By going through these Maharashtra State Board Secretarial Practice 12th Commerce Notes Chapter 9 Depository System students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Secretarial Practice Notes Chapter 9 Depository System
Introduction:
→ Joint-stock companies raise finance by issuing shares and debentures.
→ Securities can be held in two modes:
- Physical or Paper Form
- Electronic/ Digital/Dematerialized Form
→ A new system called “depository system” has been established to
- Field securities of an investor in an electronic form
- Eliminate the risk of forgery and mutilation
→ Depository system exists in all developed countries.
![]()
Terms and Constituents related to Depository System-
→ Depository System which was introduced in India by passing The Depository Act 1996.
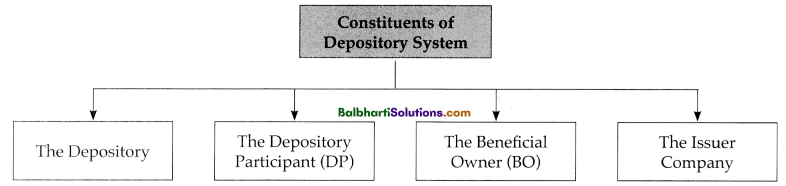
→ Constituents of Dlepository System :
- The Depository
- The Depository Participant(DP)
- The Beneficial Owner (BO)
- The Issuer Company
→ Depository contacts the customer through depository participant.
→ Depository participant is the representative of the depository.
→ An investor is known as beneficial owner.
→ Companies which issue any kind of security are known as ‘Issuer’ in the depository system.
→ Issuer Company must register with the Depository.
→ Dematerialization is the process in which share certificates are converted into electronic form.
→ Rematerialization is the process by which shares in electronic form are reconverted into physical form.
→ ISIN is a unique code that is used to identify securities.
Functioning of Depository System:
→ The investor has to open a demat account when he wants to dematerialize the share.
→ The investor intending to dematerialize his securities send a duly filled in and signed. Demat Request Form in triplicate along with scrip certificate to Depository Participant.
![]()
→ Depositories existing in India:
- NSDL – National Security Depository Limited -1996
- CDSL – Central Depository Services Limited – 1999