By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 3 Agents of Erosion students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 3 Agents of Erosion
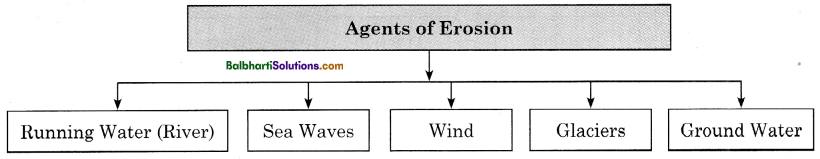
Agents of Erosion:
- Running Water(River)
- Sea Waves
- Wind
- Glaciers
- Ground Water
→ Agents of erosion cause various processes when they pick up, move and deposit rock particles. These processes lead to erosional and depositional landforms.
![]()
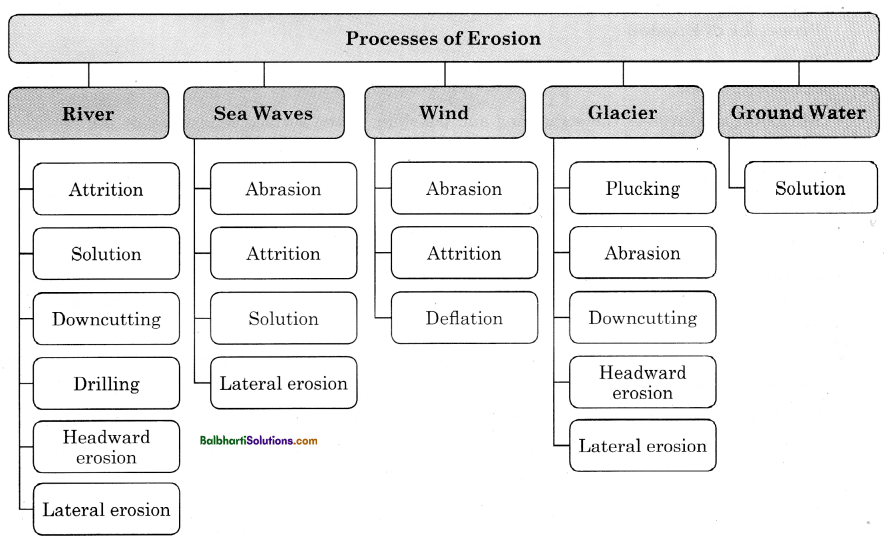
Processes of Erosion:
River-
- Attrition
- Solution
- Downcutting
- Drilling
- Headward erosion
- Lateral erosion
Sea Waves-
- Abrasion
- Attrition
- Solution
- Lateral erosion
Wind-
- Abrasion
- Attrition
- Deflation
Glacier-
- Plucking
- Abrasion
- Downcutting
- Headward erosion
- Lateral erosion
Ground Water-
Solution
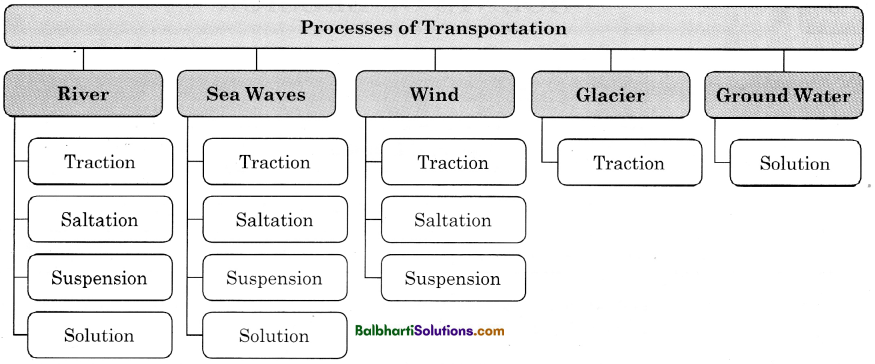
Processes of Transportation :
- Traction : The material acquired by the agents is transported by rolling, pushing and dragging along the surface.
- Saltation : Often the rock materials move forward by leaps and bounds through this process.
- Suspension : Fine light material is carried along with water or air in the upper layer.
- Solution : The material is carried in water in a dissolved state.
Processes of Transportation :
River-
- Traction
- Saltation
- Suspension
- Solution
Sea Waves-
- Traction
- Saltation
- Suspension
- Solution
Wind-
- Traction
- Saltation
- Suspension
Glacier-
Traction
Ground Water-
Solution
![]()
Processes of Erosion :
- Plucking : The process by which moving ice exerts pressure on majority portion of rocks on bed or along the bank.
- Abrasion : It involves the scratching and polishing of the surface or bedrock by the particles which are moving onto it.
- Attrition: It is when rocks and pebbles bump into each other and break up into smaller fragments.
- Solution : It is when certain types of rocks get eroded as a result of acids in the sea or river water.
- Deflation : The particles which are loosened on the surface are blown away by the wind.
- Drilling : Bedload moves along the running water. As and when this flow encounters an obstacle due to relief on the bed or joints in the bed, the flow tends to develop a circular pattern. This leads to development of a whirl.
- Downcutting : Also called downward erosion is a process of hydraulic action that deepens the channel of a stream or valley by removing material from the stream’s bed or the valley’s floor.
- Headward erosion : It is the backward erosion by river in the source region.
- Lateral erosion : It is the erosion that occurs on the sides of valleys of a river or glacier.
Agents of erosion and landforms :
Factor affecting formation of landforms – climate, type of rocks, intensity of erosion, slope of land and obstacles.
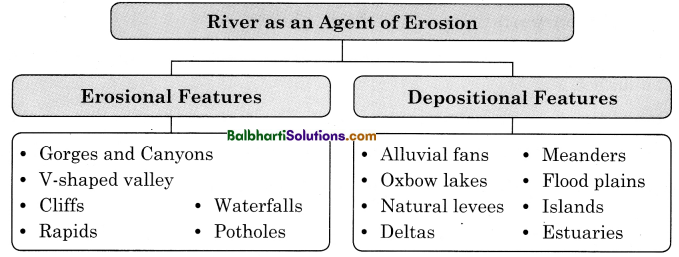
River as an Agent of Erosion:
- Erosional Features
- Depositional Features
1. Erosional Features
- Gorges and Canyons
- V-shaped valley
- Cliffs
- Waterfalls
- Rapids
- Potholes
2. Depositional Features
- Alluvial fans
- Meanders
- Oxbow lakes
- Flood plains
- Natural levees
- Islands
- Deltas
- Estuaries
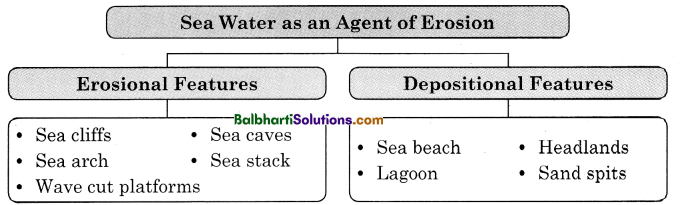
Sea Water as an Agent of Erosion:
Erosional Features-
- Sea cliffs
- Sea caves
- Sea arch
- Sea stack
- Wave cut platforms
Depositional Features-
- Sea beach
- Lagoon
- Headlands
- Sand spits
![]()
Conditions necessary for wind erosion :
- Aridity – In such areas, rate of evaporation is greater than rate of precipitation.
- Sparse vegetation cores or absence of trees.
- Presence of dry loose materials at the surface.
- A wind velocity high enough to pick up and move sediments.
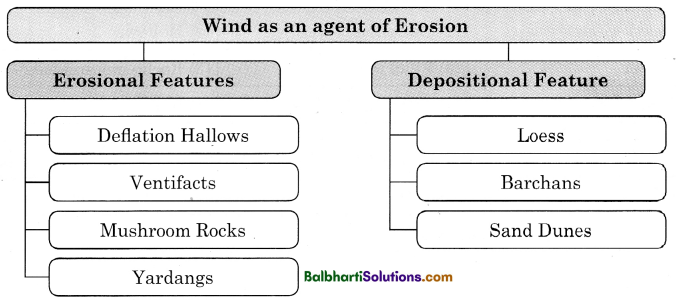
Wind as an agent of Erosion:
- Erosional Features
- Depositional Feature
1. Erosional Features:
- Deflation Hallows
- Ventifacts
- Mushroom Rocks
- Yardangs
2. Depositional Feature
- Loess
- Barchans
- Sand Dunes
Karst topography needs three important factors to develop:
- Carbon dioxide
- Active movement of underground water
- Joints
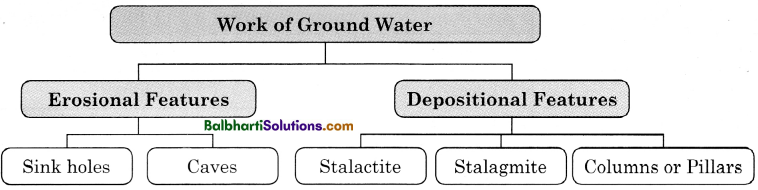
Work of Ground Water:
- Erosional Features
- Depositional Features
1. Erosional Features
- Sink Holes
- Caves
2. Depositional Features:
- Stalactite
- Stalagmite
- Columnor Pillars
![]()
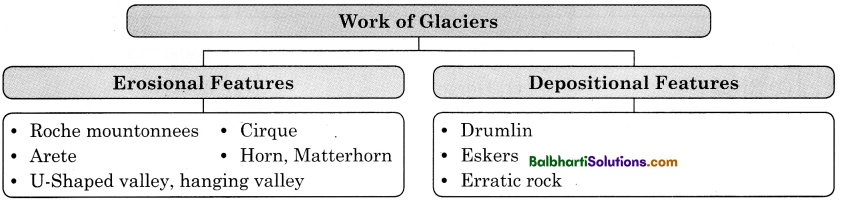
Work of Glaciers:
- Erosional Features
- De positional Features
1. Erosional Features:
- Roche mountonnees
- Cirque
- Arete
- Horn, Matterhorn
- U-Shaped valley, hanging valley
2. De positional Features:
- Drumlin
- Eskers
- Erratic rock