By going through these Maharashtra State Board Book Keeping & Accountancy Notes 12th Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership and Partnership Final Accounts students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Accounts Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership and Partnership Final Accounts
Introduction, Meaning and Definition of Partnership-
Introduction : When development of single ownership firm takes place or when expansion of the business is planned then naturally, third party help is mandatory. The partnership firm is emerged from capital and managerial limitations of single ownership firms. Hence, when two or more persons, competent to enter into a contract, make an agreement, contribute required capital, undertake certain lawful business for earning profit and sharing the same in agreed proportion, then such union is termed as ‘Partnership’.
The persons who have entered into partnership are individually known as ‘Partner’ and collectively known as a ‘Firm’.
Meaning : Partnership is a business organization, where more than one person come together, make an agreement, contribute capital to carry on a lawful business with the primary objective of earning profit.
Definition : Section 4 of the Indian Partnership Act. 1932 defines a partnership as, “The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all. ”
Prof. Haney defines partnership as, “The relation existing between persons competent to make contract who agree to carry on a lawful business in common with a view to earn private gain. ”
![]()
Features of partnership firm : The main features of partnership firm are stated below :
(1) Agreement: Foundation of partnership is agreement. Agreement may be either in oral or in written form. Written form of agreement is advisable because it can be used as a proof in the court of law, in case of any future disputes. The written agreement is termed as partnership deed.
(2) Number of partners : Minimum two persons are required to form the partnership firm. According to the Companies Act 2013, maximum number of partners is fifty.
(3) Lawful business : The business undertaken by partnership, must be lawful. It cannot undertake illegal activities or business not permitted by law.
(4) Sharing of profit and losses : Main objective of partnership is to earn maximum profits, and distribute it among the partners in agreed proportion. Profit or loss is to be shared equally among the partners if the agreement is silent on ratio.
(5) Unlimited liability : The liability of all partners except minor partner is unlimited. The creditors can claim and recover their dues from the private property of partners, if business property is not sufficient to settle their claims. If any partner is declared insolvent, then his liability is to be borne by the solvent partner.
(6) Registration : According to the Indian Partnership Act 1932, registration of partnership firm
is optional. However, registration of partnership firm is made compulsory only in the state of Maharashtra. Registration means entering the name of partnership firm in the register maintained by the Registrar after the completion of required formalities.
(7) Joint ownership and management : Each partner is joint owner of the property of the firm. So any partner of the firm cannot use property of firm for personal use. Each partner has right to participate in the management of a firm, so all the partners are jointly responsible for all the activities of the firm.
(8) Principal and Agent : Partners carrying on business, works as a Principal and Agent. A partner
act as a principal of the firm for business concerned persons or outsiders and act as a partner with other partners of a firm.
(9) Dissolution : Dissolution of firm means closure of business of the firm. Dissolution of partnership firm is simple and easy. Any one of the partners can take active part to dissolve the firm by giving fourteen days notice. Unless there is an agreement, partnership gets dissolved on death, retirement or insolvency of a partner.
Partnership Deed : A partnership is contractual relationship. Agreement may be oral or written. An agreement which is written and signed by all the partners is called Partnership Deed. It contains terms and conditions of partnership and also rules relating to internal management of the firm.
![]()
The usual contents of a partnership deed are : (1) Name and address, Telephone nos., e-mail address of the firm and its main business. (2) Name, addresses and other information of all partners and duration of the partnership. (3) The amount of capital contributed or to be contributed by each of the partners. (4) The profit and loss sharing ratio of the partners. (5) Rights, duties and liabilities of all partners. (6) Provisions for admission, retirement and death of partner. (7) Rate of interest on capital, loan and drawings, if any. (8) Salaries, commission, etc. payable to partners or any partner. (9) Procedure for dissolution of the firm and settlement of accounts after dissolution.
(10) The methods of settlement of disputes among the partners. (11) Other terms and conditions relating to the conduct of business which are agreed by all the partners.
Importance of Partnership Deed : As partnership deed contains all the terms and conditions of partnership and haying bases of mutual relationship among the partners, it is known as a very important document. With the help of partnership deed, rights, duties and liabilities of all partners and firm can be regulated. To avoid any disputes in future, Partnership Deed duly signed by all the partners and registered under the Indian Partnership Act 1932 is always advisable.
The Indian Partnership Act 1932-
At the time of commencement of partnership, partnership deed is prepared which contains all the required terms and conditions of Partnership. However, if there is no agreement, written or oral, and if partnership deed is silent about any issue among the partners, provisions of the Indian Partnership Act 1932, section 12 and 17 are made applicable, which are as follows :
(1) Distribution of Profits : In the absence of partnership deed or if partnership deed is silent about profit and loss ratio, profits or losses are to be shared equally among the partners.
(2) Interest on Drawings : As per the provisions of the Indian Partnership Act 1932, no interest is to be charged on drawings made by the partners. If provisions are made in the partnership deed in respect to payment of interest on drawings, then interest on drawings is charged. If the date of withdrawal of money is not given, then interest on drawings is charged for average period of 6 months.
(3) Interest on Partner’s Loan : As per the provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, if any partner has advanced loan to the firm over and above his capital contribution, such a loan is to carry interest @ 6 % per annum. However, if any provision is made In the partnership deed In respect to payment of interest on loan given by a partner to partnership, then interest is paid on such loan at the specified rate.
(4) Interest on Capital : As per the provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 no partner is entitled to receive any interest on his capital contribution. However, if provisions are made in the partnership deed in respect to payment of interest on capital, then partners are entitled to receive interest on their capital contributions as per the rate of interest mentioned in the agreement.
(5) Salary or Commission to Partners : As per the provisions made in the Indian Partnership Act,
1932, no salary, commission, allowance or any remuneration is to be given to any of the partners for any extra work done by partners for the firm. However, if any provision is made in partnership deed, then partners are entitled to get commission or salary as per the agreement.
(6) Admission of a new Partner : As per the provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, no outside person can be admitted into the firm as a partner without the consent of all partners.
Methods of Capital Accounts-
Amount in cash or in kind brought in by the partner to manage business activities is called Capital. The capital contribution may be in the form of cash or in the form of assets other than cash, e.g. Goods, Machinery, Land, Buildings, Furniture, etc. An amount of capital may be either in their : profit sharing ratio or in equal ratio. Such amount of capital may be in any proportion as per the mutual understanding of the partners. There are two methods of maintaining the capital accounts of the partners, viz. (1) Fixed Capital Method and (2) Fluctuating Capital Method.
The Indian Partnership Act, 1932 is silent on the point of adoption of specific method of capital by the Partnership firm. The partners themselves may decide which method of capital is to be followed and mention the method of capital adopted in the partnership deed. If partnership deed is silent on
this point, then the partnership firm has to adopt Fluctuating Capital Method.
Fixed Capital Method : Under this capital method opening balance of capital of a partner remains same upto at the end of that financial year. These capital balances will change only when partner introduces an additional capital or withdraws a part of his capital from the firm. Under Fixed Capital Method, along with capital account, a separate personal account, called Current Account is also opened and operated for every partner to record other dealings of partner with the partnership firm.
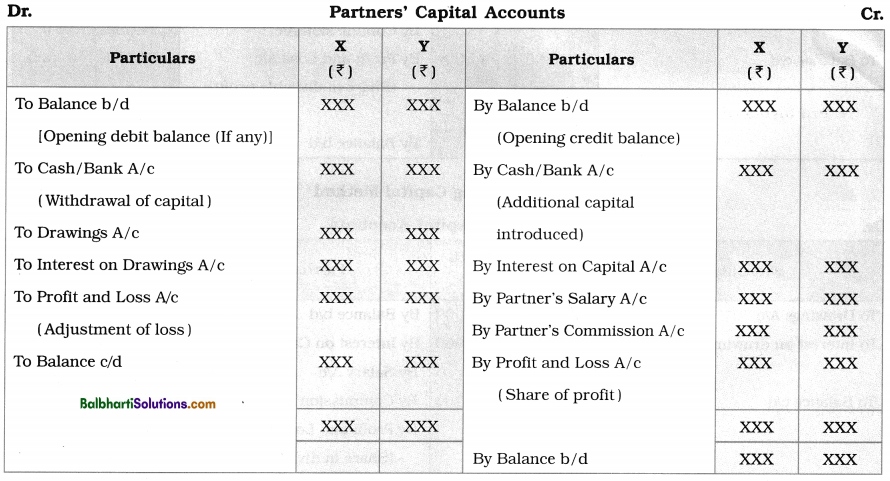
(i) Partner’s Capital Account: In this account the entries for the following transactions are recorded :
- Amount contributed by the partner in the beginning or opening balance of capital if the partnership firm is already established its business.
- Additional capital if any introduced by the partner during the accounting year.
- Part of the capital withdrawn by the partner during the accounting year.
Usually Partner’s Capital Account shows credit balance and it is shown on the Liabilities side of Balance Sheet.
![]()
Pro forma of Partners’ Capital Accounts : The pro forma of Partners’ Capital Accounts prepared under Fixed Capital Method is shown below : It is assumed that there are two partners, viz. X and Y.
Journal Entries:
(1) When cash is brought In the firm by the partner as additional capital:

(2) When additional capital is introduced in the firm by the partner in the form of Assets:

(3) When part of the capital is withdrawn by the partner:

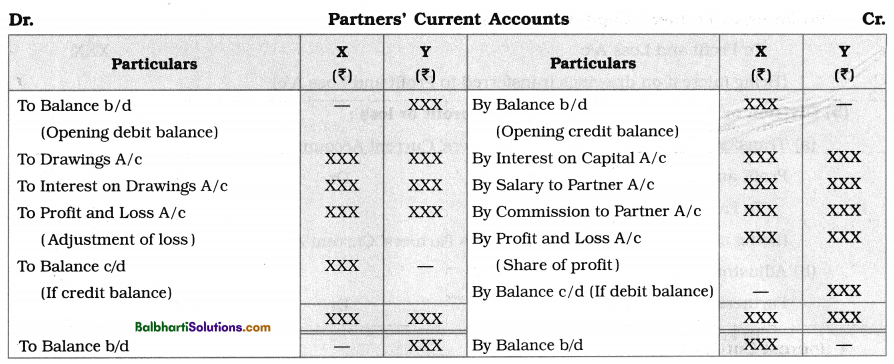
(ii) Partners’ Current Accounts : If Fixed Capital Method is adopted by the firm, then Current Account for each partner is opened and operated. In Current Account, following transactions are recorded :
- Drawings (if any) made by the partner in the current accounting year.
- Cash or goods or any other asset taken over by the partner.
- Interest on Partners’ Capital allowed by the firm.
- Interest on Partner’s Drawings charged by the firm.
- Salary, commission, rent, interest on loan, allowance, etc. payable to the partner.
- Distribution of net profit or net loss of the firm.
Pro forma of Partners’ Current Accounts : The pro forma of Partners’ Current Accounts prepared under Fixed Method is shown below : in the following pro forma ledger accounts, it is assumed that X’s Current A/c showed a credit balance and Y’s Current A/c showed a debit balance at the beginning of the year.
Journal Entries :
(1) Interest allowed on Partners’ capital :

(2) Salary/Commission allowed to Partners :

![]()
(3) Cash/Goods withdrawn by the partners from the business for their personal use :

(4) Interest charged on Partners’ Drawings :


(5) Division or distribution of net divisible profit or loss :

Partners’ Current Accounts may either show debit balance or credit balance. Credit balances of Partners’ Current Accounts are transferred to Liabilities side of Balance Sheet. Similarly, debit balances of Partners’ Current Accounts are transferred to Assets side of Balance Sheet.
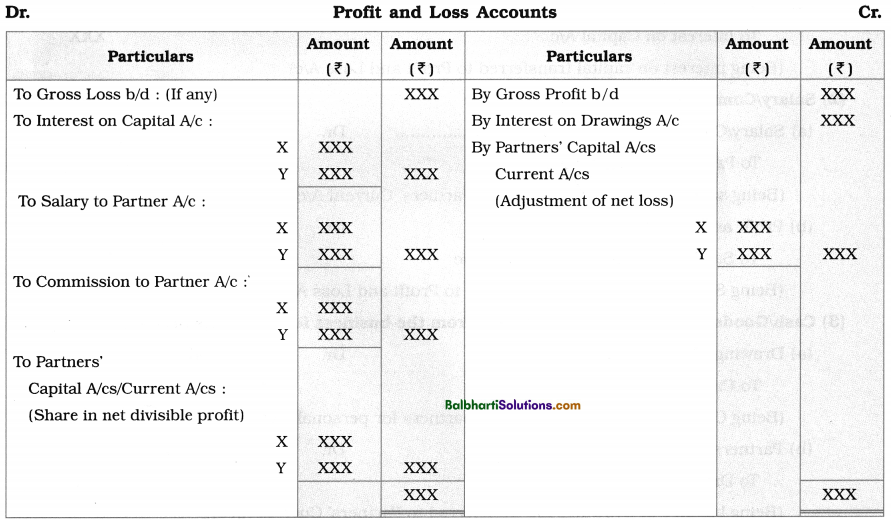
Effects of above entries in Profit and Loss A/c is as follow :
Pro forma of Profit and Loss Account :
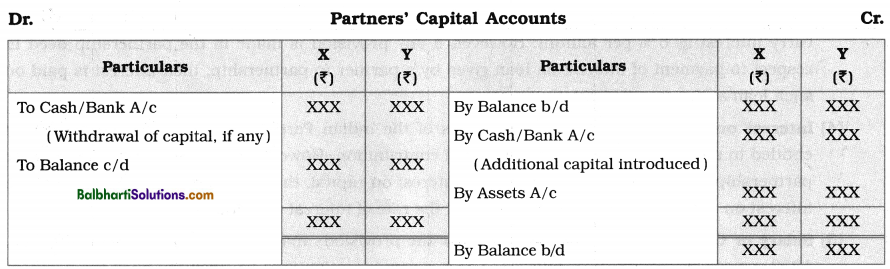
Fluctuating Capital Method : In the Fluctuating Capital method, balances on capital accounts changes every year. Under this method, to record partners dealings with partnership firm, only one account ‘Capital Account’ is opened and following transactions are recorded in it:
- Initial or opening balances of capital
- Additional capital brought in by partners in form of cash or its kind (Assets)
- Salary/Commission payable to partners
- Interest payable on capital balance to partners
- Drawings made during the year and interest payable on drawings by the partners
- Withdrawal of part of the capital by the partners
- Division and transfer of net divisible profit or net adjustable loss of the firm.
The credit balances of fluctuating capital accounts of the partners are recorded separately on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
![]()
Pro forma under Fluctuating Capital Method :