By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 4 Forms of Business Organisation – I students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 4 Forms of Business Organisation – I
Meaning Private Sector Organization-
Private Sector Organization
Meaning: The private sector is the part of the economy that is run by individuals or a group of Individuals to earn profit.
![]()
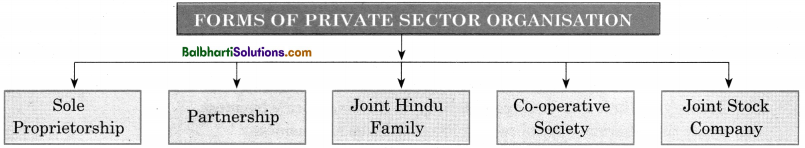
Forms of Private Sector Organization-
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Joint Hindu Family
- Co-operative Society
- Joint Stock Company
Meaning of Sole Trading Concern / STC Sole Proprietorship-
According to Prof. J. Hansen, “Sometimes known as one man business, it is a type of business unit where one person is solely responsible for providing the capital, for bearing the risk of the enterprise and for the risk of ownership”.
According to Prof. James. Lundy, “The sole proprietorship is an informal type of business owned by one person”.
Features of Sole Trading Concern-
- Suitable for some Special Business
- Unlimited Liability
- No Sharing of Profits and Risks
- Business Secrecy
- Local Market Operations
- Individual Ownership
- No separate legal status
- Direct Contacts with Customers and Employees
- Self-employment
- Freedom in Selection of Business
- Minimum Government Regulations
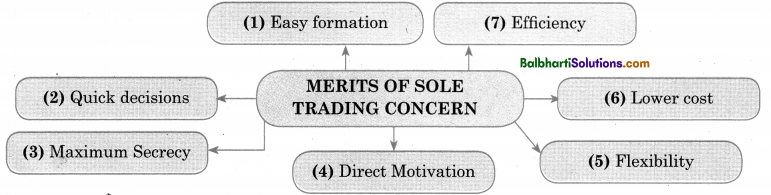
Merits of Sole Trading Concern-
- Easy formation
- Quick decisions.
- Maximum Secrecy
- Direct Motivation
- Efficiency
- Lower cost
- Flexibility
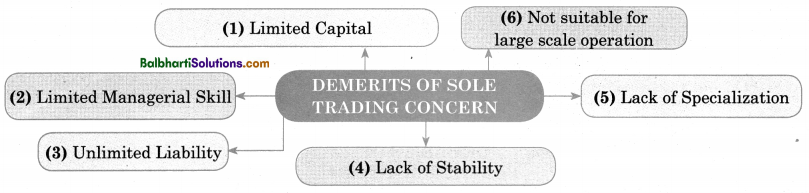
Demerits of Sole Trading Concern-
- Limited Capital
- Limited Managerial Skill
- Unlimited Liability
- Lack of Stability
- Lack of Specialization
- Not suitable for large scale operation
![]()
Meaning of Partnership Firm-
(Section 4 of Indian Partnership Act, 1932 defines partnership as -) “Partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or anyone of them acting for all”.
(Prof. L. H. Haney defines partnership as -) “Partnership is the relation existing between persons competent to make contracts, who have agreed to carry on a lawful business in common with a view to private gain”.
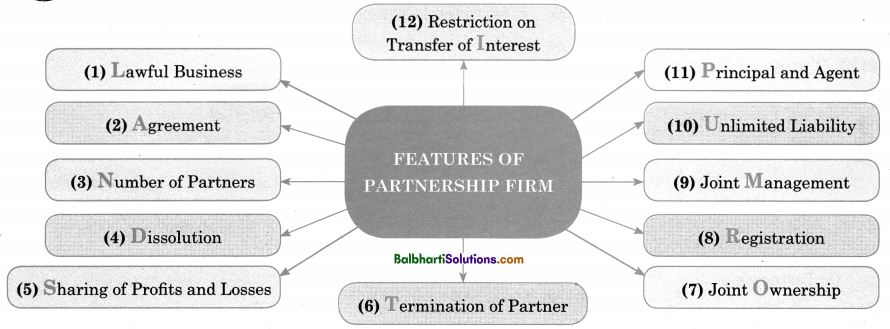
Features of Partnership Firm-
- Lawful Business
- Agreement
- Number of Partners
- Dissolution
- Sharing of Profits and Losses
- Termination of Partner
- Joint Ownership
- Registration
- Joint Management
- Unlimited Liabi1ity
- Principal and Agent
- Restriction on Transfer of Interest
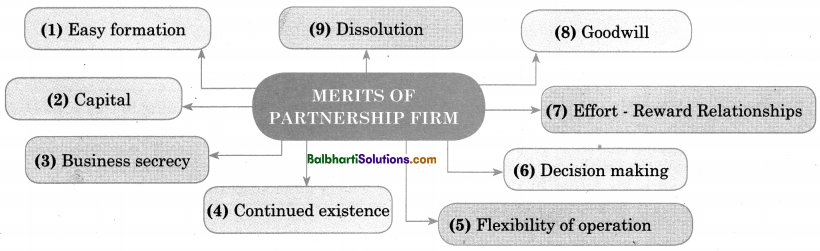
Merits of partnership Firm-
- Easy formation
- Capital
- Business secrecy
- Continued existence
- Flexibility of operation
- Decision making
- Effort- Reward Relationships
- Goodwill
- Dissolution
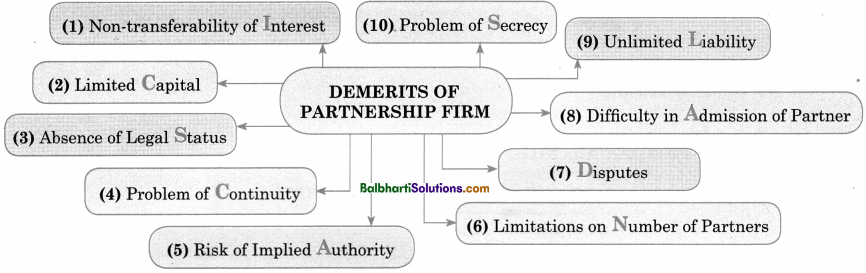
Demerits of Partnership firm-
- Non-transferability of Interest
- Limited Capital
- Absence of Legal Status
- Problem of Continuity
- Risk of Implied Authority
- Limitations on Number of Partners
- Disputes
- Difficulty in Admission of Partner
- Unlimited Liability
- Problems of Secrecy
![]()
Types of Partners-
- Active partner
- Dormant partner
- Nominal partner
- Secret partner
- Minor as partner
- Partner in profits only
- Sub-partner
- Partner with limited liability
- Quasi-partner
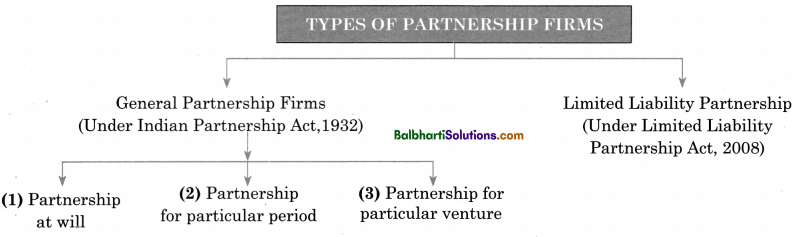
Types of Partnership Firms-
1. General Partnership Firms (Under Indian Partnership Act, 1932)
- Partnership at will
- Partiership for particular period
- Partnrship for particular venture
2. Limited Liability Partnership (Under Limited Liability, Partnership Act, 2008)
Joint Hindu Family Business-
(1) Mitakshara : According to this school, only male member of the family can inherit the family business. Hence the sons, grandsons and great grandsons become joint owners of the family property. A son gets equal rights along with his father in the ancestral property. He has a right to ask for a division of the family property.
(2) Dayabhagya : According to this school both male and female member will be co-parceners in the Hindu-undivided fami1y. e.g. after death of husband his property and business passes to his wife or other successor.
Features of Joint Hindu Family Business-
- Exists only in India
- Formation
- Membership
- Joint Ownership
- Good Credit Standing
- Management
- Profit Sharing
Merits of Joint Hindu Family Business (JHFB)-
- Easy formation
- Protection of Co.parceners Interest
- Quick and Prompt Decision
- On the job training
- Co-parcener’s liability
Demerits of Joint Hindu Family Business (JHFB)-
- Unlimited Liability of Karta
- Limited Financial and Managerial Resources
- No separate legal status
- Partition of business
- No direct relation between effort and rewards
Co operative Society-
The International Labour Organization:
‘A Co-operative Organization is an association of persons, usually of limited means, who have voluntarily joined together to achieve a common economic end through the formation of a democratically controlled organization, making equitable distributions to the capital required and accepting a fair share of risk and benefits of the undertaking”.
“Indian Co-operative Society’s Act, 1912”, Co•operative Society is a sociéty which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interest of its members in accordance with co operative principles”.
![]()
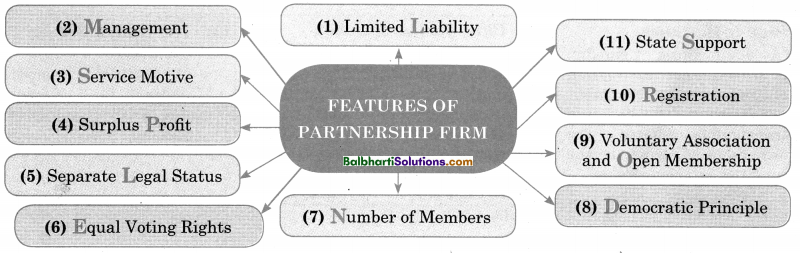
Features of Co-operative Society-
- Limited Liability
- Management
- Service Motive
- Surplus Profit
- Separate Legal
- Equal Voting Rights
- Number of Members
- Democratic Principle
- Voluntary Association rand Open Membership
- Registration
- State Support
Merits of Cooperative Society-
- Easy Formation
- Tax Concession
- Open Membership
- Stability
- Self Financing and Charity
- Less Operating Expenses
- Limited Liability
- Democratic Management
- Supply of Goods at Cheaper Rate
Demerits of Cooperative Society-
- Limited Capital
- Inefficient Management
- Lack of public confidence
- Limited scope for expansion
- Lack of motivation
Types of Cooperative Societies-
- Consumers Co-operative Societies
- Producer’s Co-operatives
- Marketing Co-operative
- Co-operative farming societies
- Housing Co-operatives
- Credit Co-operatives
Producer’s Co-operatives-
- industrial Service Co-operatives
- Manufacturing Co-operatives
![]()
Joint Stock Company-
Definition of Joint Stock Company:
Prof. L. H. Haney,
“A Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association of individuals for profit having capital divided into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition on membership”.
Chief Justice Marshal,
“A company is a person, artificial invisible intangible and existing only in the eyes of law. Being a more creature of law it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it, either expressly or as incidental to its very existence”.
The Companies Act 2013, Sec 2(20)-
“A company incorporated under the Companies Act 2013 or any previous company law”.
Features of Joint Stock Company-
- Common Seal
- Registration
- Artificial Legal Person
- Membership
- Perpetual Succession
- Separation of Ownership and
- Registered Office
- Transferability of Shares
- Voluntary Association
- Limited Liability
- Separate Legal Status
Merits of Joint Stock Company-
- Transferability of Shares
- Relief in Taxation
- More Scope for Expansion
- Public Confidence
- Limited Liability
- Expert Services
- Democratic Management
- Perpetual Succession
- Professional Management
- Large Amount of Capital
Demerits of Joint Stock Company-
- Rigid formation
- Lack of secrecy
- No personal contact
- Delay in decision making process
- High cost of management
- Reckless speculation

![]()
Types of companies-

Word Meaning:
solely – only; proprietor – owner; legal status – someone with regard to law; eyes of law – from view of law; rigid – fixed; distinction – differences; expert – good knowledge in a particular area; insanity – mental imbalance; insolvency – financial loss; evolved – to develop; proprietary concern – sole trading business; lawful – legally; collectively – as a whole; outcome – result; advisable – useful; forbidden – not permitted; pay off – payment; incurred – to arise; consent – permission; proportions – share; goodwill – established reputation; fraudulent – illegal; secrecy – not to disclose anyone; confidential – to keep secret of something; flexibility – to change easily; diversify – to expand; ethical – principle; efficiency – competent; continuity – to run for long period; dissolution – to end; disputes – arguments; object – to disagree; undue – unnecessary; restricts – to obstruct; dormant – inactive; quasi – not fully; rendered – to provide; sleeping – to be inactive; bind – to tie up; nominal – in name of; void – invalid; derived – to obtain; at will – own wish; venture – project; inherit – to receive; ancestral – belonging from ancestor; successor – a person who gets the authority from another person; descended – to go down; virtue – by behaviour; custodian – caretaker; assures – to convince; consult – to seek advice; utmost – maximum; tactics – method; manipulative – to exploit ; practices – to exercise/to use; empathizing – to understand; transparent – to be clear; exploitation – to misuse; integral – essential; democratically – with regard to laws of democracy; equitable – equally; discrimination – to differentiate; honorary – unpaid; concessions – discount; privileges – advantages; exemption – state of being free from duty; amendment – changes; charity – helping others in term of cash or material; interference – to come in between; remunerative – at good price; centralized – under one roof; eliminate – to remove; pool – to bring together; exorbitant – to much high/extremely high; drastic – major/extreme; intangible – can’t be seen or touched physically; confers – to present; charter – authorised; incidental – happening; existence – to come into survival; entity – an independent body (organisation); engraved – imprint; seal – a symbol; affixed – to fix on something; perpetual successions – never ending; comparatively – to compare something with; legal advisers – a person who gives legal advices; consultants – a person who gives expert advice in a particular area; stable – fixed; complicated – difficult; time consuming – taking too much time; undue – unnecessary; appreciated – to value; unscrupulous – corrupt/dishonest; reckless – careless; fluctuation – changes/ alteration; adversely – harmfully/not favourable; ban – to restrict/to stop; in lieu of – in place of/replace.