By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics
Meaning of Micro Economics:
Microeconomics deals with small individual economic units such as an individual consumer, individual producer, the price of a particular commodity or factor, etc.
Definition of Micro Economics:
→ According to Maurice Dobb – “Microeconomics is in fact a microscopic study of the economy. ”
→ According to Prof. A.P.Lerner – “Microeconomics consists of looking at the economy through a microscope as it were, to see how the millions of cells in the body of economy – the individuals or households as consumers and individuals or firms as producers play their part in the working of the whole economic organism.”
![]()
Scope of Microeconomics:
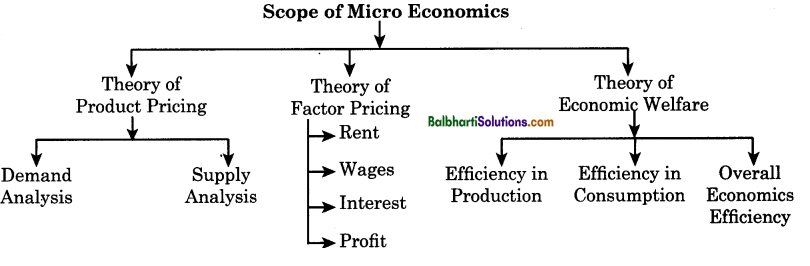
→ Theory of Product Pricing: The price of each commodity is determined by the forces of demand and supply. Microeconomics is a study of demand analysis i.e. individual consumer behaviour and supply analysis i.e. individual producer behaviour.
→ Theory of Factor Pricing: There are four main factors contributing to the production process which are land, labour, capital and entrepreneur. Microeconomics helps in determining the factor rewards like land gets rent, labour gets wages, capital gets interest and entrepreneur gets profit.
→ Theory of Economic Welfare: This theory deals with efficiency in allocation of resources which aim at maximum satisfaction of people. Three economic efficiencies are as follows :
- Efficiency in production: It means producing maximum amount of goods and services from given amount of resources.
- Efficiency in consumption: It means distribution of produced goods and services to the society for consumption in such a way to have maximum total satisfaction of people.
- Overall economics efficiency: It means to produce those goods and services which are most desired by the people.
Features of Micro Economics:
→ Study of Individual Units: Microeconomics deals with the study of behaviour of small individual units of the economy such as individual consumer, individual firm, individual industries, individual prices, etc.
→ Price Theory: Micro economics is known as price theory because it determines the prices of goods and services as well as prices of factors of production.
→ Partial Equilibrium : Micro economics analysis deals with partial equilibrium which analyses equilibrium position of an individual economic unit i.e. individual consumer, individual firm, etc.
→ Based on Certain Assumptions: Micro economics is based on ‘ceteris paribus’ assumption i.e., other things remaining constant like full employment, laissez faire policy, perfect competition, pure capitalism, etc.
→ Slicing Method: It divides or slices the economy into small units and studies each unit in detail e.g. study of a particular household demand in detail.
→ Use of Marginalism Principle : The term ‘marginal’ means change brought in total by an additional unit. Marginal analysis helps to study a variable through the changes by which producers and consumers take economic decisions using this principle.
→ Analysis of Market Structure: Microeconomics analyses different market structures such as perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, etc.
→ Limited Scope: The study of microeconomics is limited to individual economic unit only. It does not deal with macro problems like unemployment, inflation, deflation, poverty, unemployment, population, etc.
![]()
Importance of Micro Economics :
→ Price Determination: Microeconomics explains how the prices of different products and various factors of production are determined.
→ Free Market Economy: A free market economy is that economy where the economic decisions are taken at individual levels without intervention by the government. Decisions are regarding production of goods such as What to produce? How much to produce? How to produce? etc.
→ Foreign Trade: Microeconomics also explains gains from foreign trade, effects of tariffs, factors affecting exchange rate, etc.
→ Economic Model Building: Microeconomics helps in understanding various complex economic situations with the help of economic models.
→ Business Decision: Microeconomic theories are helpful to businessmen for taking important business decision related to determination of cost of production and prices of goods, maximization of output and profit, etc.
→ Useful to Government: It is useful in formulating and evaluating economic policies including pricing and distribution policies that promote economic welfare. It is useful in determining tax policy, public expenditure policy, etc.
→ Basis of Welfare Economics: It explains how optimum use of resources can be made to increase the welfare of the society. It also studies how taxes affect social welfare.
Meaning of Macro Economics: Macroeconomics is the study of aggregates which analyses the entire economy, such as national income, total employment, total consumption, inflation, total savings, etc.
Definition of Macro Economics:
→ J. L. Hansen: “Màcro economics is that branch of economics which consider the relationship between large aggregates such as the volume of employment, total amount of savings, investment, national income, etc”
→ Prof. Carl Shapiro: ‘Macroeconomics deals with the functioning of the economy as a whole.”
![]()
Scope of Macro Economics:
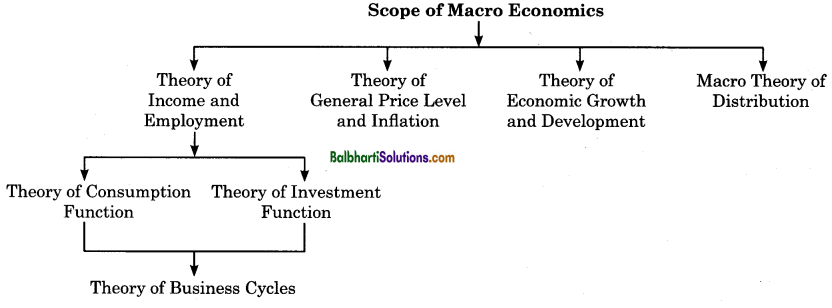
→ Theory of Income and Employment: It explains which factors determine the level of national income and employment and what causes fluctuations in the level of income, output and employment.
By studying the consumption function and investment function, we can understand how the level of employment is determined in the economy.
→ Theory of General Price Level and Inflation: Macroeconomic analysis shows how the general price level is determined and explains the causes for fluctuations in it. This study is important for understanding the problems created by inflation and deflation.
→ Theory of Economic Growth and Development: Macroeconomics studies the causes of underdevelopment and poverty in poor countries and suggests strategies for accelerating the growth and development in the country.
→ Macro Theory of Distribution: Macro theory of distribution deals with the relative share of rent, wages, interest and profit in the total national income of various classes.
Features of Macro Economics:
→ Study of Aggregate: Macroeconomics deals with the study of entire economy. It studies the overall conditions in the economy such as National Income, National Output, Total Employment, General Price levels, etc.
→ Income Theory: Macroeconomics studies the concept of National Income and causes of fluctuations in the National Income that lead to business cycles i.e. inflation and deflation.
→ General Equilibrium AnalysÍs: Macro Economics analysis is based on general equilibrium which deals with the economic system as a whole and studies the interrelationship between the various macro variables in an economy. General equilibrium deals with the behaviour of demand, supply and prices in the whole economy.
→ Interdependence: There is an element of interdependence among the macroeconomic variables such as income, output, employment, investment, price level, etc.
![]()
→ Lumping Method: Lumping method is the study of the whole economy rather than in part. It considers aggregates like National Income, Total consumption, etc. instead of personal income, PCC, etc.
→ Growth Models: Macroeconomics studies various factors that contribute to economic growth
and development. These growth models are used for studying economic development.
→ General Price Level: Macroeconomic studies the determination and changes in general price level which is the average of all prices of goods and services currently being produced in the economy.
→ Policy-Oriented: Macroeconomics is a policy-oriented science which is useful in formulating economic policies to promote economic growth, to control inflation and depression, to generate employment, etc.
Importance of Macro Economics:
→ Functioning of an Economy: It given an idea of functioning of an economic system and help us to understand the behaviour pattern of aggregate variables.
→ Economic Fluctuations: It help to analyse the causes of fluctuation in Income, output and employment.
→ National Income: It helps to study about NI and made possible to formulate correct economic policies.
→ Economic Development: It helps us to understand the problems of the developing countries such as poverty, difference in the standards of living etc., and suggest important steps to achieve economic development.
→ Performance of an Economy: It helps us to analyse the performance of an economy where Ni estimates are used to measure the same.
→ Study of Macro Economic Variables: Study of macroeconomic variables are important to understand the working of the economy.
→ Level of Employment: Macroeconomics helps to analyse the general level of employment and output in an economy.