By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 6 Institutes Supporting Business students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 6 Institutes Supporting Business
Small Industrial Development Bank of India (SIDBI)-
- Established on 2nd 1990.
- Initially subsidiary of Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
- Ownership is held by 34 public sector institutes
- Focuses on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSM,s)
- Head office Lucknow
- 15 regional offices
- 84 branches all over India

![]()
Features of SIDBI-
(1) Sustainable Development:
- Creation of economic wealth.
- Enhance awareness of benefits of climate control.
- To promote investment in clean production and energy efficient technologies.
- To reduce the emission of greenhouse gases.
(2) Nodal / Implementing Agency:
helps in implementing various subsidy schemes for upgradation, modernisation and expansion of business.
(3) Financial Institute for promotion of MSMEs (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises:):
- To provide short and long term finance to MSMEs.
- It provides refinance to banking and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC).
- To cater the specific needs of Indian MSMEs.
(4) Advisory Function:
- To expand marketing channels at domestic and international markets.
- Steps for modernization and technological upgradation.
(5) Forms of finance:
- Direct Finance
- Indirect Finance
- Micro Finance
(6) Digital initiatives:
- SIDBI Startup Mitra
- Udyami Mitra
(7) Achievements of National Goals:
- Helps in poverty alleviation and employment generation
- Promotes entrepreneurship and fosters competitiveness as well as for women and economically weaker section.
- Provides finance to industries in semi-urban areas
![]()
(8) Services to MSMEs:
- SIDBI Venture Capital Ltd. (SVCL)
- Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
- SME Rating Agency of India Ltd. (SMERA)
- India SME Technology Services Limited (ISTSL)
- India SME Asset Reconstruction Company Ltd. (ISARC)
- Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency (MUDRA)
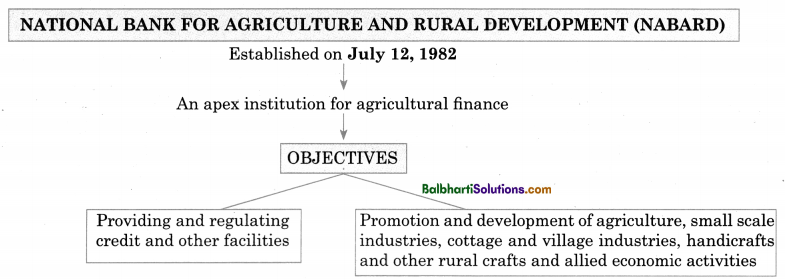
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)-
- Established on July 12,1982
- An apex institution for agricultural finance
Objectives:
- Providing and regulating credit and other facilities
- Promotion and development of agriculture, small scale industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts and other rural crafts and allied economic activities
Features of NABARD-
Financing Rural Industries:
- To refinance small scale industries and other village and cottage industries
- To promote rural employment by providing loan to commercial and co-operative banks
- To organize skill and entrepreneurship development programmes
(2) Assistance to Financial Institutes:
- To assist in preparing, developing, implementing, action plans for Co-operative Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- To provide financial assistance to improve Management Information System (MIS), Computerization of operations and development of human resources.
![]()
(3) Refinancing Facilities:
To provide refinance facilities to –
- State Co-operative Banks (SCBs)
- Land Development Banks (LDBs)
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
To provide – short term credit
- Medium term credit
- Long term credit
To help during natural calamities
(4) Credit for Rural development.
- To provide funds to State government in development and promotion of different activities
- To uplift weaker section by refinancing them.
- To provide finance for promoting non-farm activities and generating employment
(5) Apex Bank:
- To meet credit needs of all types of financial institution in field of agricultural and rural development
- To frame policies and guidelines for rural financial institution
- To monitor the flow of rural credit in India.
(6) Recommendations to Reserve Bank of India:
on issue of licenses to Co-operative Banks, opening new branches by State Co-operative Banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
(7) Development of Nation:
- To promote warehousing facilities to improve storage facilities for agricultural commodities.
- To promote export of agricultural commodities
- To help in sustainable development of the country through Green, Blue and White Revolution.
(8) Supervision of Financial Institutes engaged in Agricultural Finance.
To inspect Regional Rural Banks and Co-operative Banks, State Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (SCARDBs) on voluntary basis
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC):
- Under the Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act, 1956
- Established on April, 1957
- An Apex organization under the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Head office: Mumbai

![]()
Objectives of KVIC-
- Social Objective
providing employment - Economic Objective
providing saleable articles - Wider Objective
- creating self reliance among poor
- build strong rural community spirit

Features of KVIC-
Research and Development.
- To give training to sales staff for effective marketing of khadi products.
- To provide design support services.
- To bring technological improvements in products so as to reduce the cost of production and increase incomes.
- To promote use of non-conventional energy and electric power for sustainable development.
Other Functions:
- To plan, promote, organize and implement the programmes with relation to Khadi and other village industries.
- To organise training programme for artisans.
Marketing and Promotion:
- To hold exhibitions, seminars and lectures in Universities and Colleges.
- To generate interest, awareness and attraction among people.
- To improve the quality of products, packaging and marketing skills.
Financial Assistance:
- To finance rural industrialization projects and provide for margin money through subsidy.
- To provide higher subsidies in case of weaker sections, tribal areas and backward regions.
- To provide financial assistance for development and operation of Khadi and Village Industries.
Rural Development:
- To utilise natural resources properly in generating income for rural people
- To promote development of tiny, cottage and small scale enterprises
Employment Generation:
- To create employment opportunities with low per capital investment, promote non-farm employment opportunities.
- To focus on betterment of rural artisans and socio-economic weaker section.
Entrepreneurship Development:
- To generate self employment and help to provide additional livelihood revenue.
- To prevent migration by increasing earning capacity of rural people.
- To participate in international trade exhibitions.
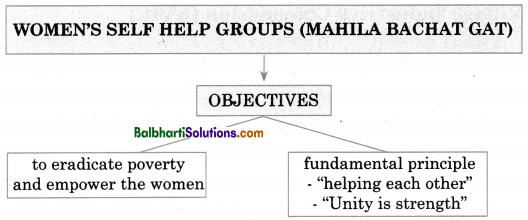
Women’s Self Help Groups (Mahila Bachat Gat)-
Objectives:
1. To eradicate poverty and empower the women
2. Fundamental principle
- “helping each other”
- “Unity is strength”
![]()
Features Women’s Self Help Groups-
(1) Formation:
- It is an informal small group of homogeneous individuals generally formed by NGOs.
- Registration under any act is not mandatory.
Membership:
- It is through a process of self selection based upon the affinity (harmony) of its members.
- At least 5 members are required. One member from one family is allowed.
Empowerment of Women:
- It is a tool for socio-economic development of women.
- To promote women entrepreneurship.
- To provide financial and non financial assistance.
Collateral Free Loan:
- To provide small loans to the poor individual to start self employment projects.
- To encourage poor individuals to participate in banking activities.
- To ensure timely repayment of loans and responsible for collecting repayment amount who borrowed the loan.
Democratic Setup.
- It is responsible for organizing themselves independently.
- To hold regular meetings, maintaining records and accounts of the group.
- To work on principle of collective leadership and mutual discussions.
Entrepreneurship Development.
- To provide capital at low interest rate to promote micro enterprise.
- To provide timely financial support and managerial skills.
- To provide skill development trainings and marketing and technical support.
Saving Habit.
- To encourage small saving habits at regular intervals.
- To generate common fund to be used to lend the members in time of need.
Mutual Trust.
- To overcome individual shortcomings and weakness with collective efforts.
- To help poor and marginalized individuals builds their lives, families and their society.
![]()
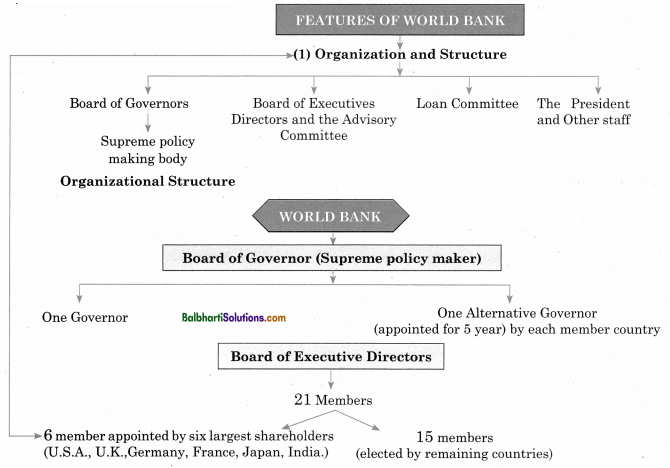
World Bank-
(1) International
‘ Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
provides debt financing to government
(2) International Development Association (IDA)
Gives interest free loans to the governments of poor countries
(3) International Finance Corporation (IFC)
Focuses on private sector and provides developing countries with investment financing and financial advisory services
(4) Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA).
Promotes Foreign Direct Investments in developing countries
(5) International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes.
Provides arbitration on international investment disputes
Features of World Bank-
Goals-
2 goals by 2030
To end extreme poverty
To promote shared prospering by fostering the
- income growth of bottom 40% for every country.
- World Bank group consists of 5 institutions which are managed by their member countries.
(3) Financial Products and Services.
Provides low-interest loans, zero to low interest credits and grants to developing countries in area of education, health, public administration, infrastructure, financial and private sector development, etc.
(4) Innovative Knowledge Sharing.
- To support in policy advice, research and analysis and technical assistance
- To sponsor host or participate in conferences and forums on issues of development
- To provide best global expertise to developing countries
(5) Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
- higher productivity leading to increased economic growth
- enhancing competitiveness and productivity by introducing new products, novel business models, new markets, etc.
- facilitates global experience, knowledge, research and-investments to develop effective innovations
![]()
(6) Social Development:L
- promotes economic growth and leads to higher quality life
- solves the problems of poor and vulnerable into development process
- undertakes social risk analysis, including poverty and social impact analyses
Word Meaning:
hurdles – difficulties; vibrant – energetic; emerge – comes out; dedicated – committed; infusing – to fill; ecosystem – interconnection of organism and environment; channels – means/medium; co-ordinate – bring together; refinance – giving loans with low rate of interest; traditional – regular; sustainable – able to maintained; creation – formation; ecological – relation of organism and surrounding; emission – to release; upgradation – to improve; associates – connected; subsidiaries – subordinate/secondary; comprehensive – complete; micro – small; semi-urban – in between rural and urban; assistance – to help; extensive – large scale; incubators – company that helps to start up new companies; mentors – guide; portal – website; accessibility – able to reach; track – path; handbolding – to support; nodal agency – a direct office which is assigned for implementing; allied along with – executing new project; review – to check; eye opener – unexpected event; plunge – to jump; apex – at top; regulating – to control; cottage – business carried on by home; guidelines – instruction; monitors – to look after; tideover – to help at difficult; computerization – use of computer in doing work; upliftment – to raise; voluntary – not compulsory; recommendations – to advice; revolution – to bring change in society; boycott – to refuse; key – important; potential – possibility; emphasis – importance; strengthen – to power; functions – activities; self reliance – self sufficient; community spirit – feeling of togetherness of one community/group; premier – main/leading; generating – to produce; masses – people; massive – huge; per capita – by each head; avenues – direction; migration – movement of people from one place to another; formulated – to prepare; schemes – plan; subsidy – a sum pf money granted by government to support; beneficiaries – recipient/receiver; cater – to provide; publicity – to make famous; disseminating – to distribute; derive – to get; organizes – to arrange; agencies – a business firm; eradicate – to remove; refused – to say no; empower – to allow; inspired – to encourage; homogeneous – same group; collateral – security; alternative – different; voluntary association – group of individuals forming a body having same goals; reasonable – fair price; enhances – increase; collective – together; out reach – influence; affinity – harmony; inculcates – to fix; thrift – budgeting; overcome – to solve; philosophy – study of particular system; marginalized – system insignificant; grassroot – basic level; scarcity – shortage; untapped – resource not used; tool – device; clutches – holds; artisans – individual with/good proficient in particular art; vested – given/ to give; fostering – to promote; unique – special; vital – important; analysis – to evaluate.