By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 1 Population Part 1 students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Geography Notes Chapter 1 Population Part 1
→ Population Geography is a branch of Human Geography.
→ In this branch, we study quantitative and qualitative composition of population, how population influences the economy and development and much more.
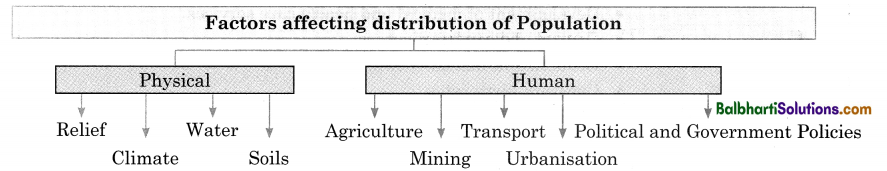
→ The distribution of population in the world is uneven.
→ Asia has 30% landmass and supports 60% of the world’s population.
→ Number of people living in a unit area is called density of population.
→ Density of population = \(\frac{\text { Total population }}{\text { Total area (sq. km) }}\)
![]()
Components of population change:
→ People from one region differ from another region. They can be distinguished from one another on the basis of age, sex, place of residence, occupation and life expectancy.
Population growth :
→ Population growth is the change in number of inhabitants of a territory during specific period of time.
→ Growth of population can be expressed either in terms of absolute number or in percentage.
→ Change of population is an economic indicator of development and social upliftment.
→ Birth rate (BR), Death rate (DR) and Migration are three components of change of population.
Crude birth rate:
Number of live births in a year per thousand population is known as crude birth rate (CBR).
CBR = \(\frac{\text { Total number of live births in a year }}{\text { Total population in that year }}\) × 1000
Crude death rate
→ Number of deaths in particular year per 1000 population is known as crude death rate.
CDR =\(\frac{\text { Total number of deaths in a year }}{\text { Total population in that year }}\) × 1000
→ Population growth in any region occurs not only by increasing birth rate but also because of decreasing death rate
![]()
The Theory of Demographic Transition:
→ No country experiences the same rate of growth or decline of population.
→ Population growth or decline changes with the economic development, tendencies of birth rate and death rate.
→ The theory of demographic transition is based on the population trends of a country with time.
→ Any country passes through different stages of population growth.
Stages of Population Growth :
Stage 1 High stationary stage :
- High birth and death rates
- Stable population
- Poor financial position
- People engage in primary activities like agriculture
- Limited educational opportunities
- Big families
- Poor science and technological development
- Poor sanitation facilities, malnutrition and high death rate.
Stage 2 Early expanding stage
- Development of medical and health care services
- Control and combat diseases
- Reduction in mortality rate
- Constant birth rates
- Rapidly growing population
- Efforts to control population
- Increase in agricultural and industrial production.
Stage 3 Late expanding stage
- Decreasing death rates
- Decreasing birth rates
- Reduction in population
- Income of the people is slightly above subsistence level
- Slight increase in the standard of living hence, decreasing poverty
- Rise in technological growth
- Expansion of secondary and tertiary activities
- Increased education facilities, awareness of family planning
Stage 4 Low stationary stage
- Decrease in birth rate
- High standard of living
- Improved economic condition of the country
- Improved economic status of the people
- Increased engagement in secondary and tertiary activities
- Better medical facilitates, hence, low death rates
- Epidemics under control
- Health-conscious
Stage 5 Declining stage
- Equal birth rate and death rate
- Minimum population growth and negative in some countries
- Reduced population due to higher mortality
- Percentage of children is lower than elders
- Most of the country’s income comes from tertiary activities
- Best quality education and health facilities
- Healthy environment and pleasant life