By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Sociology Notes Chapter 3 Diversity and Unity in Indian Society students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Sociology Notes Chapter 3 Diversity and Unity in Indian Society
→ India is a land of diversities and yet there is a sense of we-feeling that unifies us, as a people.
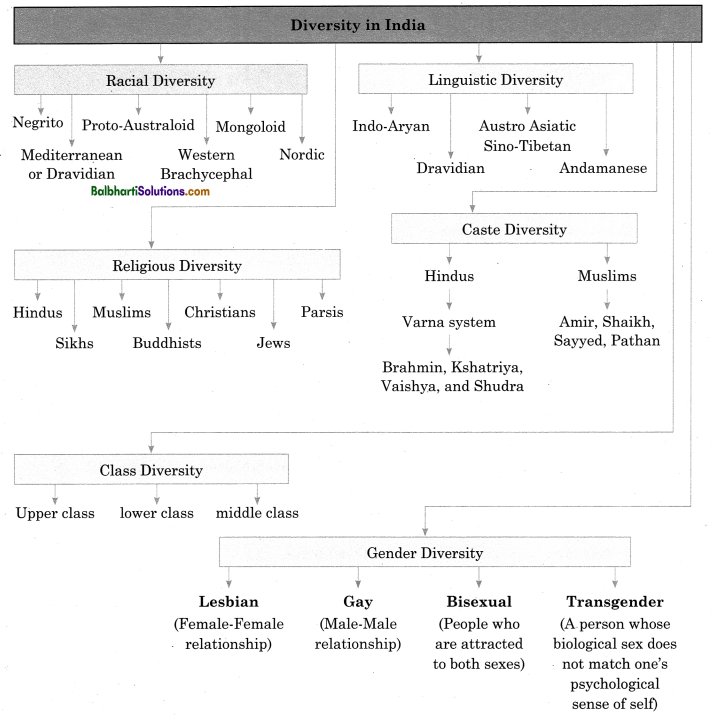
Diversities are of various kinds:
Diversity in India:
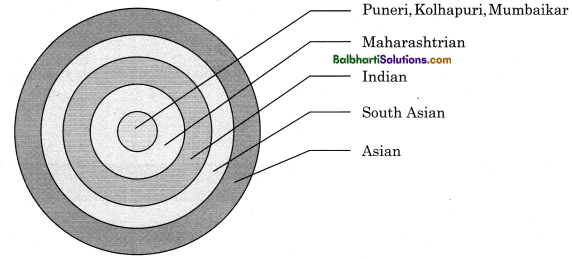
Layered Regional Identities:
![]()
Factors that have contributed towards a sense of unity:
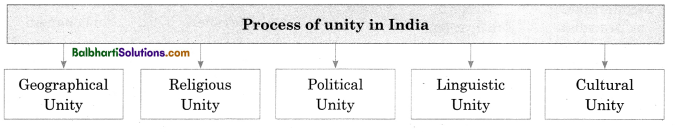
→ Geographical Unity- Sharing of the natural resources which cut across the length and breadth of India, festivals gives the people a sense of oneness.
→ Religious Unity- Religious unity in India finds its expression through places of worship scattered all over the country.
→ Political Unity- The Constitution of India has established the “rule of law” throughout the country.
Linguistic Unity:
The Three Language Formula
- 1st language: Regional Language or Mother Tongue.
- 2nd language: English or Modern Indian Language (in Hindi speaking States) Hindi or English (in non-Hindi speaking States)
- 3rd language: English or modern Indian language in Hindi speaking states
→ Cultural Unity- Festivals like Diwali, Onam, Eid, Raksha Bandhan, New Year, Christmas are remembered and celebrated all over the country.
Need for unity:
→ To strengthen and enrich our cultural Heritage
→ To protect the multiple diversities of Indian society
→ To protect Human Rights of all citizens.
→ To boost workplace, organizational and community morale.
→ For effective and inclusive Communication
→ For conflict resolution
→ For peaceful coexistence
→ For the welfare of all people irrespective of caste, creed, sex, gender, race, economic class, culture etc.
→ For prosperity of our land and its People.
![]()
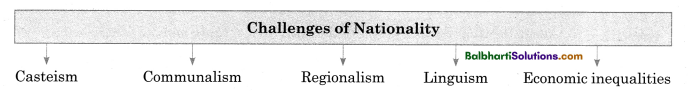
Forces that threaten national unity as well as national integration:
→ Casteism: Casteism refers to loyalty to one’s own caste before loyalty to the nation.
→ Communalism: Communalism refers to loyalty to one’s own religion before the nation.
→ Regionalism: Regionalism refers to loyalty to one’s own State or region before one’s nation.
→ Linguism: It is a form of excess loyalty towards one’s own language.
→ Economic inequality: unequal distribution of wealth.
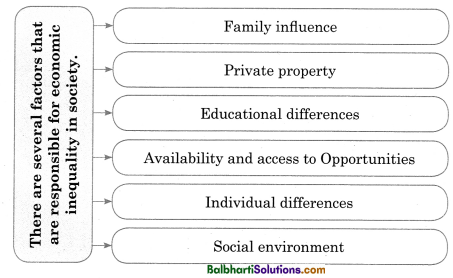
→ The need of the hour is to develop an empathetic understanding of our multiple diversities and work towards strengthening the overall sense of national unity and emotional integration.
→ Some policies must promote social cohesion and interdependence. So also, rights and responsibilities are for all.