By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 5 Forms of Business Organisation – II students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 5 Forms of Business Organisation – II
Public Sector Organizations-
Definition of Public Sector Organizations
1. Britannica Encyclopedia
“An undertaking that is owned by a central, state or local government, supplies services or goods at a price and is operated on more or less self-supporting basis is called as Public Sector Organisation.”
2. Prof. Hansen
“Public Enterprise means state ownership and operation of industrial, agricultural, financial and commercial undertaking.”
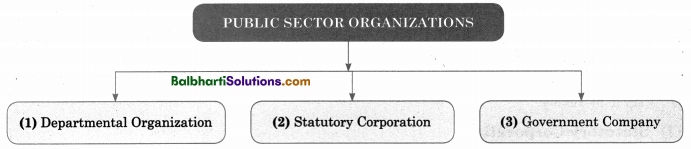
Classification of Public Sector Organizations-
- Departmental Oranization
- Statutory Corporation
- Government Company
![]()
Department Organisation-
- Meaning : Organization which is owned, managed, controlled and financed by government is known as “Departmental Organisation”.
- Example : Post Office, Railways, Defence Industries, Radio, Public Utility Services, etc.
Features of Departmental Oraganisation-
- Delegation of Authority
- Organizational Structure
- Government Employees
- Financed by the Government
- Useful for Secret
- No Legal Status
- Government Sanction for Expansion
- Examples of Departmental Organization
- Run by Government
- Managed by Government
- Accounting Control
- Accountability
Merits of Departmental Organization-
- Qualified Staff
- Proper use of Funds
- Social Welfare
- Public Accountability
- Maintain secrecy
- Easy Formation
- Direct control
- Direct revenue to Government
- Less Overheads
- Easy Finance
- Development of Public Utilities
Demerits Of Departmental Organisation-
- Delay in Action
- Inefficiency and Corruption
- Less Scope for Initiative
- Instability
- Delayed
- Lack of Flexibility
- Incurring Losses/Huge Losses
- Absence of professionalism
- Political Interference
- Red Tapism and Bureaucracy
- Insensitive to Consumer Needs
- Lack of Autonomy
![]()
Statutory Corporation-
Meaning : A Statutory Corporation is an autonomous corporate body created by the Special Act of the parliament or state legislature with defined powers, functions and duties. State helps statutory corporation by subscribing to its capital.
Example : Reserve Bank of India, LIC, etc.
Features of Statutory Corporation
- No political Interference
- Own Staffing System
- No Political Interference
- Financial Autonomy
- Independent Identity
- Special Act
- Corporate Body
- Answerable to the Legislature
- Legal Status
- Independent Accounting System
- Public Accountability
- Objective
Merits of Statutory Corporations-
- Professional Management,
- Rapid Decisions
- Efficient Staff
- Motivated Staff
- Service Motive
- Easy to Raise Capital
- Administrative Autonomy
- Public Accountability
- Initiative and Flexibility
- Enjoys Economies of Scale
- Creates Employment Opportunities
- Enjoy Monopoly
![]()
Demerits of Statutory Corporations-
- Clashes Amongst Interests
- Autonomy on Paper Only
- Rigid Structure
- Lack of Initiative
- Unfair Practices
Government Company-
Meaning : “The company which is registered under Companies Act, 2013 having minimum 51% of paid- up share capital held by the central government or any state government or partly by central government and partly by one or more state governments is known as Government Company.”
Example :
- National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC)
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
- Hindustan Machines Tools (HMT)
Features of Government Company-
- Free from Procedural Controls
- Majority of Government Directors
- Public Accountability
- Registration under the Companies Act
- Own Staff
- Promotes Social Welfare
- Objective
- Separate Legal Entity
- Exemptions
- Suitability
Merits of Government Company-
- Profitability and Accountability
- Internal Autonomy
- Government Ownership
- Foreign Capital and Technical Know how
- Acquisition of Sick Units
- Concessions and Privileges
- Efficiency
- Professional Management
- Easy Formation
- Flexibility
- Easy to Alter
- Enjoys Private and Public Objective
![]()
Demerits of Government Company-
- (1) Inefficiency and Corruption
- (2) Lack of Professional view
- (3) Domination of Ministers and Politicians
- (4) Red Tapism and Delay
- (5) Autonomy only in Name
- Weak Public Accountability
- Fear of Expoaure
- Lack of Expertise
- Ineffective Control of Parliament
- Poor Labour Management Relation
Multinational Corporations (MNC)-
Meaning : “A multinational corporation is a business organisation that operates in many different countries at the same time.
In other words, “It’s a Company that has business activities in more than one country.”
Example : Indian Multinationals
- Bata India
- Infosys
- Tata Motors
Features Multinational Corporation-
Features of Multinational Corporation-
- Advanced and Sophisticated Technology
- Legal Existence
- Government
- Origin
- Research & Development
- International Operations
- Target Profitoriented
- Huge Assets and Turnover
- Mighty economic power
- Centralized Control
- Area of Operation
- Professional management
![]()
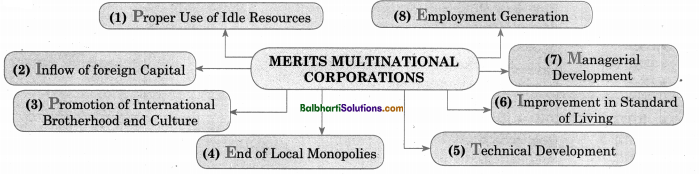
Merits Multinational Corporation-
- Proper Use of Idle Resources
- Inflow of foreign Capital
- Promotion of International 1 Brotherhood and Culture
- End of Local Monopolies
- technical Development
- Improvement in Standard) of Living
- Managerial Development
- Employment Generation
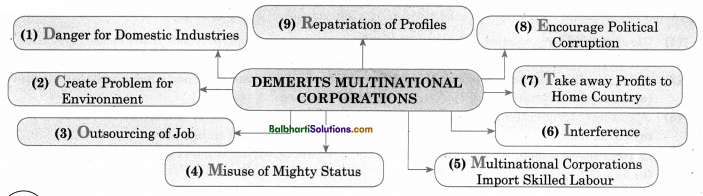
Demerits Multinational Corporation
- Danger for Domestic Industries
- Create Problem for Environment
- Outsourcing of Job
- Misuse of Mighty Status
- Multinational Corporations Import Skilled Labour
- Interference
- Take away Profits to Home Country
- Encourage Political Corruption
- Repatriation of Profiles
Word Meaning:
co-existence – to exist in same time; criticism – disapproval; reliable – genuine / good; supervision – to look after; annual budget – yearly estimated income and expenditure; sanctioning – to approve; autonomous – to manage its work independently; legislature – Government body; subscribing – to enroll / to be a member; revenues – income; statutory – as per the law; government treasury – funds available with the government; interfere – to check / disturb; budgeting – to allocate; recruited – to appoint; integral – essential; remunerated
– to pay salary; centralisation – concentration of control; operations – working; red tapism – process of excessive paper work and rigid formalities; nominated – to be selected; floating – to fluctuate / change; bureaucracy – a government system where important decisions are taken by the officials; trustworthiness – truthful; initiative – to do independently; guided – to show; smooth – without any problems; hampered – to suffer; characters – nature; indulge – to involve; demoralized – to lose hope; inefficiency – not achieving maximum productivity; innovative – new ideas; comptroller – controller; expertise – skill to do best; auditor general – government officer charged with accounts auditing; bounded – to restrict; professional – person qualified in particular profession; affiliates – connected with; productivity – output; modifications – to change; framework – a structure; acquire – to get; entities – independent organizations; deputation – to give charge; host – a place or person who holds the event; budgetary – to allocate the fund; sophisticated – highly developed; undertakings – agreements; intensive – concentrated / focused; executive – administrative; boost – to encourage; relatively – in comparison; inflow – movement of large thing; active – energetic; monopolies – control of trade; personnel – human resource; exploitative – treating others unfairly; debated – discuss; brotherhood – friendship; peace – freedom from disturbance; repatriation – to send money; prosperity – being success; implicit – indirect; chronic – for a long time; challenges – problems; wipe off – clean off; wind up – to end; depletion – reduction; non renewable – resources which cannot be produced again; threat – warning; alien – foreign; synthetic – chemical substance; setback – in reverse of; injurious – harmful; concentration – at centre; enrich – improve the quality, legal entity – legal rights and obligation, overheads – expenses, of business, interference – the illegal obstruction.