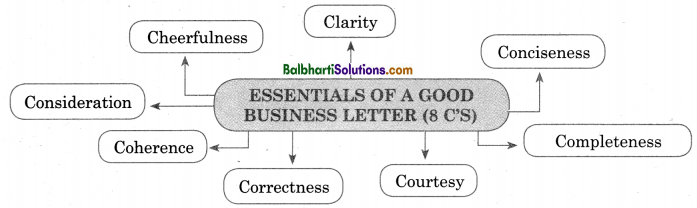
Essentials of a Good Bussiness Letter (8 C’S)
- Clarity
- Cheerfulness
- Conciseness
- Consideration
- Coherence
- Completeness
- Correctness
- Courtesy
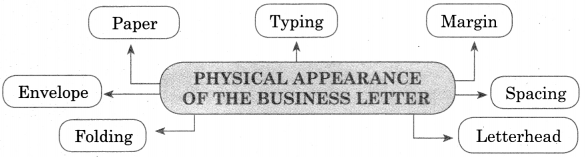
Physical Appearance of the Business Letter-
- Paper
- Typing
- Margin
- Envelope
- Spacing
- Folding
- Letterhead
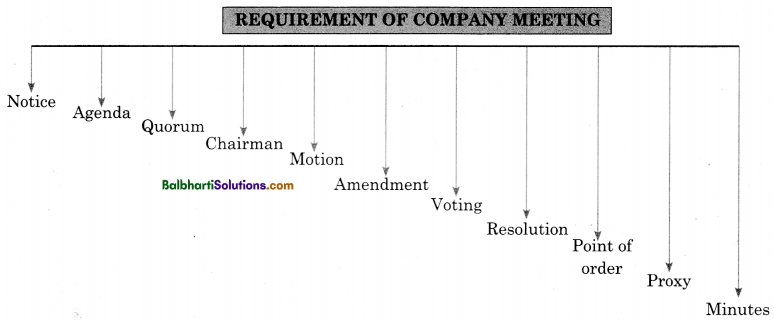
Notice : It is an intimation given by the company to the member about day, date, time, place of the meeting and business to be transacted at the meeting.
![]()
Report: It is a statement of facts or opinion along with conclusion (with or without some recommendations)
Minutes :
- It is a written summary of the business transacted at the meeting.
- It is prepared by secretary, confirmed by members or directors, singed by a Chairman and counter signed by a secretary.
- It is written in past tense within 15 days of a meeting.
- It is written in minutes book in proper format.
Word Meaning:
entities – organization; verbal – oral; conveying – sending; circulars- written information distributed among people; layout – process of setting matter on a page; custom – procedure required: memos – a warning letter in written; draft – outline; authenticity – originality; factual – actual; precision – correctness; insistence – demands; economical – low cost; nominal – reasonable / less; blog – informal written material regularly updated on website; conferring – take part in a conference (meeting); pitch – the rate of sound produced low or high; gestures – to express an idea; empathy – ability to understand other; alignment – arranging in straight line; reference – mention; salutation – greeting; conclusion – finish / to end; brevity – in short; enclosure- additional documents attach to a letter; coherence – put in proper order.