By going through these Maharashtra State Board Secretarial Practice 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 2 Joint Stock Company students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Secretarial Practice Notes Chapter 2 Joint Stock Company
Evolution of Business Organization –
- Sole Trading Concern
- Joint Hindu Family Business
- Partnership Firm
- Limited Liability Partnership
- Co-operative Society
- Joint Stock Company

![]()
Sole Trading Concern
Owned, managed and controlled by one person. It is also called as ‘One Man Business’. A person who conducts the business is called “Sole Trader”.
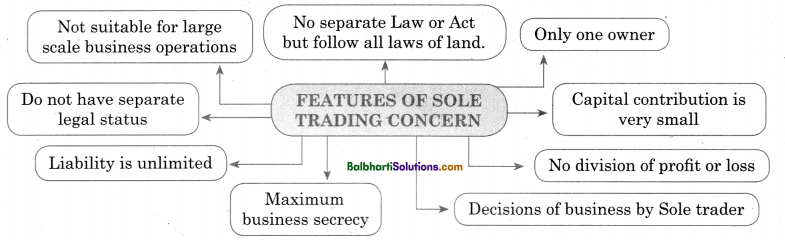
Features of Sole Trading Concern –
- Not suitable for large scale business operations
- No separate Law or Act but follow all laws of land
- Only one owner
- Do not have separate legal status
- Capital contribution is very small
- Liability is unlimited
- No division of profit or loss
- Decisions of business by Sole trader
- Maximum business secrecy
Joint Hindu Family Business-
- When a Hindu Undivided Family conducts business, inherited by it as per Hindu Law, it is called a Joint Hindu Family Business.
- Exists only in India governed by Hindu Succession Act 1956.
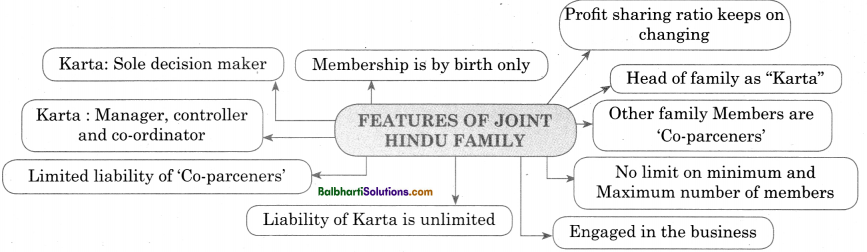
Features of Joint Hindu Family Business-
- Karta decision maker
- Membership is by birth only
- Karta : Manager, controller and co-ordinator
- Limited liability of ‘Co-parceners’
- Liability of Karta is unlimited
- Profit sharing ratio keeps on changing
- Head of family as “Karta”
- Other family Members are ‘Co-parceners’
- No limit on minimum and Maximum number of members
- Engaged in the business
Partnership Firm-
- The business organization which is owned, managed and controlled by two or more person is called a partnership firm.
- Owners are called Partners, Organization is called a firm.
- It is governed by Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
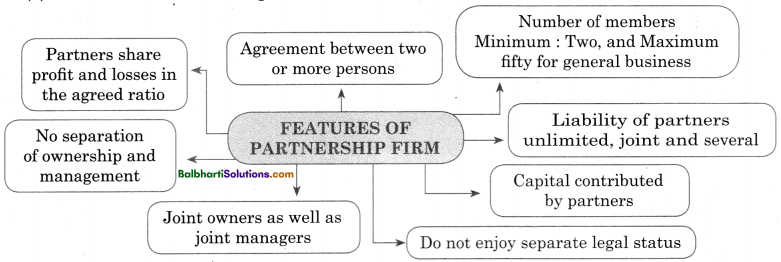
Features of Partnership Firm-
- Partners share profit and losses in agreed ratio
- NO separation of ownership and management
- Agreement between two or more persons
- Number of members Minimum : Two, and Maximum fifty for general business
- Joint owners as well as joint managers Liability of partners unlimited, joint and several
- Capital contributed by partners
- DO not enjoy separate legal status
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)-
- It has a combination of features of both partnership and joint stock company.
- Partners have limited liability
- Governed by the Limited Liability Partnership Act of 2008.
Features of Limited Liability Partnership-
- Separate legal entity i.e. a body corporate
- Number of partners- Minimum- two. Maximum- unlimited.
- No minimum requirements of capital contribution.
- Simple to form and easy to operate.
- Liability of each partner is limited to his share as written in the agreement.
- Low cost of formation.
- No restriction on joining and leaving the LLP except as stated in partnership agreement.
- Double taxation is avoided, no tax on profit share.
![]()
Co – operative Society-
- It is a voluntary association of persons formed to achieve certain economic objectives.
- It is service oriented.
- Governed under the Maharashtra State Co-operative Societies Act 1960.
Features of Co- operative Society-
- Compulsory Registration
- Membership open to all.
- Number of members- Minimum- ten, Maximum- no limit.
- Limited liability of a member.
- Aim is not maximization of profit but to provide services to its members.
- Independent legal status.
- Democratic in nature, equality in voting right One member one vote’.
- Control and supervision by the state government.
Joint Stock Company (JSC)-
- It is a more formal form of business organization.
- Satisfies requirement of modern industry
- Convenient to conduct large scale business industry
- Types of Joint Stock Companies
- Public
- Private
- Government
- Statutory etc.
![]()
Definition of Joint Stock Company-
- According to Section 2(20) of the Companies Act 2013. “Company means a company incorporated under this Act or under any previous company law.”
- According to Prof. H. L. Haney “A Joint stock company is a voluntary association of individual for profit, having its capital divided into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition of membership.”
Features of Joint Stock Company-
1. Voluntary Association –
- Membership is open to all
- Can become a member or leave subject to the provisions of Articles of Association of the company.
2. Incorporated Association-
- Registration or incorporation is compulsory.
- After registration an association obtains the status of a Joint Stock Company.
3. Separate Legal Entity
- Members are the owners and are liable in limited way.
- Members are conferred with rights and duties.
4. Artificial Person
- Created by law.
- Legal process and own independent personality.
- Legal rights to enter into contracts, purchase and sell assets and property etc.
5. Perpetual Succession
- Continuous in existence.
- Not affected by death, insolvency or retirement of any of any members.
- Very long and stable life.
6. Common Seal
- It is a device that acts as a signature of the company.
- Affixed on all the important documents and contracts.
- Usually signed by two directors and the secretary as a witness after the seal is affixed.
7. Limited Liability
- Shareholders have limited liability.
- Shareholder is liable to pay only the unpaid amount of his shares.
- Shareholder is not concerned with debts and liabilities of the company.
8. Separation of Ownership and Management
- Shareholders are real owners of the company, but large and scattered.
- Unable to manage the day to day affairs of the company.
- Board of Directors look after the management and policy decisions of the company. They are elected representative of shareholders.
9. Transferability of shares
- Shares of public company are freely transferable.
- Shares of private company are not freely transferable.
10. Number of Members
- Owned by a large number of persons.
- Private limited company — minimum 2 members maximum — 200 members
- Public limited company — minimum 7 members maximum — no limit
11. Capital
- Raise huge capital.
- In form of shares, debentures, bonds, public deposits
- Obtain loans from banks and financial institutions.
![]()
12. Government Control
- Company is controlled and supervised by the Government.
- Registered company follow rules and regulations of company law.
- Accounts are audited.
- Copy of profit and loss, balance sheet, financial statement are submitted to the registrar.
- To protect the financial interest of small investors.
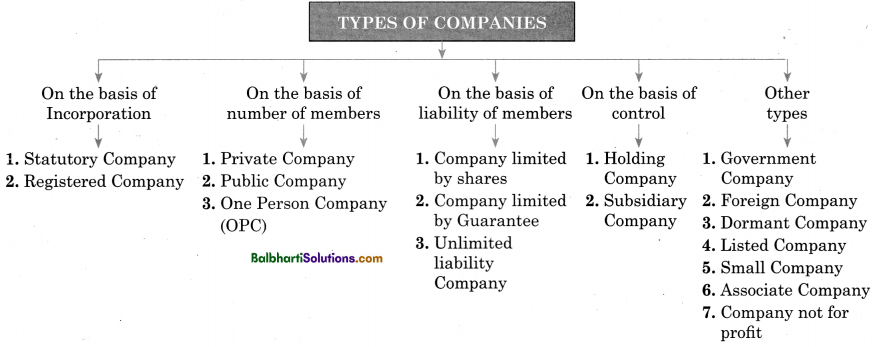
Types of Companies-
- On the basis of Incorporation
- On the basis of number of members
- On the basis of liability of members
- On the basis of control
- Other types
On the basis of Incorporation:
- Statutory Company
- Registered Company
On the basis of number of members
- Private Company
- Public Company
- One Person Company (OPC)
On the basis of liability of members-
- Company limited by shares
- Company limited by Guarantee
- Unlimited liability Company
On the basis of control-
- Holding Company
- Subsidiary Company
Others types –
- Government Company
- Foreign Company
- Dormant Company
- Listed Company
- Small Company
- Associate Company
- Company not for profit
![]()
On the basis of Incorporation-
- Statutory Company
- Registered Company
Statutory Company:
Companies incorporated by Special Act passed by Central or State legislative, e.g. Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India, Unit Trust of India, Life Insurance Corporation, etc.
Registered Company:
Companies incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 or any previous company law.
On the basis of Number of Members
Private Company (SECTION 2(68)):
- Restrict the right of members to transfer its shares.
- Maximum number of members upto 200.
- Prohibits any invitation to the public for any securities or deposits of company.
- Company limited by shares or company limited by guarantee or an unlimited company.
- Must add the words “Private Limited” at the end of its
Public Company (Section 2 (71)):
- Has no restriction on the transfer of its shares.
- Minimum number of members should be seven.
- Has minimum paid up share capital.
- Does not prohibit any invitation or acceptance.
- Must add the word “Limited” after the name of the company.
One Person Company (Section 2 (62)):
- Single Promoter who has limited liability.
- Can have one or more directors.
- No need to hold Annual General Meeting.
- Better form of sole proprietorship.
On the basis of Liabilities of Members:
Company Limited By Shares Section 2(22):
- Have share capital and liability limited to the unpaid part of face value of shares purchased by member.
- May be a public company or a private company.
- Most popular type of companies.
Company Limited By Guarantee: Section 2(21)
- May or may not have a share capital.
- Member promises to pay a fixed sum of money specified in the Memorandum of the company.
- Non-profit making companies.
- Purpose of promotion of art, science, culture etc.
Unlimited Liability Company Section 2(92)
- Not having any limit on the liability of its members.
- Members are fully liable to cover the debts of the company.
- Can be either a private or . a public company or a one person private company.
![]()
On the basis of Control –
- Holding Company Section 2(46)
- Subsidiary company section2(87 )
Holding Company Section 2(46):
- Company holds more than one half of thetotal share capital of another company
- Has power to appoint or remove Directors of another Company.
Subsidiary company section2(87):
Company which is controlled by holding company.
Other Types-
1. Government Company:
Section 2(45):
Company in which not less than 51% of the paid up share capital is held by
- Central Government or
- State Government or Governments or
- Partly by Central Government and partly by one or more State Governments
- Subsidiary company of a government company. e.g. H.M.T, BHEL, ONGC etc.
2. Foreign Company:
Section 2(42):
Company incorporated outside India, but having a place of business in India.
e.g. Bata India Ltd, Nestle India Ltd.
3. Dormant Company:
Registered for a future project or has not made any significant accounting transactions in last two years or has not filed financial statements or annual returns in last two years, after making application u/s 455.
4. Listed Company: Section 2(52)
Company which has any of its securities listed on any recognized stock exchange following SEBI’s guidelines and the provisions of the Companies Act.
5. Small Company:
Section 2 (85):
- Paid up share capital of which does not exceed 50 lakh or such higher amount as may be prescribed
- whose turnover as per last profit and loss account does not exceed 2 crores or such higher amount as may be prescribed.
6. Associate Company: Section 2(6)
Company which controls at least 20% of total capital or of business decisions over a subsidiary company.
7. Company not for profit:
Registered u/s 8 of Companies Act.
Word Meaning:
revolution – complete change; radical – entire; anticipation – expectation; evolved – to come in existence; inadequate – insufficient/ not enough; emerged – came into existence; proprietor – single owner of business; operations – working; inherited – getting from ancestors; contribution – collection; formation – coming into being; achieve – to get; differs – unlike; democratic – representatives are elected; stability – fixed; Managerial ability – ability to manage various works at a given time; Statutory – owned by Government company; enactment – passed by; reveal – tells; conclude – end; Perpetual succession – Continuation; obtains – to get; conferred – grant; scattered – spread all over; desires – want; registrar – a person who looks after registration of company; obligations – responsibilities; penalized – fine; prohibit – restricted/stop from doing something; promoter – person who starts with an idea of starting an organization: memorandum – written document specifying the policies of a company; liquidation – converting assets into cash; significant – important; insolvency – financial loss to an individual or company.