By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 7 Region and Regional Development students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 7 Region and Regional Development
→ Natural (physical) or man-made (administrative boundaries, political or linguistic) feature of a small or large area of land having common features help us to identify them separately.
→ Demarcated boundary separates one region from the other. The geographical area that distinguishes itself from another area is called a region.
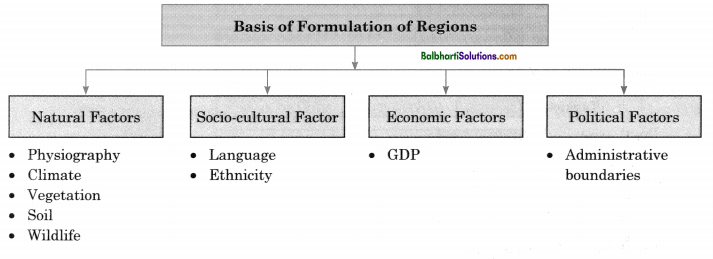
→ The classification of regions is based on common characteristics and is homogeneous in nature, which constitutes of a region.
→ A region is a basic unit in any geographical studies and helps us to differentiate one area from another.
![]()
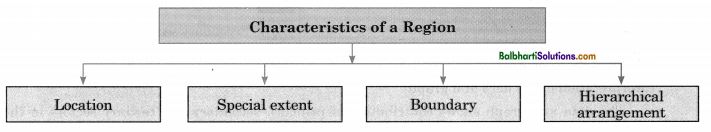
Types of regions
→ Formal regions and functional regions are the two types of regions.
→ A formal region is an area inhabited by people who have one or more characteristics in common.
→ On the basis of characteristics, a formal region is divided into a physical region or political region.
→ A functional region is an area organized to function socially and economically as a single unit.
→ Functional region involves more than one type of physical or political regions.
Factors affecting regional development
→ Development is a relative term. Therefore, while considering regional development the physical, economic, social, environmental aspects of a region are taken into consideration.
Physical factors and regional development
→ Regional development is affected by physical factors like climate and relief of the region.
→ Areas where land is less fertile, water is scarce and diseases flourish will be less developed.
→ A region with a large number of resources, but climate is not suitable, or lack of population to exploit resources, the region will not develop.
![]()
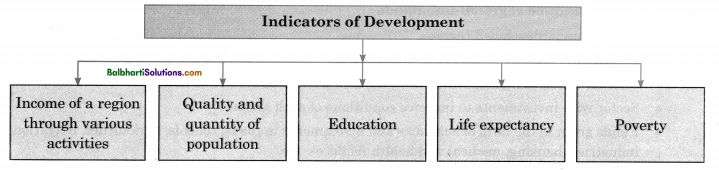
Population and regional development
- Population and regional development are closely interrelated. The parameters of development are measured keeping in mind the population of a region.
- The important factors of development are the quantity and quality of population as well as the efficiency of resources used by the population in a region.
Land use and regional development
→ There is a difference in the percentage of land use in developed and underdeveloped regions.
→ Demand for land use changes according to the society’s needs as well as the changes in the socio-economic conditions.
Primary, secondary and tertiary economic activities and regional development
→ Primary, secondary and tertiary economic activities carried out in any region, give an idea about the regional development in that region.
→ Regions are developed if they contribute more in the tertiary sector and depend less on primary activities.
→ The Human Development Index (HDI) is used to access various aspects of development in a region.
![]()
Regional imbalance:
→ The balanced regional development policy is considered on economic, social and political grounds.
→ The policy is adopted to reduce inequalities between different regions of a country and also increasing the standard of living to a higher level at a uniform rate.
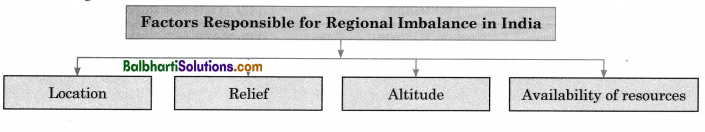
Causes of regional imbalance in India:
→ There is regional imbalance in India since the level of development is not similar in all sub-regions.
Policies to reduce regional imbalance
→ Identify underdeveloped regions.
→ Identify the reasons behind non-development.
→ Allocate funds to regions which need them in particular sectors or fields.
→ Sector-wise investments to improve conditions of such areas.
→ Funds are given in the form of subsidies and investments in roads, schools, agriculture, irrigation, industries, housing, medical and health facilities, etc.
→ Special care for regions that have been identified as deserts, drought-prone, hilly, and areas dominated by tribal population.
→ Decentralisation of industries to reduce the regional imbalance.