By going through these Maharashtra State Board Book Keeping & Accountancy Notes 12th Chapter 2 Accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ Concerns students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Accounts Notes Chapter 2 Accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ Concerns
Introduction-
In the society we come across with two types of organisations viz. (1) Trading organisation or Profit making organisation and (2) Non-trading organisation or Not for profit-making organisation.
Aim of Trading organisation/concern is to earn maximum profit by undertaking process of manufacturing goods or purchase of goods and sells them at a profit or to earn income by rendering services to its customers. Trading concerns prepare Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet to ascertain the profit of the firm and financial position of the firm. Examples of trading organisations are : Sole proprietorship firm, Partnership firm, Public and Private companies, Co-operative organisations, etc. Other type of organisations are Non-trading organisations and the aim of these type of concerns is not to earn profit but to give services to its members or services to the society at large.
Non-trading organisation prepare Receipts and Payments Account to get summary of cash transactions, prepare Income-Expenditure Account to ascertain whether their incomes are sufficient enough to meet their expenditures and prepare Balance sheet to know financial position of organisation as on a particular
date.
![]()
Not for Profit Organisation:
- Formed for promotion of art, culture, religion, sports, charity, health, education, etc.
- Main objective is to provide services to its members or society without profit motive.
- Collects income through subscriptions, donations, admission fees from members and grants, subsidies, concessions from Government.
- Spends its income to promote its objectives.
- Never pays dividend to its members.
Meaning of ‘Not for Profit’ Concern-
A concern or an organisation which is formed and established to serve its members and society or general public by undertaking various activities without any profit motive is called a ‘Not for Profit’ concern or organisation. Main objective of these concerns, is to provide social service and to promote art, culture, sports, education, etc. ‘Not for Profit’ concerns collects income through different sources such as subscription from its members, entrance fees / admission fees, donations, government grants or aid, subsidies, etc.
Features of ‘Not for Profit’ Concern-
The features of ‘Not for Profit’ concern are explained as follows :
- Objective :‘Not for Profit’ concern undertakes various activities without any profit motive to promote art, culture, education, religion, sports, charity, health, etc. Its primary objective is to provide goods and services to its members.
- Dividend : ‘Not for Profit’ concern is not allowed to make the payment of any dividend to its members.
- Membership :Any person who is interested in the organisation can become its member by contributing towards entrance fees, life membership fees, subscriptions, etc.
- Democratic Management : The management of this organisation or concern is looked after by the elected representatives of the members. The elected representatives form themselves into a managing committee or governing body. They elect a Chairman and other office bearers such as secretary, treasurer, etc. The Chairman is the official head of the concern. Usually office bearers are working on an honorary basis.
- Accounts to be prepared : It prepares Income and Expenditure Account to record incomes and expenses of the concern and to find out surplus or deficit. Excess of income over expenditure is called surplus while excess of expenditure over income is called deficit.
- Capital fund : It is necessary for every such organisation to have its capital fund. The capital fund of the organisation includes entrance fees, surplus, legacies and donations specifically received, for creating capital fund, etc. The excess of assets over liabilities is also termed as ‘Capital Fund’.
- Special funds :Any receipts, donations or grants received for creation of a certain funds, e.g. Prize fund, Building fund, etc. are credited to such specific funds.
![]()
Difference between Profit Organisation and ‘Not for Profit’ Organisation-
Profit Organisation:
- Meaning: An organisation which Is established with the objective of earning profit and serving society through undertaking production or distribution of goods or services is called Profit organlsat1on.
- Primary Objective: Primary objective is to earn profit.
- Trial Balance: It prepares Trial Balance.
- Net Result: It prepares Profit and Loss A/c to ascertain net result in the form of profit or loss.
- Accounting Statements: It prepares the following accounting statements:
(1) Trading Account (2) Profit and Loss Account and (3) Balance Sheet. - Owner’s Fund /Capital Fund: Capital balance and balances in Reserves and Surplus together constitute owners fund/capital fund.
‘Not for Profit’ Organisation:
- Meaning: An organisation which is established to serve its members and society or general public by undertaking various activities without any profit motive, is called a ‘Not for Profit’ organisation.
- Primary Objective: Primary objective is to provide services.
- Trial Balance: It prepares Receipts and Payments Account.
- Net Result: It prepares Income and Expenditure A/c to find out net result in the form of deficit or surplus.
- Accounting Statements: It prepares the following statements: (1) Receipts and Payments Account (2) Income and Expenditure Account and (3) Balance Sheet.
- Owner’s Fund/ Capital Fund: Capital fund includes accumulated amount of surplus. surp1us shown by Income and Expenditure A/c, Subscriptions, Donations, etc.
Need for Maintaining Books of Accounts and Preparing Final Accounts-
‘Not for Profit’ concern never engages itself in any field of activity where the object of earning profit is present. As ‘Not for Profit’ concern deals with public money (i.e. subscriptions and donations received from its members and general public, grants received from government), it is answerable to society or public. It is required to maintain the various books of accounts for the following reasons :
- To have control over the cash transactions i.e. inflow and outflow of cash.
- To know the sources of funds and its application i.e. different heads of expenditures on which amount is spent.
- To comply with the provisions of laws applicable to such organisation, e.g. co-operative society registered under the Co-operative Society’s Act, is required to follow the provisions to make budget, audit the accounts, maintain books of accounts, etc.
- To find out surplus or deficit of the concern during a particular period.
- To know the financial position and net worth of the concern on a particular day.
- To avoid illegal or wrong practices and misappropriation of funds and assets.
Meaning of Receipts and Payments Account:
An account which is prepared by a ‘Not for Profit’ concern to record summary of all types of cash receipts and cash payments inclusive of bank transactions is called Receipts and Payments Account. It discloses the various sources from which cash comes in and the various ways through which cash goes
out. It is just similar to the cash book maintained by the trading concerns. Like Cash Account, it has two sides, viz. debit side and credit side. On the debit side, all the receipts of cash and on credit side, all disbursements or payments of cash are recorded.
The opening balance of Cash and Bank balance are shown on the debit side of this book. Bank overdraft is shown on the credit side of this book. This book closes with cash balance and bank balance or overdraft at the end of the accounting year. All receipts and expenditures irrespective of their nature i.e. revenue or capital are recorded in this book. Receipts tand payments related to previous year, current year or next year are also recorded in this book.
Features of Receipts and Payments Account-
The features of Receipts and Payments Account are explained as follows :
- Receipts and Payments Account is a Real Account.
- It is similar to Cash Book and gives a summary of cash transactions and bank transactions.
- The receipts and payments of all kinds i.e. revenue as well as capital are recorded in this account.
- The receipts and payments relating to past, current and future accounting years, if received and paid during the current year are recorded in this account.
- It records the amount actually received as well as paid during the current year. However, amount receivable as well as amount payable (outstanding) are not recorded in this account.
- It provides base for preparation of final accounts consisting of Income and Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet of ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
- Opening balances of the Cash and Bank Account are brought down to this account from the last Balance Sheet and the closing balances of these accounts are transferred to the Balance Sheet prepared at the end of that accounting year.
- Accounting items such as Bad debts, R.D.D., Depreciation provided on the fixed assets, etc. are not recorded in this book because they are non-cash items of the business.
![]()
Types of Receipts-
Receipts may be of two types viz. (i) Capital Receipts and (ii) Revenue Receipts.
Capital Receipts :
Receipts which are non-recurring in nature and do not form the part of regular flow of business income are called Capital Receipts.
Examples : Sale proceeds of fixed assets, life membership fees, donation received for building construction, etc.
Capital receipts may be either added to capital fund or treated separately on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
Revenue Receipts :
Receipts which are recurring in nature and also form the part of regular flow of business income are called Revenue Receipts.
Examples : Subscriptions received from members, interest on investments received, rent received, entrance/ admission fees, etc.
Types of Payments-
Payments may be classified into three categories viz. (i) Capital expenditure (ii) Revenue expenditure and (iii) Deferred Revenue expenditure.
Capital Expenditure :
An expenditure which is non-recurring in nature and benefits of which are likely to be received for a long period of time is called Capital expenditure. It is usually spent to increase fixed assets units, to increase earning capacity, efficiency and life span of the fixed assets and to achieve economy of operation of existing fixed assets.
Examples : Amount spent on purchase of land, building, machinery, furniture, etc.
Revenue Expenditure :
An expenditure which is incurred for carrying out day-to-day business activities and maintaining fixed assets in working condition is called Revenue expenditure. It is recurring in nature and benefits of which are enjoyed immediately.
Examples : Amount spent on payment of wages and salaries, rent, taxes, insurance premium, commission, etc.
Deferred Revenue Expenditure :
Expenditure which is basically of revenue nature but benefits of which are received for more than one or more years is called Deferred revenue expenditure.
Example : Advertisement expenditure paid at a stretch for 4 years say ₹ 40,000. In this case, 1/4 of ₹ 40,000 i.e. ₹ 10,000 is required to be written off to Income and Expenditure A/c in the Current year and balance of ₹ 30,000 is required to be shown on the Assets side of Balance Sheet.
Specimen of Receipts and Payments Account-
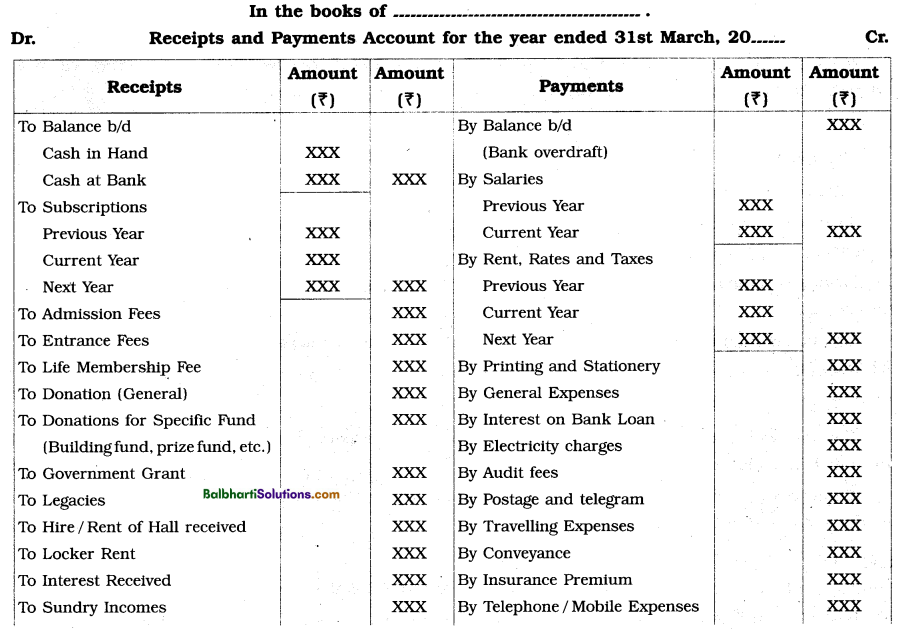
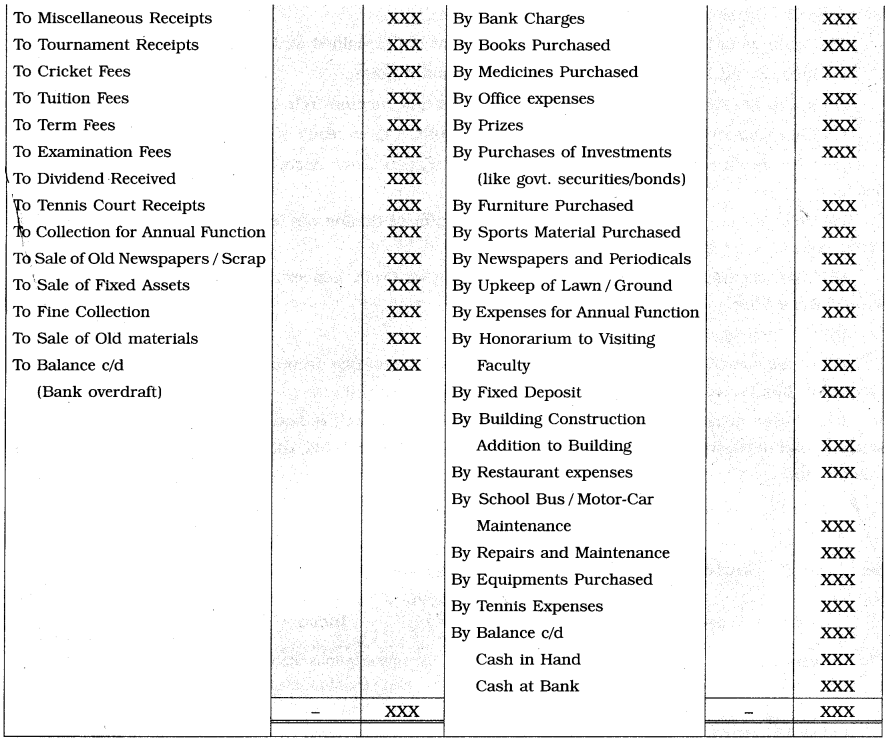
Meaning of Income and Expenditure Account-
An account which is prepared by the ‘Not for Profit’ concern to record expenses and incomes of revenue nature and to ascertain whether the concern has sufficient incomes to meet its expenses, is called Income and Expenditure Account. It is just similar to the Profit and Loss Account of the trading concerns.
Other Information : In this Account only incomes or gains of revenue nature that too of the current year are recorded on the credit side.
Examples : Subscriptions received, Entrance fees received, Sundry receipts, Donations (General) received, etc.
Please note that revenue incomes pertaining to current year whether actually received or not or received during past year are recorded in this account.
Similarly, in this account only revenue expenditure of current year whether actually paid or not or paid during previous year are recorded on debit side.
Debit balance of Income and Expenditure A/c indicates deficit which is deducted from the Capital fund and Credit balance of Income and Expenditure A/c shows surplus which is added to the Capital fund.
In this account capital receipts and capital expenditure are not recorded. They are directly recorded in the Balance Sheet.
![]()
Features of Income and Expenditure Account-
The features of Income and Expenditure Account are explained as follows :
- Income and Expenditure Account is a Nominal Account.
- In this account only revenue expenses and revenue incomes relating to current year are recorded.
- This account is just like Profit and Loss Account. It gives result of the working of the organisation. ‘Not for Profit’ concerns prepare Income and Expenditure Account in place of Profit and Loss
Account. - This account is prepared with the primary aim of finding out surplus or deficit of the ‘Not for Profit’ concern over the particular accounting year.
- This account is a part of final accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ concern and hence it is always prepared with Balance Sheet.
- No opening balance is shown in this account.
- At the end of the accounting year, the debit balance of this account shows a deficit and the credit balance of this account indicates a surplus.
- All cash items such as salaries paid, rent paid, etc. as well as non-cash items such as outstanding salaries, bad debts written off, depreciation, provisions for bad debts, discount, etc. are also recorded in this account.
Specimen of Income and Expenditure Account-
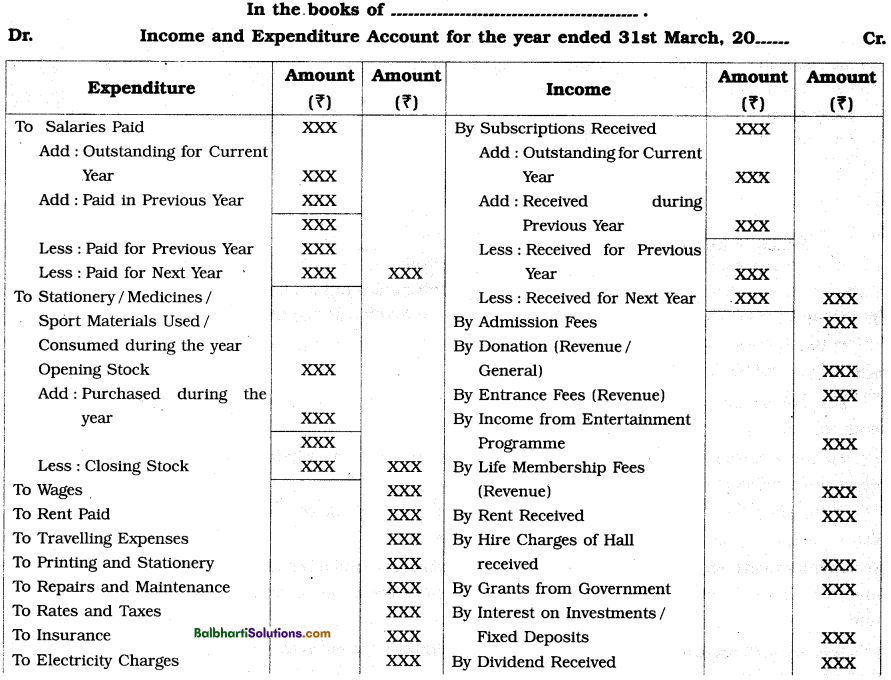
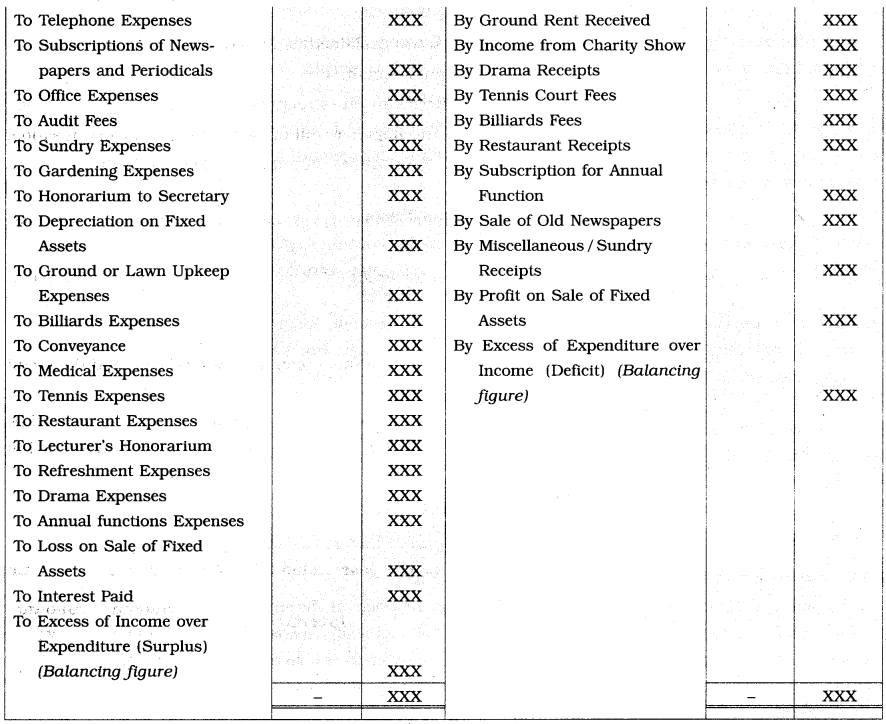
Distinction between Receipts and Payments Account and Income and Expenditure Account:
Receipts and Payments Account:
- Meaning: An account prepared by a Not for Pr’ concern to record the summary of all types of cash receipts and cash payments is called Receipts and Payments account.
- Nature: It gives the summary of the cash transactions and bank transactions. It is similar to cash book maintained by the trading organisation.
- Type of Account: Receipts and Payment Account Is a Real Account.
- Openinng Balance: This account starts with opening cash and bank balances or overdraft.
- Closinng Balance: Closing difference of this account shows either cash and bank balance or bank overdraft.
- Period: All cash transactions Irrespective of period of occurrence, if received and paid In the relevant accounting year are recorded.
- Nature of Items: In this account only cash transactions (items) are recorded.
- Concerned period: Incomes and expenditures of both capital and revenue nature if received or paid during the current year are recorded in this account.
- Contaings: In this account, tranšactions relating to all types of accounts viz. Personal Acccount, Real Account and Nominal Account are recorded.
- Balance Sheet: It Is never accompanied by a Balance Sheet.
Income and Expenditure Account:
- Meaning: An account prepared by a Not for Profit’ concern to record Its expenses and incomes of revenue nature is called Income and Expenditure account.
- Nature of Account: It gives the net result of working of the concern. It Is similar to the Profit and Loss Account prepared by the trading concern.
- Type of Account: Income and Expenditure Account Is a Nominal Account.
- Openinng Balance: No opening balance Is shown In this account.
- Closing Balance: Closing difference of this account shows either deficit or surplus.
- Period: Income and expenses relating to the relevant (current) accounting year only arc recorded.
- Nature of Items: In this account cash as well as non-cash transactions (Items) are recorded.
- Concerned Period: Only revenue incomes and expenditure related to current year whether received or not are recorded in this account.
- Contains: In this account, only transactions relating to Nominal Account are recorded.
- Balance Sheet: It Is always prepared along with Balance Sheet.
Preparation of Income and Expenditure Account-
Income and Expenditure Account is prepared on the basis of Receipts and Payaments Account and additional information if any. It is a Nominal Account and hence all expenses and losses of revenue nature are debited to this account and all incomes and gains of revenue nature are credited to this account. The method of preparation of Income and Expenditure Account is similar to that of preparation of Profit and Loss Account.
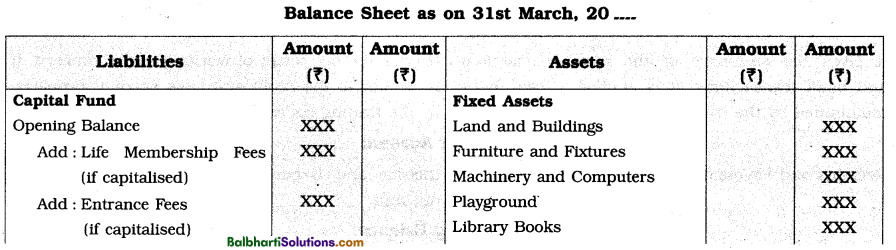
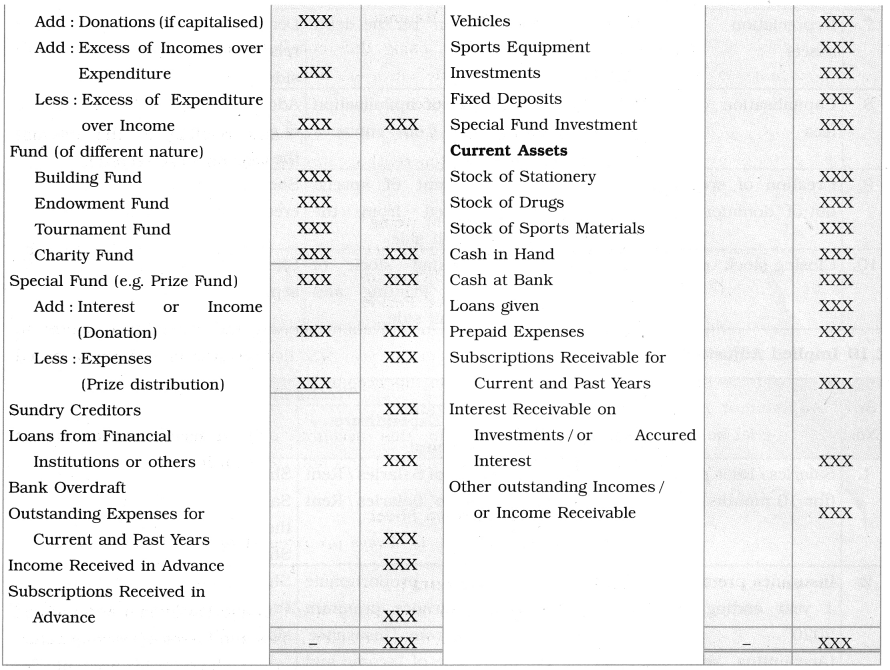
Preparation of Balance Sheet-
Balance Sheet of a Non Trading organisation is similar to Balance sheet of sole trading concern. To get the exact idea of financial position of an organisation on a particular date, Balance sheet is prepared with the capital receipts and capital Expenditures amounts. Generally, excess of Assets over Liabilities is called as capital fund. If ‘Capital Fund’ balance is not known, it can be found out by preparing opening balance sheet.
Specimen of Balance Sheet:
Adjustments-
| Adjustments | Accounting treatment in | |
| Income and Expenditure Account | Balance Sheet | |
| 1. Outstanding Expenses | Add to concerned expenses on the debit side. | Show ‘Outstanding Expenses’ on the Liabilities side |
| 2. Prepaid Expenses | Deduct from the related expenses on the debit side. | Show ‘Prepaid Expenses’ on the Assets side. |
| 3. Accured Income | Add to related income on the credit side. | Show ‘Accured Income’ on the Assets side. |
| 4. Income received in advance | Deduct from the related income on the credit side. | Show ‘ Income received in advance ‘ on Liabilities side. |
| 5. Subscriptions received in advance | Deduct the amount of subscriptions received in advance from subscriptions on the credit side. | Show ‘Subscriptions received in advance’ on the Liabilities side of Balance Sheet. |
| 6. Subscriptions outstanding (receivable) | Add the amount of subscriptions outstanding (receivable) to subscriptions on credit side. | Show ‘Subscriptions Outstanding’ (receivable) on the Assets side of Balance Sheet. |
| 7. Depreciation on fixed assets | Show ‘depreciation’ on the debit side. | Deduct ‘depreciation’ from the related fixed asset on the Assets side. |
| 8. Capitalisation of entrance fees | Deduct the amount of capitalisation of entrance fees from entrance fees on credit side. | Add the amount of capitalisation of entrance fees to capital fund on the Liabilities side. |
| 9. Creation of special funds out of donation | Deduct the amount of special funds so created from the donations on credit side. | Show separately special funds so created on the Liabilities side. |
| 10. Closing stock of stationery | Deduct the closing stock of stationery from ‘ Printing and Stationery’ on debit side. | Show ‘stock of stationery’ separately on the Assets side. |
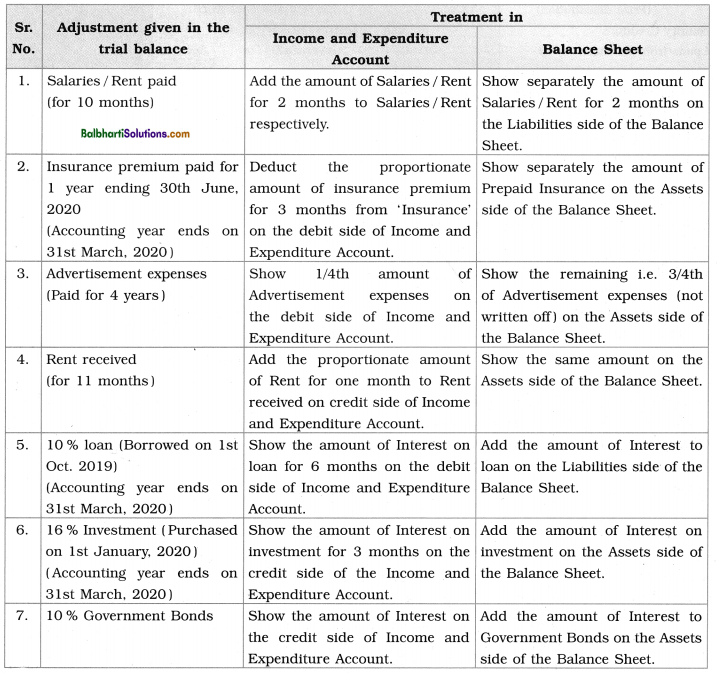
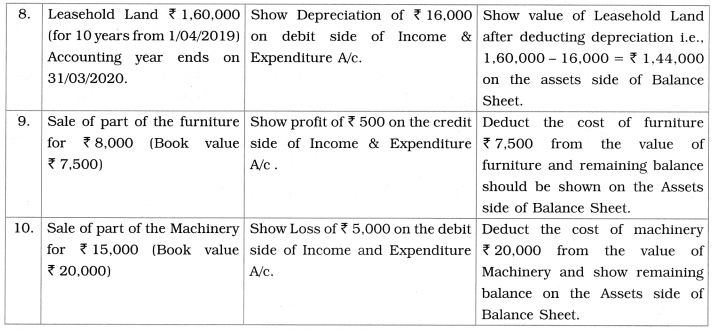
Implied Adjustments:
![]()
Accounting treatment of the important items-
(1) Capital Fund : The excess of total assets over the total liabilities is called capital fund. Capital fund is recorded on the Liabilities side of Balance Sheet prepared by the ‘Not for Profit’ concern. It is created out of capital incomes and capitalisation of funds or incomes such as donations, entrance fees, admission fees, etc. The surplus shown by the Income and Expenditure Account is added to Capital Fund and deficit if any shown by Income and Expenditure Account is deducted from Capital Fund.
(2) Entrance Fees or Admission Fees : Fees or specific amount received from the new members at the time of their entry into the ‘Not for Profit’ concern are called Entrance fees or Admission fees. It is different from annual subscription received from the members. It is paid by each member only at the time of his admission. Capital fund of ‘Not for Profit’ concern is mainly made of entrance fees received from all the past and present members. Some people argue that entrance fees are capital receipt as it is received only once from each member. It is not recurring in nature. While others have pointed out that entrance fees are revenue receipt because though it is paid only once by each member, it is received regularly by the ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Note : In the absence of any specific information given in the problem, entrance fees should be treated as revenue receipt. If any specific instruction is given in the problem, entrance fees should be treated accordingly. IJ according to instruction 60% of entrance fees is to be capitalised, then 60 % of entrance fees is to be added to capital fund on Liabilities side of Balance Sheet and remaining 40% of entrance fees is to be credited to the Income and Expenditure Account.
(3) Subscriptions : A payment as a contribution by the members towards some object or service, is called subscription received. It may be a payment or promise of payment for subscription of a magazine, newspaper, book, etc., over a specified period of time. In such a case it is called subscription paid. Subscriptions or fees received from the members constitute the main source of income for a ‘Not for Profit’ concern. All subscriptions received will be recorded on the debit side of Receipts and Payments Account. Out of such subscriptions, subscriptions relating to current accounting year are transferred and recorded on the credit side of the Income and Expenditure Account. It is considered as revenue receipt.
(4) Legacy : Any asset, property or amount of cash which ‘Not for Profit’ concern receives as per the provisions made in the will of the donor on his death is called legacy. As and when cash is received as legacy, it is recorded on the debit side of the Receipts and Payments Account. Since amount received on legacy is not of recurring nature, it is considered as capital receipt. Therefore, it is shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
(5) Life Membership Fees : The member of the ‘Not for Profit’ concern, if wants to become a life member, he is required to pay a lump sum amount of fees to the concern either at the time Of his entry or later. Such amount of fees is called life membership fees. Life membership fees are non-recurring in nature because members are required to pay the fees once in a lifetime and not periodically. Since it is a capital receipt, it is added to the capital fund on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
(6) Sale of Old Assets * Fixed assets like machinery, furniture, office equipments, etc., are sold by the ‘Not for Profit’ concern when they become old or outdated. Profit or Loss on sale of such assets is ascertained by using the following formulae :
(i) Profit on Sale of old Assets = Sales proceeds – Cost of Sale of old Assets.
(ii) Loss on Sale of old Assets = Cost of Sale of old Assets – Sales proceeds.
Sale proceeds so received are recorded in Receipts and Payments Account on receipts side. If ‘Not for Profit’ concern earn profit on sale of old assets, the amount of such profit, is recorded on the credit side of Income and Expenditure Account. In case there is a loss on sale of old assets, the amount of such loss is debited to Income and Expenditure Account.
(7) Scrap : Small piece of something larger, parts of the outdated machines, waste materials, used articles especially metals, etc. are called scrap. Scrap value refers to the net amount which is realised on the final disposal of scrap. The amount received on sale of scrap is first recorded on the debit side of Receipts and Payments Account. It is treated as miscellaneous income and as such it is credited to Income and Expenditure Account.
(8) Newspapers : Newspapers, periodicals, magazines, etc. are used by the members of the ‘Not for Profit’ concern to update their knowledge. The amount received from the sale of old newspapers, periodicals, magazines, weeklies, etc. is shown on the debit side of the Receipts and Payments Account and then posted on the credit side of the Income and Expenditure Account. It is considered as miscellaneous income.
(9) Specific Donations : Donation i.e., the gift in monetary terms received from the members or outsiders for a specific purpose like donation for building, charity, etc., is called specific donation. Donation received for specific purpose is treated as capital receipt and is added as contribution to specific fund on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. Expenses spent for acquiring such donations are not debited to Income and Expenditure Account, but they are deducted from the amount of such donations only.
![]()
(10) Genera! Donations : Donations may be classified as general donations and specific donations. Donations received for general purpose like welfare of members, achieving general aims and objectives of the concern, etc. are called general donations. General donations are treated as revenue receipts as they are expected to be received every year. In case no specific information is given in any problem, donation should be treated as revenue income and accordingly, it should be considered in Income and Expenditure Account as income.
(11) Specific; Fund : Fund created for specific purpose is called specific fund. Specific fund may be created for the construction of building, construction of operation theatre, swimming pool, awarding prizes, etc. If specific fund is created, then all incomes and expenses relating to the specific fund should not be recorded in the Income and Expenditure Account. All incomes relating to specific fund are added to that fund and all the expenses related to it are deducted from that specific fund. The balance of specific fund is shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
(12) Endowment Fund : Fund which is created or raised from bequest (means the thing that is left by a will) or gift, the income of which is used or devoted for a specific purpose is called endowment fund. In other words, fund which provides permanent source of income to the institution is called endowment fund. The amount of such fund is invested in the government or non-government securities to create a source of regular income. The amount of income or interest received from the investment of endowment fund is used for a specific purpose, e.g., distribution of prizes to the meritorious students in the society, etc. An amount received for endowment fund is considered as capital receipt because such fund provides permanent source of income to the ‘Not for Profit’ concern. It appears on the receipts side or debit side of the Receipts and Payments Account. It is shown separately on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. The amount of income or interest received from the investment of endowment fund is not credited to Income and Expenditure Account but to be added to endowment fund. Similarly all expenses relating to endowment fund are to be deducted from the amount of such fund.