By going through these Maharashtra State Board Bookkeeping and Accountancy 11th Notes Chapter 6 Bank Reconciliation Statement students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Accounts Notes Chapter 6 Bank Reconciliation Statement
Meaning, Importance, And Utilities of Accounting Documents-
The documents which explain all the basic facts (information) of cash and banking transactions such as the date, amount, parties, and purposes of transactions are called Accounting documents. Accounting documents also provide evidence of financial transactions on account of the introduction and increasing use of the Internet and mobile banking, the functioning of the modern bank has undergone a drastic change. Payments and receipts of cash through the internet and mobiles generate instant and automatic evidence useful for concerned parties. Even today payments and receipts are made through cheques and drafts. Similarly a large number of banking transactions are completed by the account holders through visiting the banks.
Types of Bank Documents-
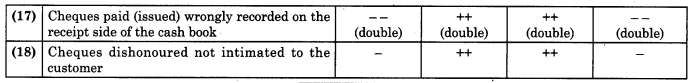
1. PAY-IN-SLIP: Pay-in-slip is an important source document used by the account holder for depositing cash as well as cheques into the bank account. A pay-in-slip book consists of 10 slips or 100 slips. Each slip is divided into two parts, each of which can be separated easily from the other. The longer part of the slip is called foil and the smaller part is called counterfoil.
Before depositing cash or cheque into the bank, account holder is required to fill up both the parts of pay-in-slip. Information regarding name of the account holder, his account number, amount in figures and words, signature, etc is required to be filled up on both the parts of the pay-in-slip. The cashier of the bank accepts cash or cheque along with the duly filled up pay-in-slip. The foil of pay-in-slip remains with the bank for making records in the books of the bank and the counter foil after stamping and signature of the cashier is given back to the account holder for his own reference. Separate pay-in-slips are used for depositing cash and cheque.
The pay-in-slip is a bank printed form provided by the bank free of charge to the account holders to facilitate them to deposit cash or cheque into the bank. On the basis of slip entries are made in the cash book as well as in the bank passbook.
![]()
Contents: The pay-in-slip contains the following details:
- Name of the bank and its branch. Usually, they are printed.
- Date of banking transaction.
- Name of the account holder.
- Account No.
- Types of Account.
- Amount deposited in words as well as in figures.
- Form of amount deposited i.e. cheque/cash.
- Signature of the depositor.
- Signature of officer in charge and stamp of bank.
- On the backside of the pay-in-slip, the details of cash or cheque deposited are given.
(a) Specimen form of pay-in-slip is given below: From side.
(b) Reverse (Back-side) of Pay-in-Jip :
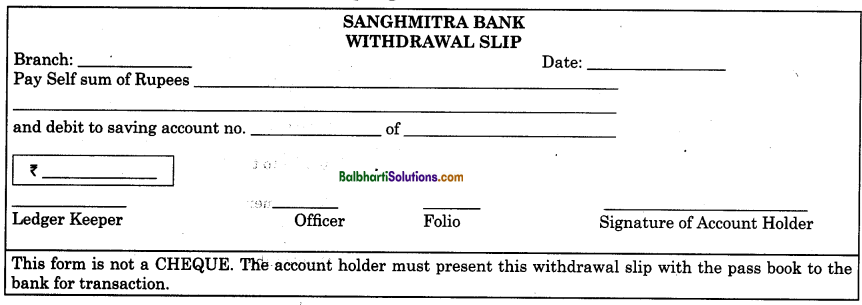
Withdrawal Slip:
A source document which is used by the account holder for withdrawing cash from the bank is called withdrawal slip. It is used to withdraw the amount from Savings Account. Before withdrawing cash from the bank, an account holder is required to fill up a withdrawal slip. Information regarding the name of the account holder, his account number, amount in figures and in words, date, signature, etc. are required to be filled up. The account holder is also required to sign on the back of the withdrawal slip. Both the signatures made on withdrawal slip must be matched with the specimen signature recorded in the computer. This is to avoid malpractices.
A person other than an account holder can also withdraw money with the help of a withdrawal slip. In such case, a person appointed to withdraw the money is required to sign on the reverse of the withdrawal slip below the signature of the account holder. While withdrawing the money from the bank, the withdrawal slip must be accompanied by the bank passbook. An account holder is not allowed to carry withdrawal slips outside the bank premises. It is a bearer document. This is because the person holding duly filled in and signed by the account holder can easily withdraw the amount from the bank by signing on the backside. In the case of use of withdrawal slip, account holder gets no document from the bank on such withdrawal.
Contents: Withdrawal slip contains the following details:
- Name of the Bank and its branch. They are generally printed.
- Date of withdrawal of cash.
- Name of the account holder.
- Account Number.
- Amount in words as well as in figures.
- Signature of account holder.
Specimen form of a withdrawal slip is given below.
Bank Pass Book:
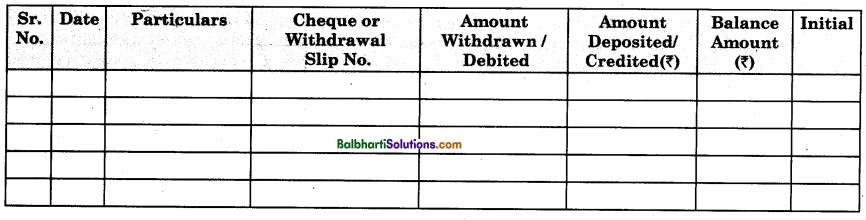
A bank passbook is a small booklet given by the bank to the account holder free of charge. In the passbook, an account holder’s transactions with the bank are recorded by the banker chronologically. A passbook is a copy of ledger account appearing in the books of bank. The entries in the passbook are made by the banker.
Nowadays printed entries in the passbook are made through computer. This book has a number of pages and on each page, there are several columns like Sr. No., date, particulars, cheque or withdrawal slip nos., amount deposited, amount withdrawn, balance amount and initials of bank clerk, etc. An account holder is required to carry a bank pass book whenever he goes to bank for a transaction. The bank passbook serves as an identity of the account holder. Account holder cannot pass any entry or make any changes on the Bank passbook.
Importance:
- Bank passbook shows the balance of amount i.e. standing position of account holder with the bank on a particular date.
- It is a documentary proof accepted as an evidence of banking transactions in the court of law.
- It gives confirmation by the bank that all the transactions are made through the bank.
![]()
Contents:
- Date of transaction.
- Particulars regarding banking transactions.
- Cheque No.
- Amount withdrawn from the bank.
- Amount deposited into the bank.
- Balance amount.
- Signature of Bank clerk or officer.
Specimen form of the Bank Pass Book is given below:
![]()
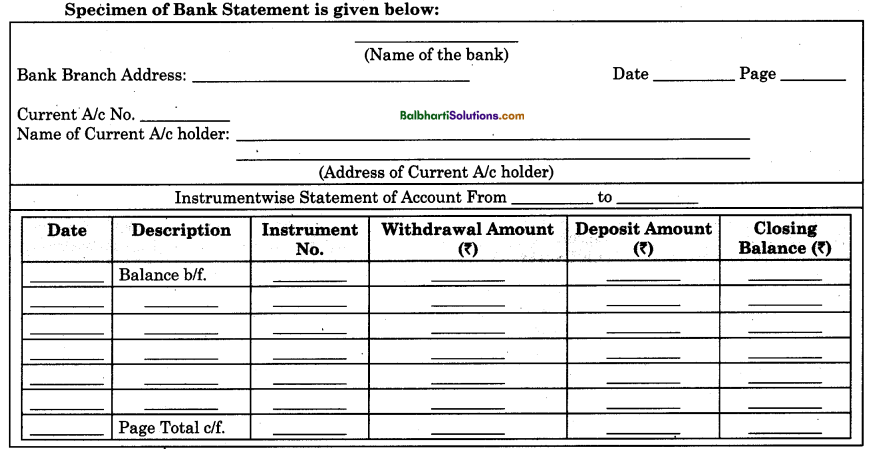
Bank Statement:
A statement which shows the details of the banking transactions of the account holder during a specific period of time is called a bank statement. It is issued by the banker to its current account holders every month or after a fixed interval of time. It is usually issued by the bank at the end of every month. It may be issued by the bank whenever demanded by the current account holders. It substitutes to the bank passbook.
The current account holder gets a bank statement in place of the bank passbook. Nowadays, many schedule bank instead of issuing the bank passbook, issues a bank statement to its current account holders as well as savings account holders. Periodical information about the deposits of money and cheques in the bank account, withdrawals, issue of cheques opening balance and closing balance, etc., are recorded in the bank statement. Information provided in the bank statement is useful to the account holder to prepare his business plans.
Under computerised accounting system, the printouts of the bank statement are issued to Current Account holders.
Importance:
- The Bank statement provides the information to current account holder about his banking transactions and balance position with the bank.
- By referring bank statement businessman makes arrangement for payments.
- By referring bank statement, the businessmen can try to arrange for overdraft facility from the bank.
- Businessman knows about the clearing of the cheque deposited and issued.
Contents:
- Date of banking transactions.
- Particulars of banking transactions entered.
- Cheque numbers.
- Withdrawal slip nos.
- Amount deposited into the bank.
- Amount withdrawn from the bank.
- Balance amount.
Specimen of Bank Statement is given below:
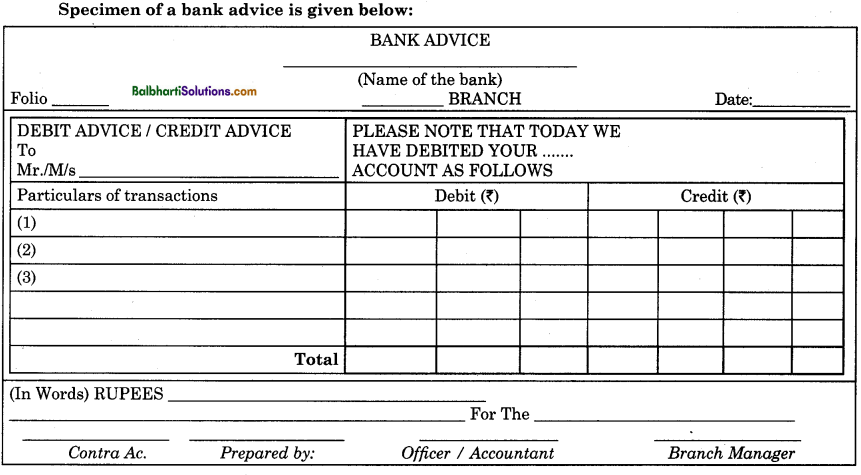
Bank Advice: Bank advice is a statement or source document prepared and issued by the bank to inform the account holder that his account has been debited or credited for the amount specified therein. If an account holder gives instructions in writing to the bank to pay certain business expenses like insurance premium, share call money, electricity bill, telephone charges, etc., the bank accordingly makes payments and debits the account of the account holder. Similarly, the bank also collects the earnings as well as incomes like salaries, rent, commission, dividend, discount, etc., of the account holders as per their instructions on their behalf and credit their accounts for the amount so collected.
When a bank makes payments to account holders, it issues debit advice to the concerned account holder to inform that his account has been debited for the payments so made by the bank. A Debit advice is also issued by the bank whenever the bank deducts certain charges or commission from the balance amount of the account holder with the bank for the services rendered. Similarly, when a bank collects the fund as per instructions of the account holder from various parties, it issues a credit advice to the concerned account holder to inform that his account has been credited for the account so collected.
Importance:
- After receiving debit advice and credit advice, the businessman can update his records from time to time.
- Bank advice serves as an evidence of the transaction made through bank.
Specimen of a bank advice is given below:
![]()
Bank Reconciliation Statement-
1. Introduction: When a businessman opens and operates a current account in a bank, he gets a bank passbook, cheque book and a pay-in-slip book free of charge from the bank to operate his bank account. The bank opens the account holder’s account in its ledger and enters therein all the banking transactions carried on with the account holder. The bank passbook is a small booklet in which banking transactions of account holder are recorded by the bank in chronological order.
Thus, the account holder’s banking transactions are recorded in two different books viz. first they are recorded by businessman (i.e. by account holder) in his three column cash book under bank column and secondly they are recorded in the bank passbook by the bank from the bank ledger. For instance, if an account holder has issued a cheque of ₹ 500 in favour of Mr. Sachin S. Shetty, it is first recorded in the three column cash book on credit side under bank column by account holder and then it is recorded on the debit side of bank passbook by the bank soon after it is paid by the bank. When all the banking transactions of account holder are systematically recorded in the cash book and in the passbook, then balance shown by cash book and balance shown by bank passbook as on particular date must agree with each other.
Many a times bank balance shown by passbook and bank balance shown by cash book do not tally with each other. The account holder prepares a statement showing causes of disagreement between two balances usually at the end of every month.
2. Meaning: Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement which attempts to explain causes of disagreement of balance shown in cash book and balance shown in Bank passbook. In short a Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement prepared to disclose causes of difference between the balances shown by cash book and passbook. Importance of Bank Reconciliation Statement lies in the fact that it ensures that the bank balance shown. by cash book is reconciled with that of the bank passbook.
Definition: “A statement which is prepared to reconcile the difference between the balance shown by bank column of cash book and balance shown by bank passbook and also showing causes of disagreement of these two balances is called Bank Reconciliation Statement.”
3. Need And Importance of Bank Reconciliation Statement-
- Proper Records: Bank Reconciliation Statement serves a check or follow up on the banker whether the bank is making proper entries in the passbook for cheque or money deposited into the bank and amount withdrawn or cheques issued from the bank.
- Explanation of Causes of Disagreement: Bank Reconciliation Statement, explains and clarifies the causes of disagreement between the balance shown in the cash book under bank column and the balance shown in the passbook.
- Rectification of Errors or Omissions: Bank Reconciliation Statement helps to rectify the mistakes or omissions that take place in the books maintained by the banker as well as the customer.
- Confidence in Bank: In the absence of a Bank Reconciliation Statement, a customer will lose confidence in the bank, because the customer cannot be sure of the correctness of the bank balance depicted in the bank passbook.
- Reduction in the chances of frauds: The Bank Reconciliation Statement helps to reduce the chances of frauds committed by the staff handling the cash.
- Delay in collection of cheques: The Bank Reconciliation Statement explains any delay in the collection of cheques.
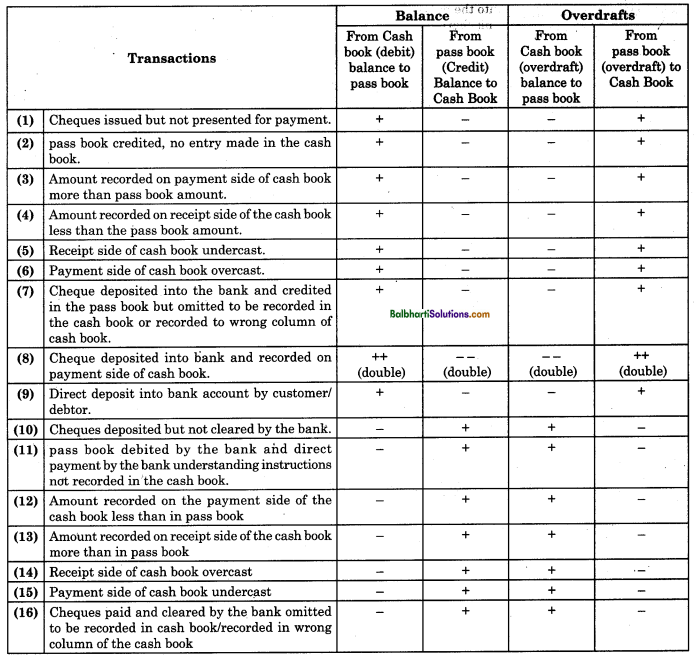
Reasons For Differences in Balances-
Reasons or causes responsible for difference in balance shown by passbook and balance shown by cash book are explained below:
1. Some of the banking transactions are entered in the cash book and pass book on different dates, e.g. as soon as cheques are sent to the bank, entries are made in the cash book. But the bank records the same in the passbook only when the cheques are realised, (cheques are deposited but not cleared), then on the date of deposit of the cheques, bank balance in cash book will go up. But passbook balance will not go up, and balance in passbook appears as it is.
2. If some mistakes or omissions are committed by the bank clerk in the pass book or if mistakes or omissions are committed by the businessman in recording business transactions in the three column cash book, then there will be a difference in the balance shown by the passbook and the balance shown by cash book.
3. If banking transactions are entered twice by the bank clerk in the passbook or if they are entered twice by businessman in his cash book, then difference in bank balance in cash book and balance in bank passbook are bound to occur.
4. If banking transactions are recorded by a businessman on the wrong side or in the wrong column of the three-column cash book, difference between balance shown by pass book and cash book are bound to occur.
5. The difference between the balance shown by the Cashbook under Bank column and the balance shown by the passbook also occurs on account of the following reasons:
- When cheques are issued but not presented for payment.
- When direct deposit is made into the bank by the client. .
- Dividend/Interest/Commission collected by the bank but not shown in the cash book.
- Bank charges/direct payment to clients made by the Bank, but not shown in the cash book.
- Dishonour of cheque intimation not received from the bank to record in the cash book.
![]()
Specimen Form of Bank Reconciliation Statement-

Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31st March, 2004-
Formulae of Bank Reconciliation Statement:
(A) When bank balance as per Cash Book is given:
- Cheque issued but not presented for payment.
- Interest and dividend collected by the bank and credited in the passbook, but are not recorded in the cash book
- Direct deposit made by the customer into the bank and credited in the passbook.
- Interest on deposit allowed by the bank and credited in the passbook, but not recorded in the cash book.
Less:
- Cheque deposited into the bank but not realised.
- Commission and bank charges debited by the bank in the passbook but same are not recorded in the cash book.
- Insurance premium or any other expenses paid by the bank recorded in the passbook but is not recorded in the cash book.
- Dishonour of a bill or cheque, recorded in the bank passbook, but not entered in the cash book.
(B) When Overdraft as per Cash Book is given :
Add:
- Cheque deposited into the bank but not realised.
- Commission and bank charges debited by the bank in the passbook but same are not recorded in the cash book.
- Insurance premium or any other expenses paid by the bank and debited in the passbook but is not recorded in the cash book.
- Dishonour of a bill or cheque, recorded in the bank passbook, but not entered in the cash book.
- Interest on Bank overdraft debited in passbook only.
Less:
- Cheque issued but not presented for payment.
- Interest and dividend collected by the bank and credited in the passbook but not recorded in the cash book.
- Direct deposit made by the customer into the bank and credited in the passbook but not entered in the cash book.
- Interest on deposit allowed by the bank and credited in the passbook, but not recorded in the cash book.
(C) When Bank balance as per pass book is given:
Add:
- Cheque deposited into the bank but not realised.
- Commission and bank charges debited in the passbook by the bank, but same are not recorded in the cash book.
- Insurance premium or any other expenses paid by the bank and debited in the passbook but same is not recorded in the cash book.
- Dishonour of cheque or bill of exchange recorded by the bank in passbook but not entered in the cash book.
Less:
- Cheque issued but not presented for payment.
- Interest and dividend collected by the bank and credited in the passbook but not recorded in the cash book.
- Direct deposit made by customer into the bank and credited in the passbook but not entered in the cash book.
- Interest on deposit allowed by the bank and credited in the passbook, but not recorded in the cash book.
(D) When Overdraft as per pass book is given:
Add:
- Cheque issued but not presented for payment.
- Interest and dividend collected by the bank and credited in the passbook but not recorded in the cash book.
- Direct deposit made by customer into the bank and credited in passbook but not entered in the cash book.
- Interest on deposit allowed by the bank and credited in the passbook but not recorded in the cash book.
Less:
- Cheque deposited into the bank but not realised.
- Commission and bank charges debited in the passbook by the bank but same are not recorded in the cash book.
- Insurance premium or any other expenses paid by the bank and debited only in the passbook.
- Dishonour of cheque or bill of exchange recorded by the bank in the passbook but not entered in the cash book.
- Interest on Bank overdraft debited in passbook only.
Position in Cash Book
- Bank balance as per cash book means debit balance as per cash book.
- Overdraft as per cash book means credit balance as per the cash book.
Position in Pass Book
- Bank balance as per pass book means credit balance as per passbook
- Overdraft, as per pass book means debit balance as per pass book,
(B) Method to ascertain items to be added to and deducted from balance.