By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 5 Culture students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 5 Culture
→ The term culture refers to the way of life of a member of various societies or groups. Culture is that complex whole that includes knowledge, beliefs, values, morals, law, customs, and any other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society.
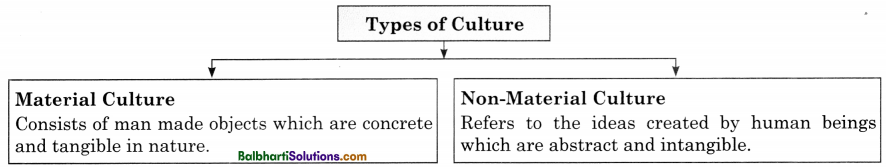
Types of Culture
- Material Culture: Consists of man-made objects which are concrete and tangible in nature.
- Non-Material Culture: Refers to the ideas created by human beings which are abstract and intangible.
![]()
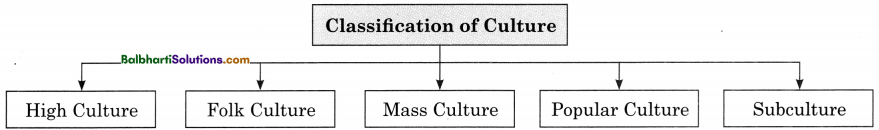
Classification of Culture:
- High Culture
- Folk Culture
- Mass Culture
- Popular Culture
- Subculture
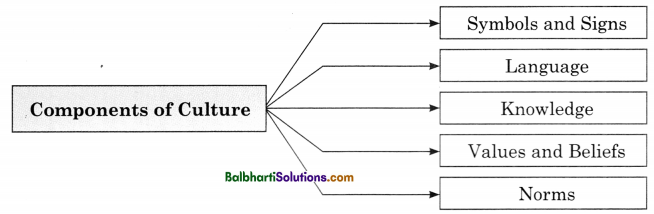
Components of Culture:
- Symbols and Signs
- Language
- Knowledge
- Values and Beliefs
- Norms
Characteristics of Culture:
- Culture is acquired
- Culture is abstract
- Culture is shared
- Culture is man-made
- Culture is idealistic
- Culture is transmitted among members of society
- Culture is continuously changing
- Culture varies from society to society
- Culture is an integrated system
- Language is the chief vehicle of culture
![]()
→ Participating in culture can benefit individuals in many different ways. Culture helps build social solidarity and cohesion. It leads to improved learning and valuable skills for the future.
→ Ethnocentrism means treating one’s own culture as superior and every culture displays a sense of ethnocentrism. Ethnocentrism has positive as well as negative effects.
→ Cultural hybridization refers to the ways in which parts of one culture get recombined with the cultures of another. It is a process where two originally distinct cultures come together and create something new and exciting.
→ Glocalisation refers to global processes interacting with the local processes.