By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 3 Basic Concepts in Sociology students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 3 Basic Concepts in Sociology
→ Sociology studies every social phenomenon Therefore, sociology is a complex social science.
→ The concepts of sociology are difficult to understand as they are abstract in nature.
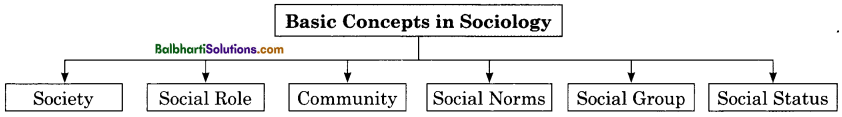
Basic Concepts in Sociology:
- Society
- Social Role
- Community
- Social Norms
- Social Group
- Social Status
→ According to Aristotle, ‘man is a social animal’ and cannot live without society.
→ Man is subjected to some elemental and derived needs that can be satisfied within the societal framework.
→ The term ‘society’ is derived from the Latin word ‘socius’ meaning companionship or friendship.
→ ‘Society’ is a broad concept and is used frequently or in day-to-day life.
→ Society denotes an ‘ association’, ‘organization’ or ‘group’.
![]()
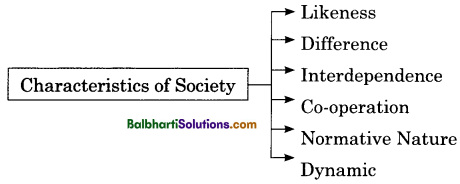
Characteristics of Society:
- Likeness
- Difference
- Interdependence
- Co-operation
- Normative Nature
- Dynamic
→ Maclver and Page stated that the community possesses a distinctively territorial character. It implies a common soil as well as shared way of life.
→ Community is referred to a group of people living in a definite territory to fulfil their common objectives and needs.
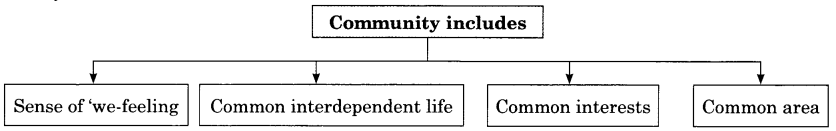
Community includes
- Sense of ‘we-feeling
- Common interdependent life
- Common interests
- Common area
Elements of Community:
- Locality
- Community Sentiment

→ The term social group is used to refer to the entire human group as well as it means a small group which consists of two individuals.
→ Human beings are social animals and hence have always lived in social groups.
![]()
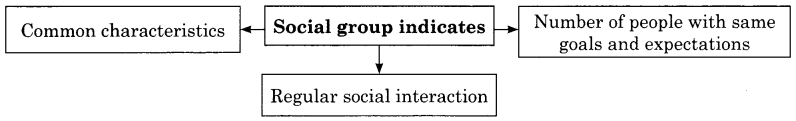
Social group indicates:
- Common characteristics
- Number of people with same goals and expectations
- Regular social interaction
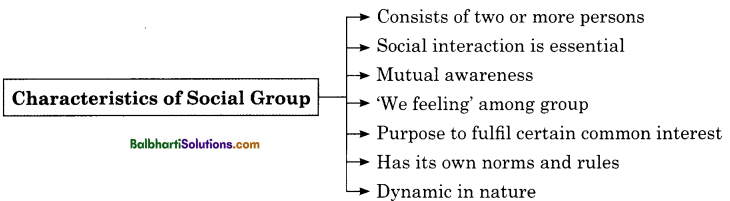
Characteristics of Social Group:
- Consists of two or more persons
- Social interaction is essential
- Mutual awareness
- ‘We feeling’ among group
- Purpose to fulfil certain common interest
- Has its own norms and rules
- Dynamic in nature
→ Through various classifications of groups given by sociologists one can understand the diverse nature of social groups.
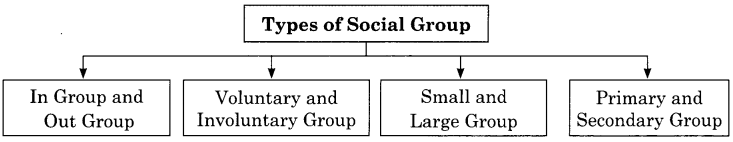
Types of Social Group:
- In Group and Out Group
- Voluntary and Involuntary Group
- Small and Large Group
- Primary and Secondary Group
![]()
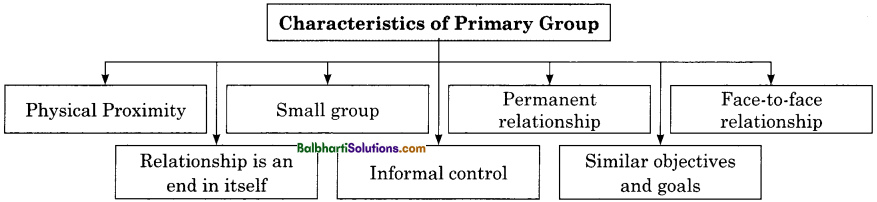
Characteristics of Primary Group:
- Physical Proximity
- Small group
- Relationship is an end in itself
- Permanent relationship
- Informal control
- Face-to- face relationship
- Similar objectives and goals
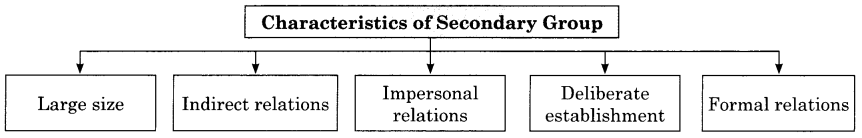
Characteristics of Secondary Group:
- Large size
- Indirect relations
- Impersonal relations
- Deliberate establishment
- Formal relations
→ The concept of Reference Group is given by Robert Merton.
→ People refer to reference group when evaluating:
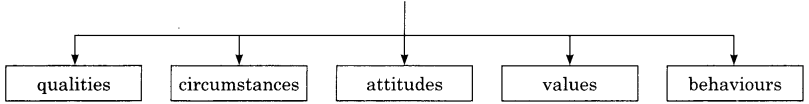
- Qualities
- Circumstances
- attitude
- values
- behaviours
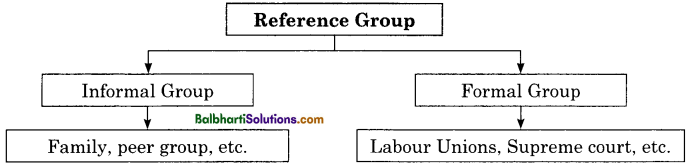
Reference Group:
- Informal Group: Family, peer group, etc.
- Formal Group: Labour Unions, Supreme court, etc.
→ Social status, social role and social norms are correlated concepts of every society.
→ Every individual has a certain status and performs their role according to the status (position) in society.
→ There are certain rules and regulations to control societal behaviour, which are known as social norms.
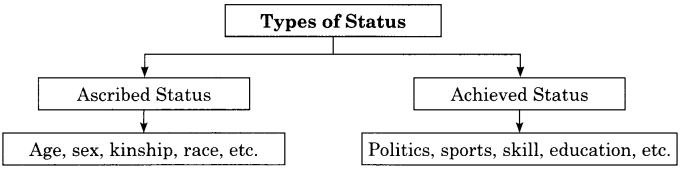
Social Status- One’s position or status according to prestige and power.
Types of Status:
- Ascribed Status: Age, sex, kinship, race, etc.
- Achieved Status: Politics, sports, skill, education, etc.
Social Role: One’s behavioural aspects of duties associated with status or position.
Role:
- Role performance
- Role exit
- Role conflict
- Role strain
- Role set
Status and role are complementary to each other. They are two sides of the same coin.
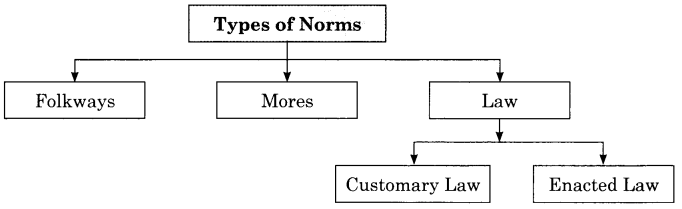
Social Norms – Norms make orders and severs individual as a guide for conduct.
Types of Norms:
- Folkways
- Mores
- Law
- Customary Law
- Enacted Law