By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Psychology Notes Chapter 5 Emotions students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Psychology Notes Chapter 5 Emotions
History of Emotions:
The word emotion is derived from the Latin word ‘remover, which means to stir up or to move An emotion refers to an involuntary, aroused state of an organism involving physical, cognitive, and behavioural components.
It is described as a combination of bodily arousal, e.g., increased heart rate, thoughts, and feelings, i.e. emotional tone, and expressive behaviour, i.e., facial expression.
The main theories of emotions are –
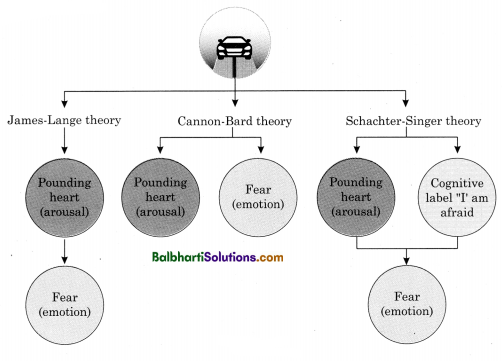
James-Lange theory:
It was one of the earliest theories to explain emotion According to William James and Carl Lange, physiological arousal instigates the experience of emotion.
It proposes that each specific emotion is attached to a different pattern of physiological arousal. For e.g., we feel sad because we cry. The sequence of events in emotional experience is Emotion Stimulus →Physiological Response Pattern → Affective Experience.
Cannon-Bard theory:
According to Walter Cannon and Philip Bard, we may experience the same physiological arousal but emotions can be different, for e.g., we don’t cry only when we are sad but we also cry when we are angry or extremely happy.
We experience physiological arousal and feelings at the same time and independently. For e.g., seeing a man with a gun prompts the feeling of fear as well as a racing heartbeat.
![]()
Schachter and Singer’s Two Factor theory:
According to Stanley Schachter and Jerome Singer, emotion is based on two factors, i.e., physiological arousal and cognitive label, for e.g., an environmental stimulus (growling dog) elicits a physiological response (increased heart rate). We cognitively label this response (fear).
Facial Feedback hypothesis:
According to the facial feedback hypothesis, our facial expressions provide feedback to our brain about our emotions. Facial expressions are the result of our emotions but also capable of Influencing emotions.
Basic Emotions:
There are two primary emotions, viz. happiness and sadness. These emotions transform as our experiences change, for e.g., sadness can transform to grief or shame.
Some characteristics of emotions are –
- Emotions may be positive, e.g., joy or negative, e.g., anger.
- Emotions may occur for a brief period or may be long-lasting.
- Emotions may be important for our survival, e.g., fear or for our psychological well-being, e.g., love.
Emotions differ in intensity in expression, for e.g., annoyance-anger-rage. - Complex emotions (higher cognitive level emotions) result from the combination of basic emotions, for e.g., surprise and sadness lead to disappointment.
According to Paul Ekman, there are six basic (universal) types of emotions, i.e., happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, disgust.
- Happiness – It is the basic positive emotion that is associated with psychological well-being.
- Sadness – It is characterized by related feelings of hopelessness, disappointment, etc.
- Anger – It is a powerful, negative emotion which includes hostility, frustration, etc.
- Fear – It is closely related to our survival from the evolutionary perspective. It is in response to some threat.
- Surprise – It occurs in response to some unexpected event. It may be positive or negative.
- Disgust – It is in response to some unwanted stimulus.
![]()
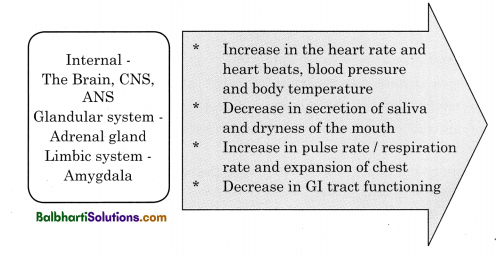
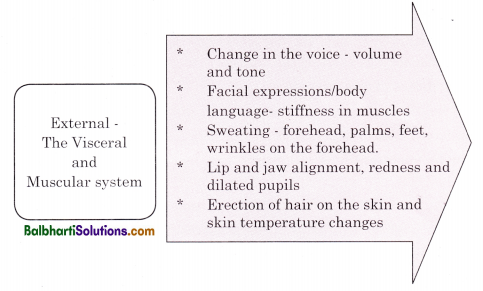
Physiological Changes During Emotions:
Physiological changes refer to automatic reactions that take place in our body in response to some stimulus, for e.g. if you saw a snake, the brain at the cognitive level perceived the stimulus as dangerous. This leads to physiological arousals such as dilated pupils, increased heart rate, increased pulse rate and sweating.
At the emotional level, you experience fear. The Autonomic Nervous System and glandular system signal the pituitary gland which activates the adrenal glands to secrete the cortisol hormone that triggers “the fight or flight” response. At the connection (behavioural) level there is an action plan such as running away or calling for help, etc.
Plutchik’s Model Of Emotions:
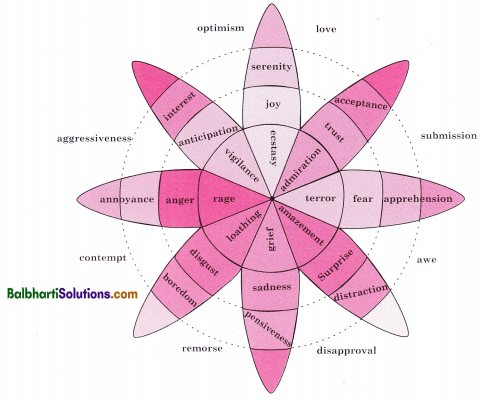
Robert Plutchik presented the wheel of emotions.
- there are eight basic emotions viz. joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, anticipation, anger and disgust.
- each primary emotion has its polar opposite such as fear is opposite of anger.
- primary emotions combine to produce complex emotions, for e.g., love (complex) is a combination of joy and trust.
- the intensity of emotions increases as we move toward the centre and decreases as we move outward. For e.g., apprehension (weak) →fear (basic) →terror (strongest). This model is important from the perspective of emotional literacy, i.e., understanding emotional levels, complexity and change as well as appropriate emotional labelling.
![]()
Emotional Well-being:
Emotional well-being is not easily observable. It can be measured on how rationally a person handles both positive and negative emotions so he/she can lead a productive, healthy life. Techniques to achieve emotional well-being are helpful at three levels viz. physical, emotional, and social.
- Physical level, i.e., well-balanced diet, exercise.
- Emotional level, i.e., practice mindfulness, raising levels of motivation and optimism.
- Social level, i.e., engaging in prosocial behaviour, meaningful relationships.
The benefits of emotional after well-being give a long dash
Persons who have high emotional well-being experience benefits such as-
- better able to deal with stress
- better self-regulation
- increased productivity in tasks undertaken
- increased creativity and openness to new experiences
- life satisfaction due to meaningful activities and relationships.
Emotional Abuse:
Emotional abuse is any kind of abuse that is emotional rather than physical in nature. It occurs when one person subjects or exposes another person to intentionally harmful behaviour that may result in anxiety, depression, and psychological trauma for the victim.
The types of emotional abuse may be-
- verbal abuse such as blaming, insulting, labeling, threatening, swearing, etc.
- non-verbal abuse such as ignoring, rejection, bullying, spying, etc.
Dealing with emotional abuse:
- Accept that emotional abuse is not because of you, i.e., don’t justify the actions of the abuser.
- Respond assertively to the abuser but seek distance from him/her.
- Give yourself time to heal.
- Prioritize your self-care, e.g., eating right, exercise, etc.
- Mobilize support from family and friends. If needed, seek professional help.
![]()
Managing Emotions:
Managing of emotions is an important life skill. Managing emotions can be defined as, ‘the ability to be open to feelings and modulate them in oneself and in others, so as to promote personal understanding and growth.
Sometimes, our emotions hijack our thinking due to which we act impulsively. This is because the limbic system (emotional section) developed before the prefrontal cortex (thinking part) and is hence, an extremely strong part of the brain. Emotional management is an art as it is a form of expression as well as a science as it is a skill that needs to be learned and practiced.
Anger Management:
Anger is a common emotion that everybody experiences in life from time to time. Anger is a normal response to some real or perceived threat. It is a protective emotion that helps us to defend ourselves against physical or psychological harm.
However, anger may also be unwanted, irrational, and destructive. When we experience anger, our amygdala goes into action and overrides the cerebral cortex which is in control of thinking and evaluation.
Triggers of Anger refer to any event that signals the brain to activate the body’s anger system. The triggers of anger maybe
- verbal, for e.g., being blamed, disrespected, or abused
- nonverbal, for e.g., being ignored unappreciated, or rejected,
- physical such as physical threats, sexual/ physical assault, etc.
There are three factors involved in the experience of anger: A trigger (causes of anger) → individual’s personality → particular interpretation of that situation.
As the experience of anger is subjective, it can be controlled too. If we understand the triggers of anger, we can anticipate potential anger episodes and provide an intentional/ acceptable response.
Anger management is an intervention programme to prevent anger from turning into a habit or obstacle. It enables the person to create an awareness of and responsibility for his/her emotions.
This involves two aspects
- managing one’s own anger
- learning to respond effectively to anger in others.
![]()
The 3 R’s in anger management are Relax, Reassess and Respond:
Relaxation – Relaxation, and connection with the inner self enhances thinking and concentration and helps to respond rather than react impulsively.
Reassess – helps to revisit the situation objectively. It involves
- taking complete responsibility for your emotion
- developing empathy for the person you perceive has wronged you
- conduct a reality check e.g., is your anger justified given the facts of what happened.
Respond – This involves using anger as a motivation to change. It includes
- consulting a trustworthy person to get another perspective
- engage in talks with the other party in a calm manner
- active listening and assertive speaking
- cage your rage i.e. establish boundaries and moderate your anger.
Glossary:
→ Anger – A basic emotion expressing dislike or displeasure.
→ Emotions – A complex response pattern that involves physiological arousal, expression of behaviors, and conscious experience.
→ Emotional abuse – It is a non-physical form of abuse in which an individual purposely subjects another to behaviors such as intimidation, isolation humiliation, rejection, and verbal abuse.
→ Emotional well-being – It is an overall positive state of one’s emotions.
→ Trigger – An event or stimuli that cause a reaction.