By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 5 Forms of Market students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 5 Forms of Market
→ Market in Economics refers to an arrangement through which buyers and sellers come in close contact with each other directly or indirectly for exchange of goods and services at a particular price. This may be by way of telephone, internet, etc. Thus, the essentials of market are
- There are many buyers and sellers.
- Market involves exchange of goods and services.
- There is a price for a commodity.
- They have either direct or indirect contact.
- They may be spread over to a place, region, country or world without knowing each other e.g. We buy things through Amazon.
Classification of Market:
Market can be classified on the basis of place, time and competition.
1. On the basis of place: These can be further divided into :
→ Local Market: When goods are produced and sold in local areas mainly then market for such goods is called local market. E.g. perishable goods or bulky goods like bricks.
→ Regional Market: When goods have market within a particular region, market for such goods is called regional market. E.g. Regional movies mainly have regional market.
→ National Market: Market confined to a domestic market in a country is called national market. E.g. cars, scooters, T.V., etc.
→ International Market: Goods which can be sold in any part of the world have international market. E.g. tea, coffee, petroleum, etc.
![]()
2. On the basis of Time: These can be further divided into :
→ Very Short Period Market: A market which lasts for a few days or maximum a week, is called very short period market. E.g. for fruits market, vegetables market, etc.
→ Short Period Market: When the supply of the product can be increased to some extent say upto one year with the help of available raw material, then market to such goods is called short period market.
→ Long Period Market: It is a market from one year to five years when the supply can be increased on demand.
→ Very Long Period Market: It is a market for more than five years when supply can be fully adjusted to demand.
![]()
On the basis of Competition: These can be of following types:
→ Perfect Competition
→ Imperfect Competition: This is further divided into :
- Monopoly,
- Oligopoly,
- Monopolistic competition.
Perfect Competition: In Perfect competition, there are large number of buyers and sellers engaged in buying and selling a homogeneous product at a single uniform price in the market. Its main features are –
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous products
- Free entry and exit of firms
- Uniform price or price taker
- Perfect knowledge
- Perfect mobility of factors
- No transport cost
- No government intervention
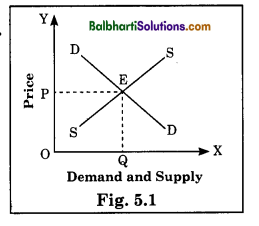
Price determination under Perfect Competition: In this market, price is determined at the point of intersection of demand and supply curves in the market. This is called equilibrium price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied as follows:
In this diagram, demand and supply curves intersect at point E, where sellers are ready to sell OQ quantity at price OP and buyers O are ready to buy OQ quantity at price OP. If price rises or falls, changes in demand and supply bring the price back to equilibrium level.
Imperfect Competition: It is a type of market which has some features of perfect competition. It may be of following types: Monopoly, Oligopoly, Monopolistic competition.
(I) Monopoly: It is a market in which there is only one seller who has complete control over the market supply and there are no close substitutes. Its main features are:
- Single seller
- Large number of buyers
- No close substitutes
- Entry barriers
- Price maker
- Price discrimination
- Control oversupply
- Aims at profit maximisation
- No difference between firm and industry
![]()
Types of Monopoly:
It can be of following types:-
- Natural monopoly
- Legal monopoly
- Joint monopoly
- Simple monopoly
- Discriminating monopoly
- Private monopoly
- Public monopoly
(II) Oligopoly: On the basis of competition, oligopoly market is one in which there are a few sellers selling homogeneous or differentiated products which are close substitutes of each other. E.g.
cement companies, baby foods, etc. Its main features are –
- Large number of buyers
- A few sellers
- Interdependence
- Selling cost
- Entry barriers
- Uncertainty
- Lack of uniformity
(III) Monopolistic Competition: It is a market in which there are large number of buyers and fairly large number of sellers producing similar or differentiated products which are close substitutes of each other. It has some elements of monopoly and some elements of competition. Therefore, this market is known as monopolistic competition. e.g. market for vegetable oil, washing powders, soaps etc. Its main features are –
- Large number of buyers
- Fairly large number of sellers
- Product differentiation
- Free entry and exit of firms
- Selling cost
- Downward sloping demand curve
- Concept of group
![]()
Thus, market is said to exist when:
- There are many buyers and sellers.
- They may be spread either to a place, region, country or world.
- Goods are bought and sold at a price.
- People have the knowledge about market price.
- Freedom of entry and exit of firms.