By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 8 Geography: Nature and Scope students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 8 Geography: Nature and Scope
→ The nature of the earth’s surface is full of variations. There are various features with variations such as mountains, hills, plains, plateaus, oceans, rivers, lakes, deserts, etc.
→ In geography, we study climatic patterns on the global and local level, its impact on vegetation and wildlife, wind patterns, soils and its types, etc.
→ Types of landforms, submarine relief, ocean currents, salinity, etc., are also studied by a geographer.
→ All the above-mentioned physical aspects affect human populations.
→ Such variations bring about changes in social and cultural features too, which changes from place to place and time to time.
→ Variations are also observed in the form of settlements, transportation networks, markets and ports and many other elements developed by man during the entire period of man’s cultural development.
→ Taking into consideration the above all factors, the subject matter of geography can be divided into two major themes – Physical Factors and Human Factors. Thus, giving rise to two branches in Geography – Physical Geography and Human Geography.
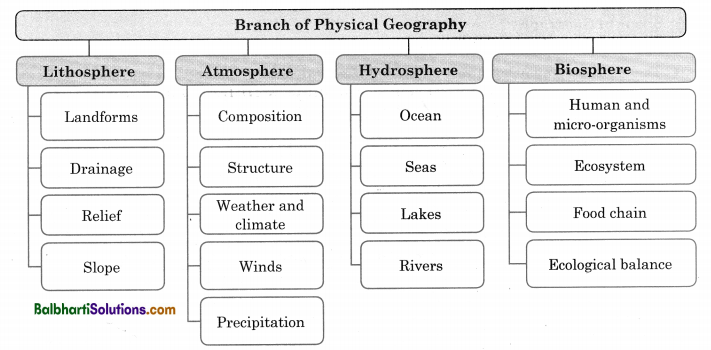
→ Human Geography studies relationship between man and environment.
→ It also studies distribution attributes related to man’s social and environmental phenomena around the world.
![]()
Nature of Geography as a discipline
- The earth is dynamic. Hence, there are variations in its physical and cultural environments.
- Geography is a study of the earth and phenomena related to it.
Geographers study –
→ Through scientific and supplemental methods with experiments, data collection, observation patterns, data analysis and research.
→ Geographical distributions, their patterns and variations as well as the causes behind these phenomena.
→ Geographical distributions of various crops in different regions. Thus, understanding the impact of climate, soil, market demand and application of technology to identify the differences.
→ The space, area, region and geographical location. Skills and techniques used in study of geography make it empirical and practical in nature.
→ Skills developed by geographers enables them to make observations and describe various phenomena on the earth; and enriched the subject and newer branches of geography went on developing.
→ There are two contrasting approaches to study geography, which is known as Dualism in geography.
There are two contrasting approaches in Geography –
- Nature is more dominant than man, which is called Environmental Determinism.
- Man dominates nature, which is called Possibilism.
→ Since there are many such dualistic approaches in geography; it makes geography dualistic in nature.
Scope of Geography
→ Almost every discipline, under natural and social sciences, is linked with Geography.
→ Therefore, geography has a very strong interface with natural and social sciences.
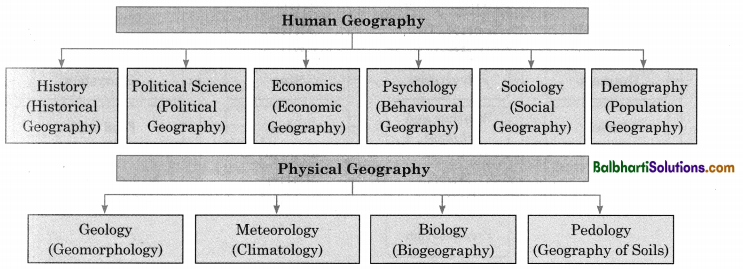
→ Since many branches of geography have developed from mainstream disciplines geography has become an interesting and interdisciplinary subject.
![]()
Latest Trends in Geography:
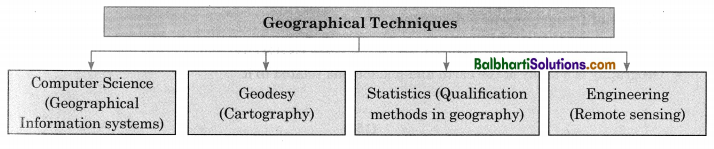
- Geographer explains the phenomena within the frame of cause and effect relationship.
- It helps to analyse and predict future through data collection and modelling.
- This results in intra and inter-disciplinary avenues and widens the scope of geography and its dynamic nature of adding new subjects.
The following are uses of geographical models:
- Population growth and density
- Land use
- Intensity of cropping
- migration patterns of population
- Industrialization
- urbanization
- Growth of cities
- Growth of Slums