9th Standard Maths 1 Practice Set 3.3 Chapter 3 Polynomials Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 3.3 Algebra 9th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 3 Polynomials.
Class 9 Maths Part 1 Practice Set 3.3 Chapter 3 Polynomials Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
Divide each of the following polynomials by synthetic division method and also by linear division method. Write the quotient and the remainder.
i. (2m2 – 3m + 10) ÷ (m – 5)
ii. (x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5) ÷ (x + 2)
iii. (y3 – 216) ÷ (y – 6)
iv. (2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2) ÷ (x + 3)
v. (x4 – 3x2 – 8) ÷ (x + 4)
vi. (y3 – 3y2 + 5y – 1) ÷ (y – 1)
Solution:
i. Synthetic division:
(2m2 – 3m + 10) ÷ (m – 5)
Dividend = 2m² – 3m + 10
∴ Coefficient form of dividend = (2, -3, 10)
Divisor = m – 5
∴ Opposite of -5 is 5.
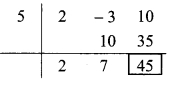
Coefficient form of quotient = (2, 7)
∴ Quotient = 2m + 7,
Remainder = 45
Linear division method:
2m2 – 3m + 10
To get the term 2m2, multiply (m – 5) by 2m and add 10m,
= 2m(m – 5) + 10m- 3m + 10
= 2m(m – 5) + 7m + 10
To get the term 7m, multiply (m – 5) by 7 and add 35
= 2m(m – 5) + 7(m- 5) + 35+ 10
= (m – 5) (2m + 7) + 45
∴ Quotient = 2m + 7,
Remainder = 45
ii. Synthetic division:
(x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5) ÷ (x + 2)
Dividend = x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
∴ Coefficient form of dividend = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
Divisor = x + 2
∴ Opposite of + 2 is -2.
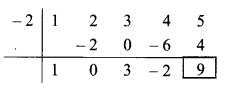
Coefficient form of quotient = (1, 0, 3, -2)
∴ Quotient = x3 + 3x – 2,
Remainder = 9
Linear division method:
x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
To get the term x4, multiply (x + 2) by x3 and subtract 2x3,
= x3(x + 2) – 2x3 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) + 3x2 + 4x + 5
To get the term 3x2, multiply (x + 2) by 3x and subtract 6x,
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 6x + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 2x + 5
To get the term -2x, multiply (x + 2) by -2 and add 4,
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 2(x + 2) + 4 + 5
= (x + 2) (x3 + 3x – 2) + 9
∴ Quotient = x3 + 3x – 2,
Remainder – 9
iii. Synthetic division:
(y3 – 216) ÷ (y – 6)
Dividend = y3 – 216
∴ Index form = y3 + 0y3 + 0y – 216
∴ Coefficient form of dividend = (1, 0, 0, -216)
Divisor = y – 6
∴ Opposite of – 6 is 6.
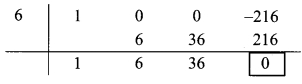
Coefficient form of quotient = (1, 6, 36)
∴ Quotient = y2 + 6y + 36,
Remainder = 0
Linear division method:
y3 – 216
To get the term y3, multiply (y – 6) by y2 and add 6y2,
= y2(y – 6) + 6y2 – 216
= y2(y – 6) + 6ysup>2 – 216
To get the, term 6 y2 multiply (y – 6) by 6y and add 36y,
= y2(y – 6) + 6y(y – 6) + 36y – 216
= y2(y – 6) + 6y(y – 6) + 36y – 216
To get the term 36y, multiply (y- 6) by 36 and add 216,
= y2 (y – 6) + 6y(y – 6) + 36(y – 6) + 216 – 216
= (y – 6) (y2 + 6y + 36) + 0
Quotient = y2 + 6y + 36
Remainder = 0
iv. Synthetic division:
(2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2) ÷ (x + 3)
Dividend = 2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2
∴ Index form = 2x4 + 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x + 0
∴ Coefficient form of the dividend = (2,3, -2,4,0)
Divisor = x + 3
∴ Opposite of + 3 is -3
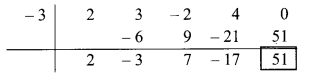
Coefficient form of quotient = (2, -3, 7, -17)
∴ Quotient = 2x3 – 3x2 + 7x – 17,
Remainder = 51
Linear division method:
2x4 + 3x3 + 4x – 2x2 = 2x2 + 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x
To get the term 2x4, multiply (x + 3) by 2x3 and subtract 6x3,
= 2x3(x + 31 – 6x3 + 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x3 – 2x2 + 4x
To get the term – 3x3, multiply (x + 3) by -3x2 and add 9x2,
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 9x2 – 2x2 + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x2 + 4x
To get the term 7x2, multiply (x + 3) by 7x and subtract 21x,
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x + 3) – 21x + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x + 3) – 17x
To get the term -17x, multiply (x + 3) by -17 and add 51,
= 2x3(x + 3) – 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x+3) – 17(x + 3) + 51
= (x + 3) (2x3 – 3x2 + 7x- 17) + 51
∴ Quotient = 2x3 – 3x2 + 7x – 17,
Remainder = 51
v. Synthetic division:
(x4 – 3x2 – 8) + (x + 4)
Dividend = x4 – 3x2 – 8
∴ Index form = x4 + 0x3 – 3x2 + 0x – 8
∴ Coefficient form of the dividend = (1,0, -3,0, -8)
Divisor = x + 4
∴ Opposite of + 4 is -4
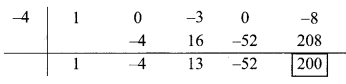
∴ Coefficient form of quotient = (1, -4, 13, -52)
∴ Quotient = x3 – 4x2 + 13x – 52,
Remainder = 200
Linear division method:
x4 – 3x2 – 8
To get the term x4, multiply (x + 4) by x3 and subtract 4x3,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x3 – 3x2 – 8
= x3(x + 4) – 4x3 – 3x2 – 8
To get the term – 4x3, multiply (x + 4) by -4x2 and add 16x2,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2 (x + 4) + 16x2 – 3x2 – 8
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2 (x + 4) + 13x2 – 8
To get the term 13x2, multiply (x + 4) by 13x and subtract 52x,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) – 52x – 8
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) – 52x – 8
To get the term -52x, multiply (x + 4) by – 52 and add 208,
= x3(x + 4) – 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) – 52(x + 4) + 208 – 8
= (x + 4) (x3 – 4x2 + 13x – 52) + 200
∴ Quotient = x3 – 4x2 + 13x – 52,
Remainder 200
vi. Synthetic division:
(y3 – 3y2 + 5y – 1) ÷ (y – 1)
Dividend = y3 – 3y2 + 5y – 1
Coefficient form of the dividend = (1, -3, 5, -1)
Divisor = y – 1
∴Opposite of -1 is 1.
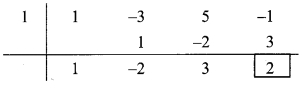
∴ Coefficient form of quotient = (1, -2, 3)
∴ Quotient = y2 – 2y + 3,
Remainder = 2
Linear division method:
y3 -3y2 + 5y – 1
To get the term y3 , multiply (y – 1) by y2 and add y2
= y2 (y – 1) + y2 – 3y2 + 5y – 1
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y2 + 5y – 1
To get the term -2y2, multiply (y – 1) by -2y and subtract 2y,
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y(y – 1) – 2y + 5y – 1
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y(y – 1) + 3y – 1
To get the term 3y, multiply (y – 1) by 3 and add 3,
= y2 (y – 1) – 2y(y – 1) + 3(y- 1) + 3 – 1
= (y – 1)(y2 – 2y + 3) + 2
∴ Quotient = y2 – 2y + 3,
Remainder = 2.
Maharashtra State Board 9th Maths Solution
- Polynomials Practice Set 3.1 Class 9 Maths Solutions
- Polynomials Practice Set 3.2 Class 9 Maths Solutions
- Polynomials Practice Set 3.3 Class 9 Maths Solutions
- Polynomials Practice Set 3.4 Class 9 Maths Solutions
- Polynomials Practice Set 3.5 Class 9 Maths Solutions
- Polynomials Practice Set 3.6 Class 9 Maths Solutions
- Polynomials Problem Set 3 Class 9 Maths Solutions