By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 2 Weathering and Mass Wasting students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 2 Weathering and Mass Wasting
→ Types of Rocks:
- Igneous
- Sedimentary
- Metamorphic
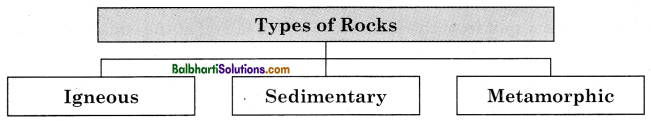
- Igneous : These rocks are formed by cooling and solidification of molten magma.
- Sedimentary : These rocks are formed due to the deposition of layers of organic and inorganic matter including dead remains of plants and animals and sand, silt, clay, gravel, etc.
Hardening and compaction. - Metamorphic : These rocks are formed when igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to immense heat and pressure.
→ Weathering:
Weathering is a process of breaking down of rocks due to physical or chemical changes in the rocks.
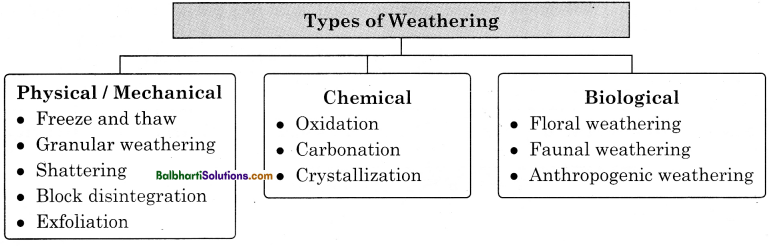
→ Types of Weathering:
1. Physical / Mechanical:
- Freeze and thaw
- Granular weathering
- Shattering
- Block disintegration
- Exfoliation
2. Chemical:
- Oxidation
- Carbonation
- Crystallization
3. Biological:
- Floral weathering
- Faunal weathering
- Anthropogenic weathering
![]()
→ Factors such as water, heat and pressure can cause both physical and chemical weathering.
→ Freeze and thaw weathering: It are particularly effective in high and mid latitudes and in mountainous areas. Where the diurnal range of temperature is high, water inside the crack’s freezes during night time and melts during day time. When water freezes its volume increases and it exerts pressure on walls of rocks and the cracks widen and eventually the rock breaks.
→ Granular disintegration due to temperature change: The coarse-grained rocks are affected in desert areas. These granules are of different colours and they absorb insolation differently. Differential expansion and contraction cause stress on rocks and eventually it disintegrates into smaller particles.
→ Shattering due to rain shower and heat: The outer shells of the rocks are shattered due to sudden light showers in hot climatic region mainly hot deserts.
→ Block disintegration due to heat: In rocks such as granite which have joints, heat can cause weathering by breaking the rocks along the joints into blocks.
→ Exfoliation: The exposed part of the rock heats more, while the inner part is comparatively cooler. As a result, the outer layers of the rocks fall apart from the main rock.
![]()
→ Oxidation: Oxygen in the air and water reacts with certain elements in the minerals inside the rock. In this process the minerals in the rocks react with oxygen in the air and water.
→ Carbonation: It involves reaction of carbon dioxide with minerals in the soil. The decomposition of dead matter produces C02 which reacts with minerals.
→ Crystallization: The salts of calcium, sodium, magnesium, potassium etc., present in the rocks have a tendency to expand due to their thermal properties. This leads to crystallization of salts and individual grains split from the main rocks which fall off at the end. It is dominant in coastal areas with alternate dry and wet periods.
→ Biological Weathering : This is caused because of roots of plants, which penetrates into cracks. Microorganism such as algae, moss, lichens and bacteria grow on the rock surface and produce chemicals that can break the rock.
→ Certain burrowing animals like rats, moles etc. are responsible for breaking of rocks.
→ Anthropological Weathering : Man is a biological agent affecting weathering, mining, blasting of hills and ridges for constructions of roads, railways, dams causing disintegration of rocks.
→ Importance of Weathering:
- It prepares the way for formation of soils and various landforms that we see on earth.
- It helps in enrichment and concentration of ores.
![]()
→ Mass Movement or Mass Wasting :
It is the down slope movement of loose mixture of soil, land rock particles by the force of gravity
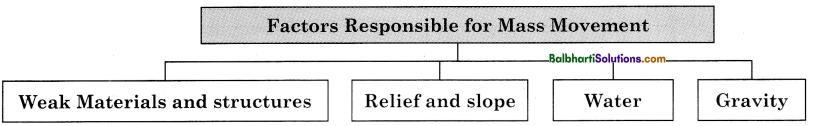
→ Factors Responsible for Mass Movement:
- Weak Materials and structures
- Relief and slope
- Water
- Gravity
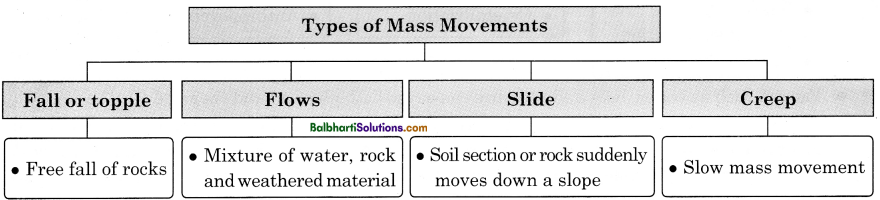
→ Types of Mass Movements:
- Fall or topple
- Flows
- Slide
- Creep
1. Fall or topple:
Free fall of rocks
2. Flows:
Mixture of water, rock and weathered material
3. Slide:
Soil section or rock suddenly moves down a slope
4. Creep:
Slow mass movement
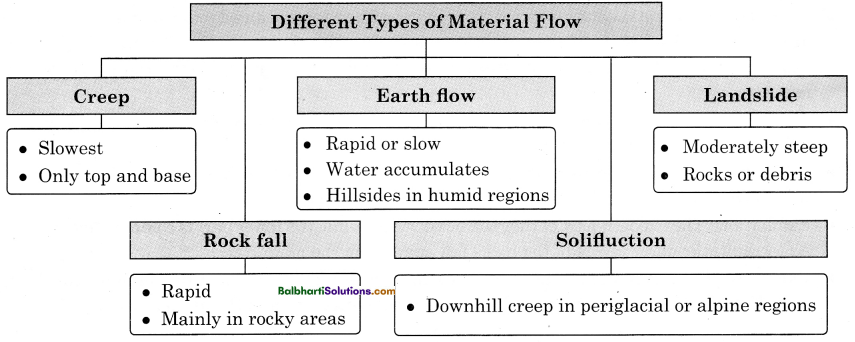
→ Different Types of Material Flow:
- Creep
- Slowest
- Only top and base
1. Creep-
- Slowest
- Only top and base
2. Rock fall-
- Rapid
- Mainly in rocky areas
3. Earth flow-
- Rapid or slow
- Water accumulates
- Hillsides in humid regions
4. Solifluction-
Downhill creep in periglacial or alpine regions
5. Landslide-
- Moderately steep
- Rocks or debris